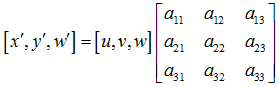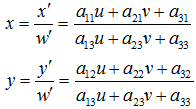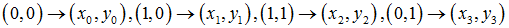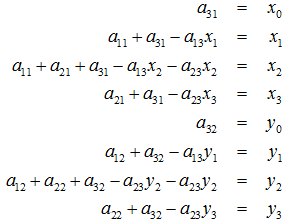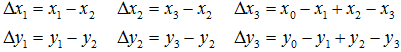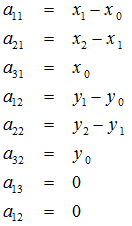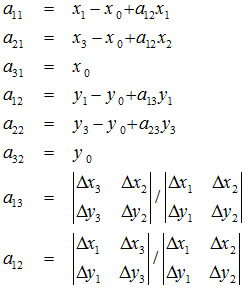透视变换(Perspective Transformation)是将图片投影到一个新的视平面(Viewing Plane),也称作投影映射(Projective Mapping)。通用的变换公式为:
u,v是原始图片左边,对应得到变换后的图片坐标x,y,其中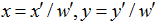
变换矩阵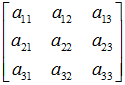
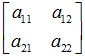
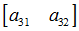
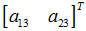
备注: w = 1 a33 = 1
重写之前的变换公式可以得到:
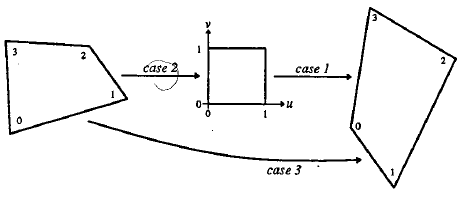
所以,已知变换对应的几个点就可以求取变换公式。反之,特定的变换公式也能新的变换后的图片。简单的看一个正方形到四边形的变换:
变换的4组对应点可以表示成:
根据变换公式得到:
定义几个辅助变量:
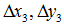
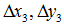
求解出的变换矩阵就可以将一个正方形变换到四边形。反之,四边形变换到正方形也是一样的。于是,我们通过两次变换:四边形变换到正方形+正方形变换到四边形就可以将任意一个四边形变换到另一个四边形。
看一段代码:
PerspectiveTransform::PerspectiveTransform(float inA11, float inA21,
float inA31, float inA12,
float inA22, float inA32,
float inA13, float inA23,
float inA33) :
a11(inA11), a12(inA12), a13(inA13), a21(inA21), a22(inA22), a23(inA23),
a31(inA31), a32(inA32), a33(inA33) {}
PerspectiveTransform PerspectiveTransform::quadrilateralToQuadrilateral(float x0, float y0, float x1, float y1,
float x2, float y2, float x3, float y3, float x0p, float y0p, float x1p, float y1p, float x2p, float y2p,
float x3p, float y3p) {
PerspectiveTransform qToS = PerspectiveTransform::quadrilateralToSquare(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3);
PerspectiveTransform sToQ =
PerspectiveTransform::squareToQuadrilateral(x0p, y0p, x1p, y1p, x2p, y2p, x3p, y3p);
return sToQ.times(qToS);
}
PerspectiveTransform PerspectiveTransform::squareToQuadrilateral(float x0, float y0, float x1, float y1, float x2,
float y2, float x3, float y3) {
float dx3 = x0 - x1 + x2 - x3;
float dy3 = y0 - y1 + y2 - y3;
if (dx3 == 0.0f && dy3 == 0.0f) {
PerspectiveTransform result(PerspectiveTransform(x1 - x0, x2 - x1, x0, y1 - y0, y2 - y1, y0, 0.0f,
0.0f, 1.0f));
return result;
} else {
float dx1 = x1 - x2;
float dx2 = x3 - x2;
float dy1 = y1 - y2;
float dy2 = y3 - y2;
float denominator = dx1 * dy2 - dx2 * dy1;
float a13 = (dx3 * dy2 - dx2 * dy3) / denominator;
float a23 = (dx1 * dy3 - dx3 * dy1) / denominator;
PerspectiveTransform result(PerspectiveTransform(x1 - x0 + a13 * x1, x3 - x0 + a23 * x3, x0, y1 - y0
+ a13 * y1, y3 - y0 + a23 * y3, y0, a13, a23, 1.0f));
return result;
}
}
PerspectiveTransform PerspectiveTransform::quadrilateralToSquare(float x0, float y0, float x1, float y1, float x2,
