# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #导入所需模块 import tensorflow as tf from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import numpy as np import pandas as pd #读入数据/标签,生成x_train, y_train df = pd.read_csv("F:\\tensorflow tutorial\\中国大学MOOCTF笔记2.1共享给所有学习者\\class2\\dot.csv") x_data = np.array(df[["x1", "x2"]]) y_data = np.array(df["y_c"]) x_train = x_data y_train = y_data.reshape(-1, 1) Y_c = [["red" if y else "blue"] for y in y_train] #转换x的数据类型,否则后面矩阵相乘时会因数据类型问题报错 x_train = tf.cast(x_train, tf.float32) y_train = tf.cast(y_train, tf.float32) #from_tensor_slices函数切分传入的张量的第一个维度,生成对应的数据集,使输入特征和标签值一一对应 train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train)).batch(32) #用tf.Variable()保证参数可训练 w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([2, 11]), dtype=tf.float32) b1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.01, shape=[32])) print(b1) print(b1.shape) w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([11, 1], dtype=tf.float32)) b2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.01, shape=[1])) lr = 0.005 #学习率 epoch = 800 #循环轮数 #训练部分 for epoch in range(epoch): for step, (x_train, y_train) in enumerate(train_db): with tf.GradientTape() as tape: #记录梯度信息 h1 = tf.matmul(x_train, w1) + b1 #记录神经网络乘加运算 h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1) y = tf.matmul(h1, w2) + b2 #采用均方误差损失函数mse = mean(sum(y-out)^2) loss_mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_train - y))
""" #添加L2正则化 loss_regularization = [] #tf.nn.l2_loss(w) = sum(w ** 2) / 2 loss_regularization.append(tf.nn.l2_loss(w1)) loss_regularization.append(tf.nn.l2_loss(w2)) #求和 #例: x=tf.constant([1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]) # tf.reduce_sum(x) # >>>6 loss_regularization = tf.reduce_sum(loss_regularization) loss = loss_mse + 0.03 * loss_regularization #REGULARIZER = 0.03 """ loss = loss_mse #计算loss对各个参数的梯度 variables = [w1, b1, w2, b2] grads = tape.gradient(loss, variables) #实现梯度更新 #w1 = w1 - lr * w1_grad w1.assign_sub(lr * grads[0]) b1.assign_sub(lr * grads[1]) w2.assign_sub(lr * grads[2]) b2.assign_sub(lr * grads[3]) #每200个epoch, 打印loss信息 if epoch % 50 ==0: print("epoch:", epoch, "loss:", float(loss)) #预测部分 print("***********predict****************") #xx在-3到3之间以步长为0.01, yy在-3到3之间以步长0.01,生成间隔数值点 xx, yy = np.mgrid[-3:3:.1, -3:3:.1] #将xx, yy拉直,并合并配对为二维张量,生成二维坐标点 grid = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()] grid = tf.cast(grid, tf.float32) #将网格坐标点喂入神经网络,进行预测,probs为输出 probs = [] for x_predict in grid: #使用训练好的参数进行预测 h1 = tf.matmul([x_predict], w1) + b1 h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1) y = tf.matmul(h1, w2) + b2 #y为预测结果 probs.append(y) #取第0列给x1,取第1列给x2 x1 = x_data[:, 0] x2 = x_data[:, 1] #probs的shape调整成xx的样子 probs = np.array(probs).reshape(xx.shape) plt.scatter(x1, x2, color=np.squeeze(Y_c)) #把坐标xx, yy和对应的值probs放入contour函数,给probs值为0.5的所有点上色,plt.show()后,显示的是红蓝点的分界线 plt.contour(xx, yy, probs, levels=[.5]) plt.show()
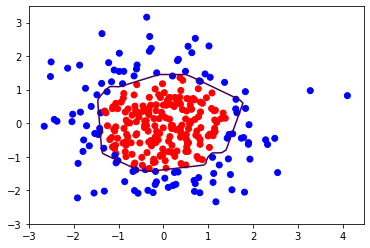
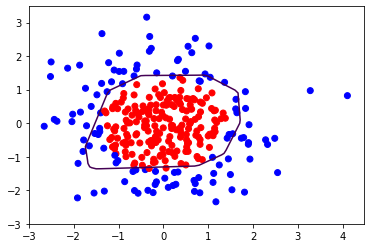
不含正则化 含正则化