总结
- 指数型:state[]
- 排列型:state[] used[]
- 组合型:state[] startIndex(startIndex标记从输入数组的哪一个位置开始遍历)
指数型枚举
每个数字要么选要么不选
方法1:数组
dfs思考递归搜索树,用state[]数组记录状态
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static boolean[] state; //记录选择状态 为true表示选择
static int n;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
state = new boolean[n + 1];
dfs(1);
}
public static void dfs(int index){
if(index > n){
//输出
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(state[i]) System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
state[index] = true;
dfs(index + 1);
state[index] = false;
dfs(index + 1);
}
}
方法2:List
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static LinkedList<Integer> path;
static List<List<Integer>> res;
static int n;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
path = new LinkedList<>();
res = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(1);
for(List<Integer> path : res){
for(int i : path) System.out.print(i + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void dfs(int index){
if(index > n){
//输出
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
path.add(index);
dfs(index + 1);
path.removeLast();
dfs(index + 1);
}
}
例题:lc784. 字母大小写全排列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/letter-case-permutation/description/
tips1:
-
查看ASCII表可以发现ASCII在 65-90 之间是大写字母,97-122 是小写字母,即大小写相差32,可以使用位运算进行快捷转换
-
位运算进行字母大小写转换
arr[index] ^= 32;
tips2:
- 使用Character.isDigit(arr[index])快捷判断是否是数字
代码
class Solution {
List<String> res;
int len;
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String s) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
len = s.length();
dfs(s.toCharArray(),0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(char[] arr, int index){
while(index < len && Character.isDigit(arr[index])) index++;
//最底端
if(index == len){
res.add(new String(arr));
return;
}
//先变大小写
arr[index] ^= 32;
dfs(arr,index + 1);
//变回来
arr[index] ^= 32;
dfs(arr,index + 1);
}
}
遍历过程
[A1B2,A1b2,a1b2,a1B2]
排列型枚举
排列型
https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations/description/
方法1:数组
两个数组记录状态
state[]数组记录每个位置的状态
used[]数组记录数值是否用过
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int n;
static int[] state; //记录路径
static boolean[] used; //记录当前数字是否用过
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
used = new boolean[n + 1];
state = new int[n + 1];
dfs(1);//因为答案要求从1开始
}
public static void dfs(int index){
if(index > n){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
System.out.print(state[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(used[i]) continue;
used[i] = true; //记录已经使用过
state[index] = i; //记录路径
dfs(index + 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
方法2:List
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int n;
static LinkedList<Integer> path;
static List<List<Integer>> res;
static boolean[] used; //记录当前数字是否用过
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
used = new boolean[n + 1];
path = new LinkedList<>();
res = new ArrayList<>();
// state = new int[n + 1];
dfs(1);//因为答案要求从1开始
for(List<Integer> path : res){
for(int i : path) System.out.print(i + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void dfs(int index){
if(index > n){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(used[i]) continue;
used[i] = true; //记录已经使用过
path.add(i);
dfs(index + 1);
used[i] = false;
