Problem Description
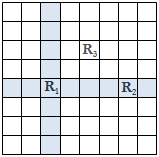
A rook is a piece used in the game of chess which is played on a board of square grids. A rook can only move vertically or horizontally from its current position and two rooks attack each other if one is on the path of the other. In the following figure, the dark squares represent the reachable locations for rook R1 from its current position. The figure also shows that the rook R1 and R2 are in attacking positions where R1 and R3 are not. R2 and R3 are also in non-attacking positions.
Now, given two numbers n and k, your job is to determine the number of ways one can put k rooks on an n x n chessboard so that no two of them are in attacking positions.
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 350), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case contains two integers n (1 ≤ n ≤ 30) and k (0 ≤ k ≤ n2).
Output
For each case, print the case number and total number of ways one can put the given number of rooks on a chessboard of the given size so that no two of them are in attacking positions. You may safely assume that this number will be less than 1017.
Sample Input
8
1 1
2 1
3 1
4 1
4 2
4 3
4 4
4 5Sample Output
Case 1: 1
Case 2: 4
Case 3: 9
Case 4: 16
Case 5: 72
Case 6: 96
Case 7: 24
Case 8: 0
题意:t 组数据,给出一个 n 行 k 列的格子,要求每行每列最多只放 1 个棋子,问有几种放法
思路:由于每行每列只能放一个,那么可以在 n 行中选出 k 行,然后再从 n 列选出 k 列中随便放,即 C(n,m)*A(n,m)
Source Program
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define E 1e-9
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define LL long long
const int MOD=1000000007;
const int N=200+5;
const int dx[]= {-1,1,0,0};
const int dy[]= {0,0,-1,1};
using namespace std;
LL dp[N][N];
void init(){
for(int i=1;i<=30;i++){
dp[i][0]=1;
dp[i][1]=i*i;
}
for(int i=2;i<=30;i++)
for(int j=2;j<=i;j++)
dp[i][j]=dp[i][1]*dp[i-1][j-1]/j;
}
int main(){
init();
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
int Case=1;
while(t--){
int n,k;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
printf("Case %d: %lld\n",Case++,dp[n][k]);
}
return 0;
}