float y2, float x3, float y3) {
// Here, the adjoint serves as the inverse:
return squareToQuadrilateral(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3).buildAdjoint();
}
PerspectiveTransform PerspectiveTransform::buildAdjoint() {
// Adjoint is the transpose of the cofactor matrix:
PerspectiveTransform result(PerspectiveTransform(a22 * a33 - a23 * a32, a23 * a31 - a21 * a33, a21 * a32
- a22 * a31, a13 * a32 - a12 * a33, a11 * a33 - a13 * a31, a12 * a31 - a11 * a32, a12 * a23 - a13 * a22,
a13 * a21 - a11 * a23, a11 * a22 - a12 * a21));
return result;
}
PerspectiveTransform PerspectiveTransform::times(PerspectiveTransform other) {
PerspectiveTransform result(PerspectiveTransform(a11 * other.a11 + a21 * other.a12 + a31 * other.a13,
a11 * other.a21 + a21 * other.a22 + a31 * other.a23, a11 * other.a31 + a21 * other.a32 + a31
* other.a33, a12 * other.a11 + a22 * other.a12 + a32 * other.a13, a12 * other.a21 + a22
* other.a22 + a32 * other.a23, a12 * other.a31 + a22 * other.a32 + a32 * other.a33, a13
* other.a11 + a23 * other.a12 + a33 * other.a13, a13 * other.a21 + a23 * other.a22 + a33
* other.a23, a13 * other.a31 + a23 * other.a32 + a33 * other.a33));
return result;
}
void PerspectiveTransform::transformPoints(vector<float> &points) {
int max = points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < max; i += 2) {
float x = points[i];
float y = points[i + 1];
float denominator = a13 * x + a23 * y + a33;
points[i] = (a11 * x + a21 * y + a31) / denominator;
points[i + 1] = (a12 * x + a22 * y + a32) / denominator;
}
}对一张透视图片变换回正面图的效果:
int main(){
Mat img=imread("boy.png");
int img_height = img.rows;
int img_width = img.cols;
Mat img_trans = Mat::zeros(img_height,img_width,CV_8UC3);
PerspectiveTransform tansform = PerspectiveTransform::quadrilateralToQuadrilateral(
0,0,
img_width-1,0,
0,img_height-1,
img_width-1,img_height-1,
150,250, // top left
771,0, // top right
0,1023,// bottom left
650,1023
);
vector<float> ponits;
for(int i=0;i<img_height;i++){
for(int j=0;j<img_width;j++){
ponits.push_back(j);
ponits.push_back(i);
}
}
tansform.transformPoints(ponits);
for(int i=0;i<img_height;i++){
uchar* t= img_trans.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j=0;j<img_width;j++){
int tmp = i*img_width+j;
int x = ponits[tmp*2];
int y = ponits[tmp*2+1];
if(x<0||x>(img_width-1)||y<0||y>(img_height-1))
continue;
uchar* p = img.ptr<uchar>(y);
t[j*3] = p[x*3];
t[j*3+1] = p[x*3+1];
t[j*3+2] = p[x*3+2];
}
}
imwrite("trans.png",img_trans);
return 0;
}
另外在OpenCV中也实现了基础的透视变换操作,有关函数使用请见下一篇:
【OpenCV】透视变换 Perspective Transformation(续)