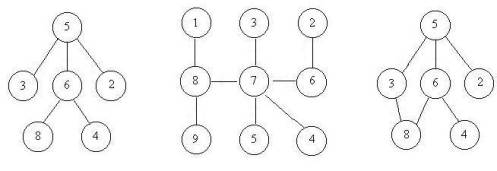
上次Gardon的迷宫城堡小希玩了很久(见Problem B),现在她也想设计一个迷宫让Gardon来走。但是她设计迷宫的思路不一样,首先她认为所有的通道都应该是双向连通的,就是说如果有一个通道连通了房间A和B,那么既可以通过它从房间A走到房间B,也可以通过它从房间B走到房间A,为了提高难度,小希希望任意两个房间有且仅有一条路径可以相通(除非走了回头路)。小希现在把她的设计图给你,让你帮忙判断她的设计图是否符合她的设计思路。比如下面的例子,前两个是符合条件的,但是最后一个却有两种方法从5到达8。
input
输入包含多组数据,每组数据是一个以0 0结尾的整数对列表,表示了一条通道连接的两个房间的编号。房间的编号至少为1,且不超过100000。每两组数据之间有一个空行。
整个文件以两个-1结尾。
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4
5 6 0 0
8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5
7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0
3 8 6 8 6 4
5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0
-1 -1
output
对于输入的每一组数据,输出仅包括一行。如果该迷宫符合小希的思路,那么输出"Yes",否则输出"No"。
Yes
Yes
No
code
//Siberian Squirrel
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<set>
#define ACM_LOCAL
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const double eps = 1e-7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int UP = 1e2 + 10;
int pre[N];
bool f = true;
set<int> st;
void Init(int n){
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++ i){
pre[i] = i;
}
}
int Find(int x) {
// while(pre[x] != x) x = pre[x];
// return pre[x];
return x == pre[x]? x: pre[x] = Find(pre[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y){
int fx = Find(x);
int fy = Find(y);
if(fx != fy){
pre[fy] = fx;
} else f = false;
}
inline bool solve(int n, int m, ll res = 0) {
st.clear();
Init(N);
merge(n, m);
st.insert(n);
st.insert(m);
res ++;
while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) && n + m) {
merge(n, m);
st.insert(n);
st.insert(m);
res ++;
}
return f && st.size() == res + 1? true: false;
}
int main() {
#ifdef ACM_LOCAL
freopen("input", "r", stdin);
freopen("output", "w", stdout);
#endif
int o = 1, n, m;
// scanf("%d", &o);
while(o --) {
while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) && n != -1 && m != -1) {
if(n + m == 0) puts("Yes");
else
printf("%s\n", solve(n, m)? "Yes": "No");
}
}
return 0;
}