文章目录
Lecture 1 The Learning Problem
本篇博客是学习《Machine Learning Foundations》(机器学习基石)—— Hsuan-Tien Lin (林轩田)所做的学习笔记,其中图片和内容皆为林轩田老师团队的智慧结晶,版权所有皆归林轩田老师团队所有。
在此感谢林轩田老师团队的付出。
希望能与大家分享,一起学习,共同进步。
Course Introduction
本课程是由台湾大学林轩田教授于2018秋季开设的《Machine Learning Foundations》(机器学习基石),内含数学推导,丰富举例,老师诙谐有趣,生动活跃,是学习机器学习基础的优秀课程。
本课程主要从以下四个方面讲述Machine Learning:
-
When Can Machines Learn?
-
Why Can Machines Learn?
-
How Can Machines Learn?
-
How Can Machines Learn Better?
像基石一样基础,像讲故事一样诙谐有趣。
What is Machine Learning
learning: for people(or other creatures) acquiring skill
with experience accumulated from observations
machine learning: for computer, acquiring skill
with experience accumulated/computed from data
skill means improving some performance measure
学习就是获取知识和掌握技能的过程
人类根据视觉、听觉、嗅觉,味觉,触觉来感知世界,通过大脑加工,获取知识和掌握技能
计算机根据数据,通过机器学习演算法,探究数据之中潜藏的规律
Key Essence of Machine Learning
(1)pattern(performance measure can be improved)
(2)definition(no programmable definition, so choose ML)
(3)data(computed from data about the pattern )
Fun Time
Which of the following is best suited for machine learning?
1. predicting whether the next cry of the baby girl happens at an even-numbered minute or not
2. determining whether a given graph contains a cycle
3. deciding whether to approve credit card to some customer
4. guessing whether the earth will be destroyed by the misuse of nuclear power in the next ten years
Explanation
使用机器学习的三个要素:(1)要有规律;(2)不能直接编程实现规则;(3)要有数据。
1.预测一个小孩子奇数分钟哭还是偶数分钟哭,没有规律。
2.判断一个图形中是否有圆,可以直接编程实现。
3.给不给信用卡基于一定规则;这个规则直接编程效果不好;银行拥有大量基于用户信息发放信用卡的样本;满足三要素,这个实例将贯穿我们整个课程。
4.没有训练数据(地球目前还未因为核爆炸毁灭过)。
Applications of Machine Learning
机器学习是一种构建复杂系统的可替代方案。
-
衣
Abu-Mostafa, 2012
根据销售数据和用户调查,推荐衣物穿搭风格。 -
食
Sadilek et al., 2013
根据推特用户的评语及定位,探究一家餐馆食物中毒的可能性:-) -
住
Tsanas and Xifara, 2012
根据建筑物的特征和它们的能源消耗,预测它们附近建筑物的能源消耗。 -
行
Stallkamp et al., 2012
根据交通标识图片及其含义,准确识别交通标志的含义。 -
育
根据学生在数学辅导系统中的测试及记录,判断学生是否能做对一道题。 -
娱乐
competition held by Netflix in 2006
根据用户对电影的评分,预测用户对未观赏电影的评分。
机器学习无处不在
Fun Time
Which of the following field cannot use machine learning?
