一、论文简述
1. 第一作者:Qingshan Xu
2. 发表年份:2020
3. 发表期刊:arxiv
4. 关键词:MVS、3D重建、可见性、代价体、训练策略
5. 探索动机:ETH3D基准测试提供的图像包含强烈的视图变化,这就要求MVS方法考虑不同相邻图像的像素可见性信息。现有的基于学习的方法是针对连续视图变化的视频序列定制的。由于他们假设存在与参考图像具有较强可见性关联的相邻图像,通常从全局视图选择的角度选择这些图像作为输入,并对这些图像一视同仁,构建不加区分的多视图聚合代价体。因此,可见性估计在这些网络中被完全忽略。但是,同等对待每个相邻图像会使代价体容易受到不相关的相邻图像噪声的影响。
- Unlike the Tanks and Temples dataset, the images provided by ETH3D high-res benchmark contain strong variations in viewpoint, resulting in complicated visibility association. This requires MVS methods to consider the pixelwise visibility information of different neighboring images.
- The existing learning-based methods are tailored for video sequences with continuous viewpoint changes. Since they assume that there exist neighboring images that have strong visibility association with the reference image, they usually select these images as input from the perspective of global view selection and treat these images equally to construct an indiscriminate multi-view aggregated cost volume. Therefore, visibility estimation is totally ignored in these networks. However, treating each neighboring image equally will make the cost volume susceptible to the noise from unrelated neighboring images. This greatly limits the performance of learning-based methods on datasets like ETH3D high-res benchmark with strong variations in viewpoint.
6. 工作目标:学习深度网络中相邻图像的像素可见性信息是一个迫切需要解决的问题。
In real-world scenarios, especially in large-scale 3D reconstruction, the viewpoint of input images usually changes greatly. Therefore, to make learning-based methods truly feasible in practice, it is an urgent problem to learn the pixelwise visibility information of neighboring images in deep networks.
7. 核心思想:
- We propose Pixelwise Visibility-aware multiview Stereo Network (PVSNet) for robust multi view depth estimation. To the best of our knowledge, PVSNet is the first deep learning framework that is able to capture the visibility information of neighboring images and can be truly applied to datasets with strong viewpoint changes.
- We propose a way to regress 2D visibility maps from two-view cost volumes. The visibility maps can reflect the influence of occlusion, illumination, and unstructured viewing geometry. This allows good views to occupy more weights in the final cost volume representation.
- We present a new training strategy that introduces disturbing views to improve the robustness of our pixelwise visibility network.
8. 实验结果:
- the visibility estimation, which is validated in our subsequent experiments, is not only necessary for the datasets with strong viewpoint changes like the ETH3D high-res benchmark, but also crucial for the datasets with video sequences as input like the Tanks and Temples dataset.
- Extensive experiments have been conducted to elaborate on the superiority of our proposed pixelwise visibility-aware multi-view similarity measure. We demonstrate our novel PVSNet achieves state-of-the-art performance on various datasets.