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
变形:数组中有重复元素 需要返回结果不能重复
- 剑指Offer 38. 字符串的排列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/zi-fu-chuan-de-pai-lie-lcof/description/
注意点:排序以及加入树层去重
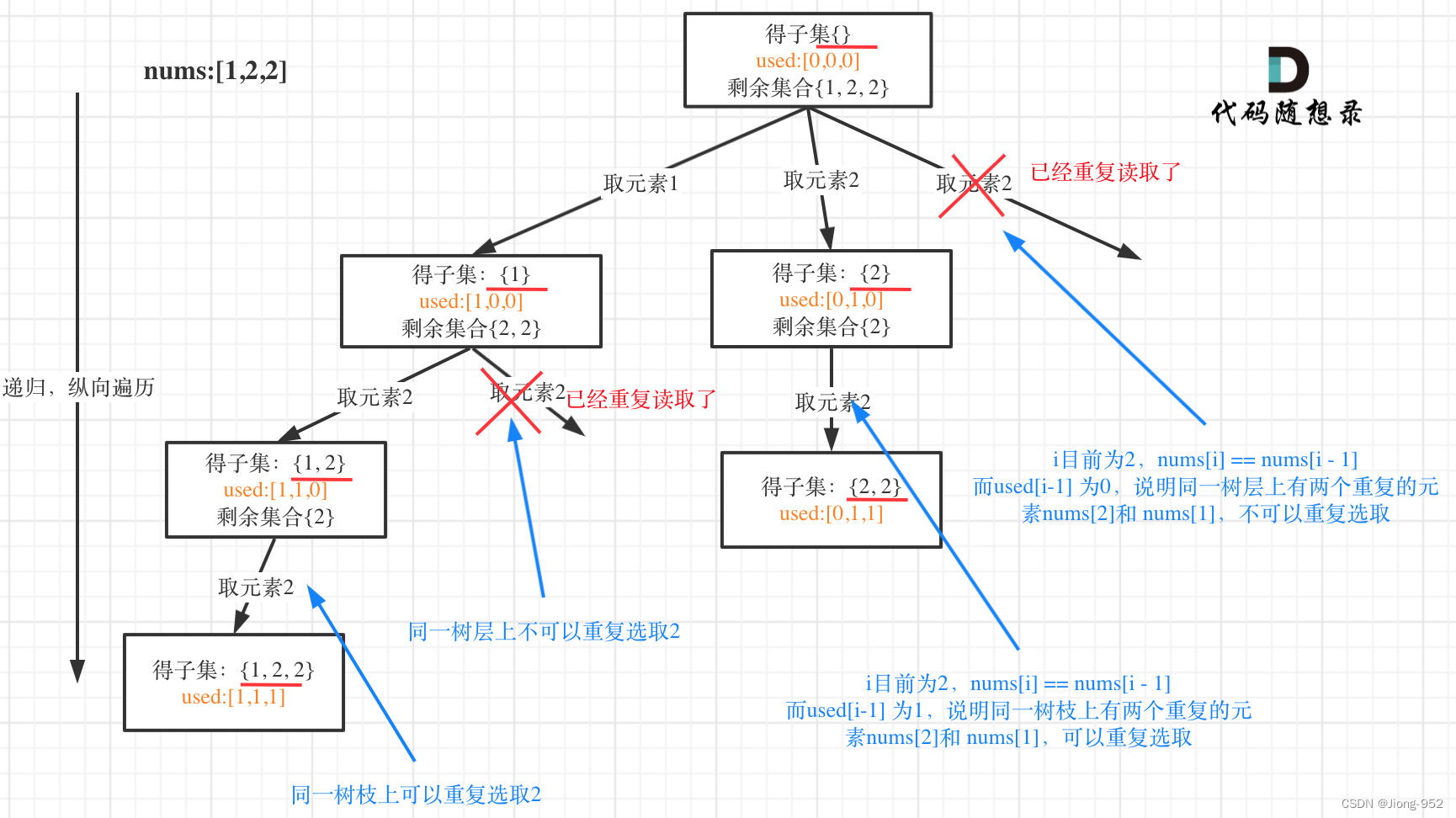
Arrays.sort(arr);
if(i - 1 >= 0 && arr[i - 1] == arr[i] && used[i-1] == false) continue;
class Solution {
//全排列问题
char[] arr;
StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] used;
public String[] permutation(String s) {
arr = s.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(arr);
used = new boolean[arr.length];
dfs(0);
String[] ans = new String[res.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++){
ans[i] = res.get(i);
}
return ans;
}
public void dfs(int index){
if(index == arr.length){
res.add(path.toString());
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
//加入同一层去重 如果前面已经用过则不再使用防止重复
if(i - 1 >= 0 && arr[i - 1] == arr[i] && used[i-1] == false) continue;
if(!used[i]){
used[i] = true;
path.append(arr[i]);
dfs(index + 1);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
lc47. 全排列 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations-ii/description/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res;
LinkedList<Integer> path;
boolean[] used;
int[] nums;
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
//去重的核心是排序
res = new ArrayList<>();
path = new LinkedList<>();
used = new boolean[nums.length];
Arrays.sort(nums);
this.nums = nums;
backtracking();
return res;
}
public void backtracking(){
if(path.size() == nums.length){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
//nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false表明当前和上一个值一样,但是上一个已经用过
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) continue;
if(used[i] == false){
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
backtracking();
used[i] = false;
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
}
组合型枚举
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combinations/description/
方法1:数组
state[]数组记录每个位置的状态,即路径
startIndex记录遍历位置
n相当于树的宽度,m相当于树的深度
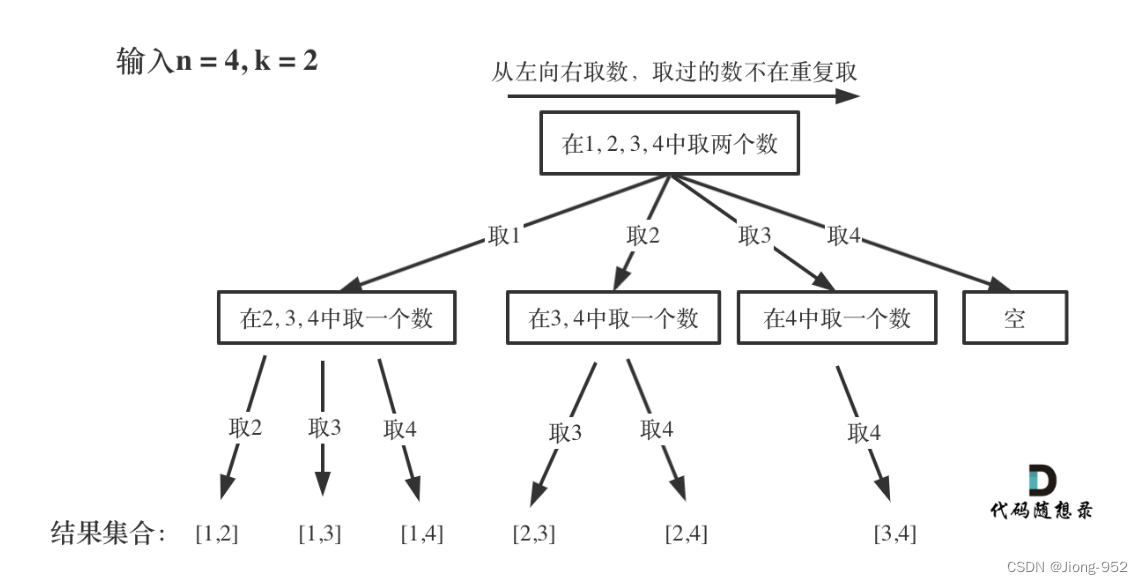
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int[] state; //记录路径,m个位置都放的是什么数
static int n;
static int m;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
state = new int[m];
dfs(0,1);
}
public static void dfs(int index,int startIndex){
// 剪枝
//已经不足m个
if(index + n - startIndex + 1 < m) return;
if(index == m){
//叶子结点
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) System.out.print(state[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++){
state[index] = i;
dfs(index + 1, i + 1);
state[index] = 0;
}
}
}
方法2:List
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
// static int[] state; //记录路径,m个位置都放的是什么数
static int n;
static int m;
static LinkedList<Integer> path;
static List<List<Integer>> res;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
path = new LinkedList<>();
res = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(0,1);
for(List<Integer> path : res){
for(int i : path) System.out.print(i + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void dfs(int index,int startIndex){
// 剪枝
if(index + n - startIndex + 1 < m) return;
if(index == m){
//叶子结点
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++){
path.add(i);
dfs(index + 1, i + 1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
