title:Smooth-AP: Smoothing the Path Towards Large-Scale Image Retrieval
link:https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.12163
Presentation:Smooth-AP: Smoothing the Path Towards Large-Scale Image Retrieval, ECCV 2020
code:https://github.com/Andrew-Brown1/Smooth_AP
author:VGG
1. 问题/目标:
不同于以往基于度量学习的损失函数,作者提出了基于优化排序的损失函数。选择的优化对象是AP,但是AP是不可微的,所以提出了smooth AP
2. 如何解决:
AP估值计算后,将其中的不可微部分换成sigmoid函数
3. 解决效果:
在Stanford Online products,VehicleID,INaturalist,VGGFace2 and IJB-C上做了实验,在已经商用的人脸检测任务上提升AP 2~4%, recall提升不明显,有升有降低;
4. 公式:


4.1 Smooth AP
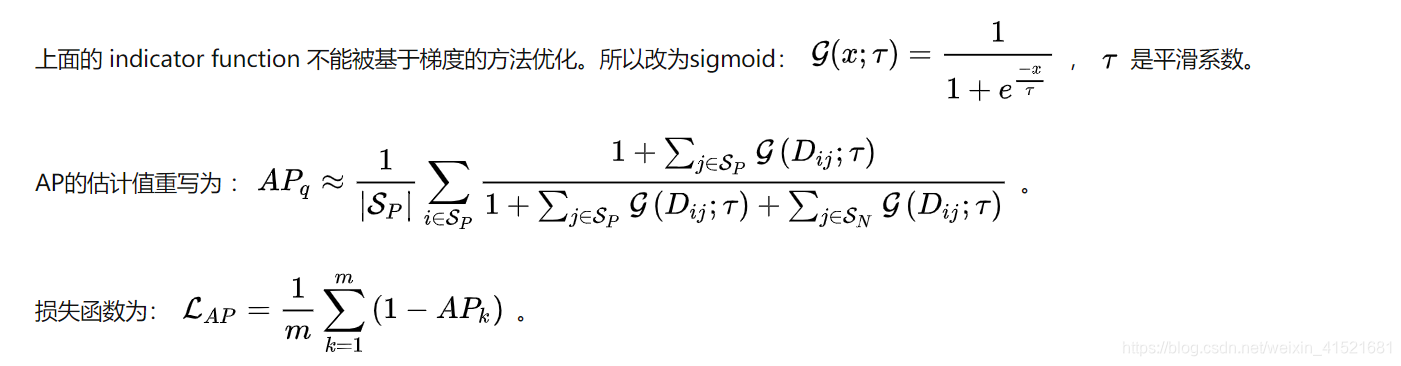
4.2 三点分析:
-
第一点是平滑系数越小,AP的估计值越接近真实AP,而越大的平滑系数会带来更大的操作空间,就是图二里求导后的曲线下方面积,可以提供更多的梯度信息(并没有理解,原文如下)。
Smoothing parameter τ governs the temperature of the sigmoid that replaces the Indicator function 1{·}. It defines an operating region, where terms of the difference matrix are given a gradient by the Smooth-AP loss. If the terms are mis-ranked, Smooth-AP will attempt to shift them to the correct order. Specifically, a small value of τ results in a small operating region (Figure 2 (b) – note the small region with gradient seen in the sigmoid derivative), and a tighter approximation of true AP. The strong acceleration in gradient around the zero point (Figure 2 (b)-© second row) is essential to replicating the desired qualities of AP, as it encourages the shifting of instances in the embedding space that result in a change of rank (and hence change in AP), rather than shifting instances by some large distance but not changing the rank. A large value of τ offers a large operating region, however, at the cost of a looser approximation to AP due to its divergence from the indicator function.
-
第二点是triplet loss 更像是度量损失而不是优化排序。
-
第三点是相对于其他优化AP的方法 FastAP and Blackbox AP,本方法更简单,并且估计的更准。而且这俩方法和triplet loss 一样,可能更像度量损失。