9.论文下载:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2007.07714.pdf
二、实现过程
1. PVSNet概述
PVSNet的总体结构如下图所示。给定参考图像Iref,源图像Isrc,首先对所有输入图像使用共享的特征提取模块提取多尺度图像特征。然后通过单应性变化经构造每个源图像与参考图像之间的两视图代价体。与大多数现有方法直接对多个双视图代价体进行均值运算或方差计算相比,该方法的关键新颖之处在于在计算聚合的代价体之前估计不同源图像的像素可见性信息(图中红框)。基于可见性信息,将两个视图的代价体聚合为一个加权的代价体。最后,通过代价体滤波和深度推理来预测参考图像的深度图。
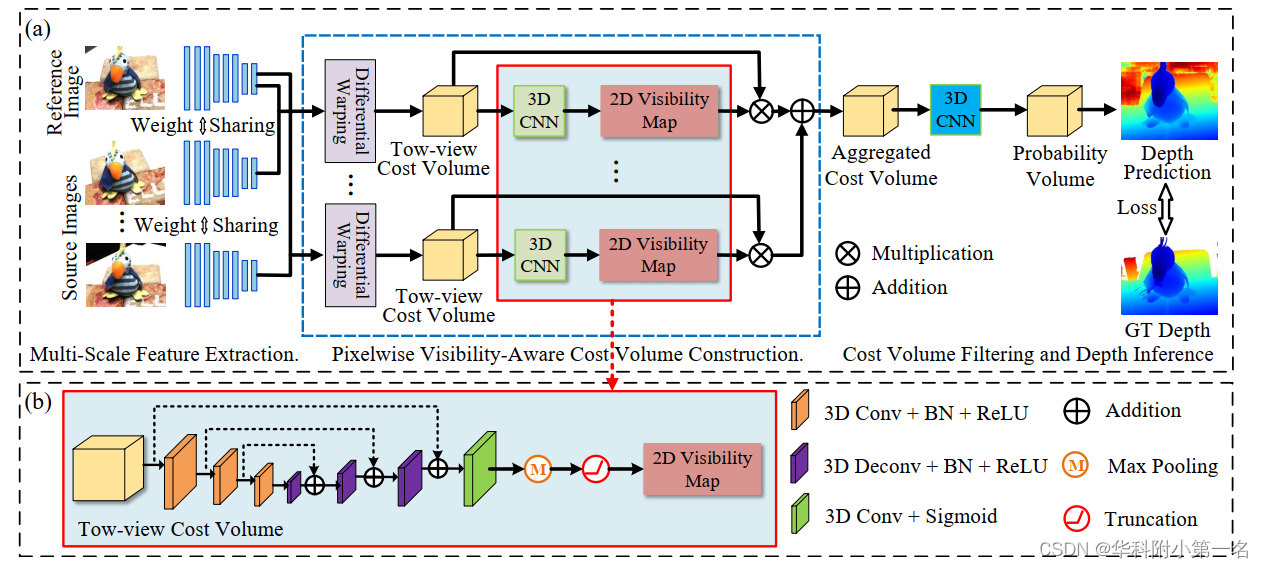
2. 多尺度特征提取
使用一个八层2D CNN将原始图像大小(3×H×W)降采样到F×H/4×W/4,F=32为特征通道数。
3. 像素可见性代价体构建
首先在每个源图像和参考图像之间构造两视图代价体。根据每个代价体回归每个源图像的可见性图。通过这些可见性图,多个双视图代价体被进一步聚合为统一的代价体。
两视图代价体构建。基于多个采样深度假设,将每个源图像提取的深度特征变化为参考图像的相机坐标,通过组相关计算出变化后的源图像特征与参考图像特征之间的多通道相似性图。构建两视图代价体。然后根据D个采样深度假设,计算D个相似图。将这些相似图进行打包,构造大小为G×H/4×W/4×D的两视图代价体,其中G=8为通道数。
像素可见性代价体聚合。在获得两视图代价体后,利用它来回归源图像的可见性图,因为两视图代价体编码了不同采样深度的置信度。由于两视图代价体的分布通常不具有区别性,因此首先应用3D U-Net来调制,其中U-Net使用三尺度编码器-解码器结构来增加感受野。除了最后一个卷积层产生一个通道特征,然后是sigmoid激活函数,其他卷积层后面是BN层和一ReLU。源图像的可见性图Vi定义为:

P(j,p)为像素P在第j个采样深度值处的概率估计。为了进一步消除不相关源图像的影响,去除可见概率低于一定阈值的图像。然后,将每个源图像的可见性图修改为:
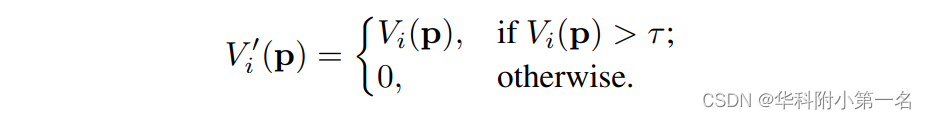
其中τ=0.05是控制源图像激活的阈值。上面的方程类似于ReLU,整个网络可以通过反向传播进行端到端训练。最终聚合的代价体由:
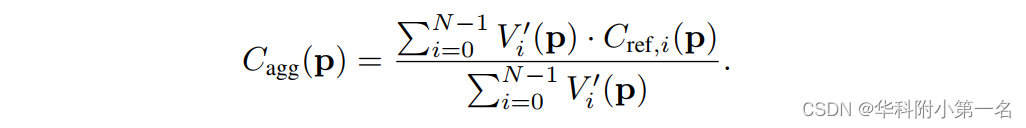