变形
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-iii/description/
找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合,且满足下列条件:
- 只使用数字1到9
- 每个数字 最多使用一次
返回 所有可能的有效组合的列表 。该列表不能包含相同的组合两次,组合可以以任何顺序返回。
示例 1:
输入: k = 3, n = 7
输出: [[1,2,4]]
解释:
1 + 2 + 4 = 7
没有其他符合的组合了。
示例 2:
输入: k = 3, n = 9
输出: [[1,2,6], [1,3,5], [2,3,4]]
解释:
1 + 2 + 6 = 9
1 + 3 + 5 = 9
2 + 3 + 4 = 9
没有其他符合的组合了。
示例 3:
输入: k = 4, n = 1
输出: []
解释: 不存在有效的组合。
在[1,9]范围内使用4个不同的数字,我们可以得到的最小和是1+2+3+4 = 10,因为10 > 1,没有有效的组合。
提示:
2 <= k <= 91 <= n <= 60
code
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
dfs(k,n,1,0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int k, int target, int startIndex, int sum){
// 剪枝
if(sum > target) return;
if(path.size() + 9 - startIndex + 1 < k) return;
// 到底
if(path.size() == k && sum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex; i <= 9; i++){
path.add(i);
dfs(k,target,i+1,sum+i);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
带分数
方法1:
暴力全排列+枚举
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int target; //目标等式的左边
static int[] nums; //目标等式的右边
static boolean[] used; //记录用过的数字
static int cnt; //记录结果数
static int N = 10;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
target = sc.nextInt();
nums = new int[N];
used = new boolean[N];
dfs(0);
System.out.println(cnt);
}
//根据数组左右返回数值
public static int cal(int l, int r){
int res = 0;
for(int i = l; i <= r; i++){
res = res * 10 + nums[i];
}
return res;
}
public static void dfs(int index){
if(index == 9){
//新的全排列
//开始枚举a b c
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++){
for(int j = i + 1; j < 8; j++){
int a = cal(0,i);
int b = cal(i + 1, j);
int c = cal(j + 1, 8);
//去掉0
if(a == 0 || b ==0 || c == 0) continue;
//判断是符合
if(c * target == c * a + b) cnt++;
}
}
return;
}
//继续搜索
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++){
if(!used[i]){
used[i] = true;
nums[index] = i;
dfs(index + 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
方法2:
剪枝优化,暴力枚举a ,c b自动得出,判断是否满足
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int target;
static boolean[] used;
static int N = 10;
static int cnt;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
target = sc.nextInt();
used = new boolean[N];
dfs_a(0,0);
System.out.println(cnt);
}
//index表示当前遍历到第几位
//a表示当前a的值
public static void dfs_a(int index, int a){
if(index == 8 || a >= target) return;
if(a > 0) dfs_c(index, a , 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++){
if(!used[i]){
used[i] = true;
dfs_a(index + 1, a * 10 + i);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
public static void dfs_c(int index, int a, int c){
if(index == 9) return;
if(c > 0 && check(a,c)) cnt++;
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++){
if(!used[i]){
used[i] = true;
dfs_c(index + 1, a, c * 10 + i);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
//判断当前的a c是否符合条件
public static boolean check(int a, int c){
int b = (target - a) * c;
if(a == 0 || b == 0 || c == 0) return false;
boolean[] backup = used.clone();
//先判断b中的数字是否有了,没有就标记为true
while(b > 0){
int x = b % 10;
b /= 10;
if(x == 0 | backup[x]) return false;
backup[x] = true;
}
//判断used是否全部都用过了
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++){
if(!backup[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
array.clone()可以用于复制数组
- array:要复制的数组
- 方法返回一个copy数组