<题目链接>
小希的迷宫
Problem Description
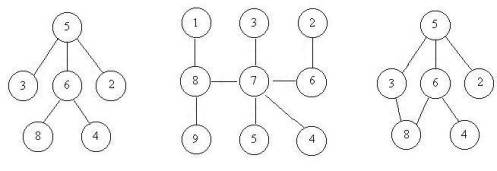
上次Gardon的迷宫城堡小希玩了很久(见Problem B),现在她也想设计一个迷宫让Gardon来走。但是她设计迷宫的思路不一样,首先她认为所有的通道都应该是双向连通的,就是说如果有一个通道连通了房间A和B,那么既可以通过它从房间A走到房间B,也可以通过它从房间B走到房间A,为了提高难度,小希希望任意两个房间有且仅有一条路径可以相通(除非走了回头路)。小希现在把她的设计图给你,让你帮忙判断她的设计图是否符合她的设计思路。比如下面的例子,前两个是符合条件的,但是最后一个却有两种方法从5到达8。

Input
输入包含多组数据,每组数据是一个以0 0结尾的整数对列表,表示了一条通道连接的两个房间的编号。房间的编号至少为1,且不超过100000。每两组数据之间有一个空行。
整个文件以两个-1结尾。
整个文件以两个-1结尾。
Output
对于输入的每一组数据,输出仅包括一行。如果该迷宫符合小希的思路,那么输出"Yes",否则输出"No"。
Sample Input
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4 5 6 0 0
8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5 7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0
3 8 6 8 6 4 5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0
-1 -1
Sample Output
Yes
Yes
No
解题分析:
此题不难,就是要看清题目的限制条件,这必须是一个连通的无环图,还有就是要注意当输入没有点的时候,也符合题目条件,输出Yes。
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <set> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn=100000+100; int father[maxn]; int flag; int find(int x) { int r=x; while(father[r]!=r)r=father[r]; int i=x,j; while(father[i]!=r) { j=father[i]; father[i]=r; i=j; } return r; } void Union(int a,int b) { int f1=find(a); int f2=find(b); if(f1!=f2) { father[f2]=f1; } else //判断该无向图是否有环 { flag=1; } } int main() { int a,b; while(scanf("%d %d",&a,&b)!=EOF) { if(a==-1&&b==-1)break; if(a==0&&b==0) { printf("Yes\n"); continue; } //如果该图无点,也符合题意,所以输出Yes,这一点很难想到 set<int>s; //由于不知道它输入了哪些编号的点,所以用set记录 s.insert(a); s.insert(b); for(int i=1;i<=maxn;i++)father[i]=i; Union(a,b); flag=0; while(scanf("%d %d",&a,&b)) { if(a==0&&b==0)break; s.insert(a); s.insert(b); Union(a,b); } if(flag){ printf("No\n"); continue; } int root=0; //判断是否只有一个根节点 set<int>::iterator it; for(it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++) { if(father[*it]==*it)root++; if(root>=2) { flag=1;break; } } if(flag)printf("No\n"); else printf("Yes\n"); } return 0; }
2018-07-29