4. 代价体滤波和深度推理
为了进一步聚合空间域和深度域的上下文,应用具有堆叠正则化模块的3D CNN,用于过滤聚合代价体。过滤模块由一个3D ResNet和两个3D U-Net组成。为了适应大规模场景重建,实现亚像素深度估计,采用逆深度回归得到深度预测:
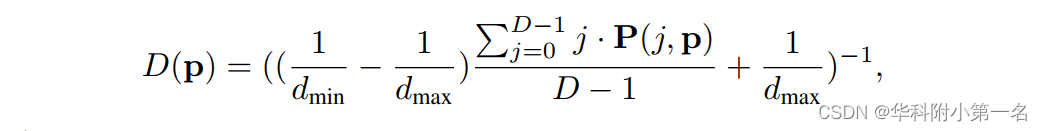
P(j,p)为沿深度方向经softmax操作归一化后的概率体。对于三个正则化模块,网络产生三个深度预测,Dpred0, Dpred1和Dpred2。采用L1损失函数来训练我们的网络。低分辨率预测的损失函数定义为:
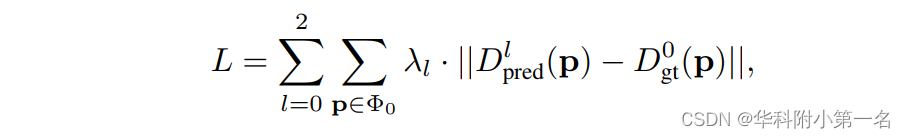
5. 高分辨率估计的延伸
利用低分辨率可见性估计来帮助薄代价体的构建。具体而言,在获得某一阶段的预测序数和概率体后,采用中基于方差的不确定性估计来计算下一阶段的深度采样范围。前一阶段的可见性图直接上采样到当前阶段,以计算可见性敏感的薄代价体。然后利用简单的3D U-Net得到概率体,利用逆深度回归来推断深度图。重复同样的过程,直到深度图达到原始图像分辨率。高分辨率预测的训练损失定义为:
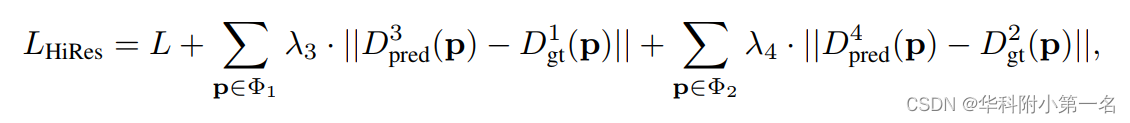
Dpred3和Dpred4是第二阶段和第三阶段的预测深度图。
6. 抗噪声训练策略
之前所有基于学习的方法[遵循MVSNet,通过全局视图来选择最好的两个相邻视图进行模型训练。然而,这两个选择的视图有如此强的可见性关联,只有少量可见性信息负样本参与模型训练的参考图像。正负之间的极端不平衡阻止了该方法充分利用像素可见性网络的潜力。为了缓解这一问题,提出引入干扰视图的抗噪声训练策略(AN)。具体来说,采用MVSNet中的方法来计算全局视图选择得分。然后,选择最好的两个视图和最差的两个视图来训练我们的模型。这种训练策略引入了更多的负样本,使我们的网络对不相关的视图更加鲁棒。
7. 实验
7.1. 数据集和评估指标
DTU dataset, Tanks and Temples dataset,ETH3D high-res benchmark is a dataset with strong viewpoint variations.
7.2. 实现细节
全局视图选择包括20个相邻视图。网络是使用PyTorch实现的。使用RMSprop优化器在两个NVIDIA GTX 1080Ti GPU上训练网络。初始学习率设置为0:001。
7.3. 与先进技术的比较