1. Finance
2. Medicine
3. Law
4. None of the above
Explanation
机器学习应用广泛(衣食住行育等),无所不在。
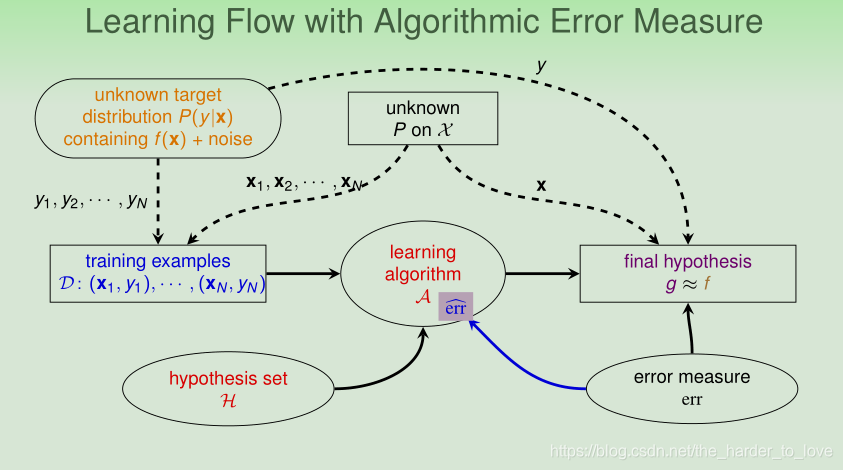
Components of Machine Learning
| property | value |
|---|---|
| age | 23 years |
| annual salary | NTD 1,000,000 |
| year in residence | 1 year |
| year in job | 0.5 year |
| current debt | 200,000 |
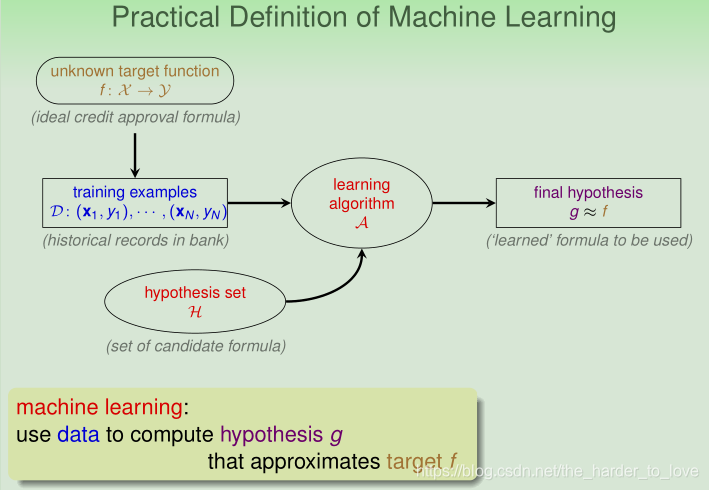
Basic Notations
- input: (i.e. customer application)
- output: (i.e. good/bad after approving credit card)
- unknown pattern to be learned ⇔ target function:
(i.e. ideal credit approval formula) - data ⇔ training examples: D = { (i.e. historical records in bank)
- hypothesis set : set of candidate formula(i.e. {annual salary > NTD 800,000, debt > NTD 100,000, year in job ≤ 2, …})
- hypothesis ⇔ skill with hopefully good performance:
(‘learned’ formula to be used) - learning algorithm : the method to approximate target f
Learning Model = and
Machine Learning: use data to compute hypothesis g that approximates target f.
Fun Time
How to use the four sets below to form a learning problem for song recommendation?
= [0,100]
= all possible (userid, songid) pairs
= all formula that ‘multiplies’ user factors & song factors,indexed by all possible combinations of such factors
= 1,000,000 pairs of ((userid, songid), rating)
1.
2.
3.
4.
Explanation
为用户对歌曲的评分集;
为用户和歌曲的集合;
为用户喜好歌曲因素的集合;
为样本数据;
Machine Learning, Data Mining, Statistics and Artificial Intelligence
Machine Learning(机器学习):use data to compute hypothesis g that approximates target f.
Data Mining(数据挖掘):use (huge) data to find property that is interesting.
Statistics:use data to make inference about an unknown process.
Artificial Intelligence:compute something that shows intelligent behavior.
机器学习侧重潜藏规律,数据挖掘侧重关联属性,他们互帮互助,密不可分。
统计学是数学的一个分支,很多工具用于机器学习。
从广义上说,人工智能是使某些事物表现出智能的技术,而机器学习是实现人工智能的一种方式。
Fun Time
Which of the following claim is not totally true?
1. machine learning is a route to realize artificial intelligence
2. machine learning, data mining and statistics all need data
3. data mining is just another name for machine learning
4. statistics can be used for data mining
Explanation
机器学习和数据挖掘很类似,但两者有所侧重,不是同一个概念。
Summary
讲义总结
机器学习基石课程总结
学完这门课,大家最终会掌握机器学习的完整概念和流程。
机器学习技法课程预告
学完这门课,可以继续学进阶课程——《Machine Learning Techniques》(机器学习技法),大家最终会学习和掌握各种不同的机器学习算法。

参考文献
《Machine Learning Foundations》(机器学习基石)—— Hsuan-Tien Lin (林轩田)
《Machine Learning Techniques》(机器学习技法)—— Hsuan-Tien Lin (林轩田)