在神经网络优化中,通过对损失函数进行正则化来缓解过拟合
方法:通过在损失函数中引入模型复杂度指标,利用给W加权值,弱化了训练数据的噪声
公式为:
loss = loss(y与y_) + regularizer * loss(w)
其中 loss(y与y_)为一般损失函数,可以为交叉熵损失函数,或者均方误差损失函数
regularizer为正则化权重
regularizer * loss(w) 在python中用一下代码实现:
tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(regularizer)(w)
下面是全部代码及运行截图
#coding:utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #引入图形可视化工具
#正则化损失函数
#loss = loss(y与y_) + regularizer * loss(w) 此为正则化损失函数
BATCH_SIZE = 30 #批处理量,一次神经网络训练量
#基于seed产生随机数
seed = 2
rdm = np.random.RandomState(seed)
#将随机数输入300行2列的矩阵,作为输入数据集
X = rdm.randn(300,2)
#从输入数据集矩阵依次取出每行(x0,x1),若 x0*x0 + x1*x1 <2 ,则将 Y_ 赋值为1 ,否则赋值为0
Y_ = [int(x0*x0 + x1*x1 <2 ) for (x0,x1) in X]
#根据 Y_ 的值给出颜色,若为1,赋值为红色,否则赋值为蓝色
Y_c = [['red' if y else 'blue'] for y in Y_]
#对 X 和 Y_ 的形状进行整理,将 X 变成 n 行 2 列的矩阵,将 Y_ 整理成 n 行 1 列的矩阵,其中 n 用 -1 表示
X = np.vstack(X).reshape(-1,2)
Y_ = np.vstack(Y_).reshape(-1,1)
#将 X , Y_ , Y_c 打印出来
print(X)
print(Y_)
print(Y_c)
#用plt.scatter画出数据集X各行中的第0列和第1列元素组成的点(x0,x1),用Y_c对点进行着色(c代表color)
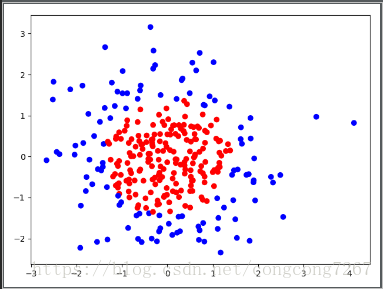
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c = np.squeeze(Y_c))
plt.show()
#loss = loss(y与y_) + regularizer * loss(w) 此为正则化损失函数
# regularizer * loss(w) 可用 tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(regularizer)(w) 实现
def get_weight(shape,regularizer): #shape为列表,regularizer为正则化权重
w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape),dtype=tf.float32)
tf.add_to_collection('losses',tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(regularizer)(w)) #正则化,来缓解过拟合,将所有计算好的正则化了的 w 加在 losses 赋值在上
return w
def get_bias(shape):
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.01,shape=shape)) #初始化赋值为0.01,用shape传入参数赋值给b
return b
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=(None,2))
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=(None,1))
#第一层神经网络
w1 = get_weight([2,11],0.01)
b1 = get_bias([11])
y1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x,w1)+b1) #relu激活函数,除了输出层一定用sigmoid激活函数外,其它层基本都用relu激活函数
#第二层神经网络,输出层
w2 = get_weight([11,1],0.01)
b2 = get_bias([1])
y = tf.matmul(y1,w2)+b2 #输出层不用激活
#损失函数
loss_mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-y_)) #均方误差损失函数,此为原始损失函数 loss(y与y_)
#loss = loss(y与y_) + regularizer * loss(w) 此为正则化损失函数
loss_total = loss_mse + tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('losses')) #将均方误差损失函数和正则化了的所有的 w 的和的值相加得到更有效的损失函数
#训练方法,用不同的损失函数,效果不同,正则化了的损失函数效果更好
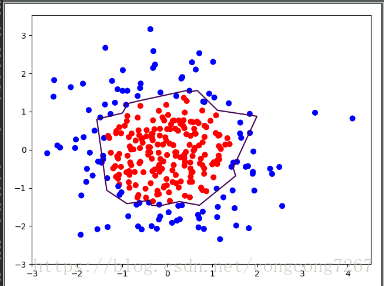
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss_mse)
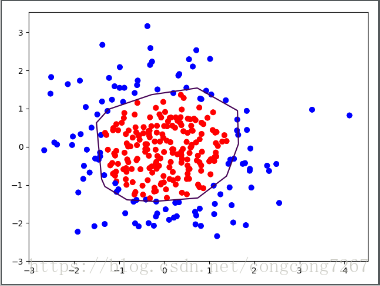
#train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss_total)
#生成会话,开始训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
#初始化所有参数
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init_op)
STEPS = 40000 #训练轮数
for i in range(STEPS):
start = (i*BATCH_SIZE)%300
end = start + BATCH_SIZE
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:X[start:end],y_:Y_[start:end]}) #喂入数据,开始训练
if i % 2000 == 0:
loss_mse_v = sess.run(loss_mse,feed_dict={x:X,y_:Y_})
print("Aftre %d steps ,the loss is %f"%(i,loss_mse_v))
xx ,yy = np.mgrid[-3:3:.01 ,-3:3:.01] #np.mgrid[起:止:步长,起:止:步长] 表示x轴,y轴的起点,终点,两点之间的步长
grid = np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()] #通过eavel()函数将xx,yy拉直,并通过np.c_上述xx,yy组成矩阵,形成网格坐标点
probs = sess.run(y,feed_dict={x:grid}) #将所有的网格坐标点喂入神经网络,经神经网络计算推测得出结果y,将y赋值给probs ,此probs为所有红色点或者蓝色点的量化值
probs = probs.reshape(xx.shape) #将probs整理为xx的矩阵的形状
print("")
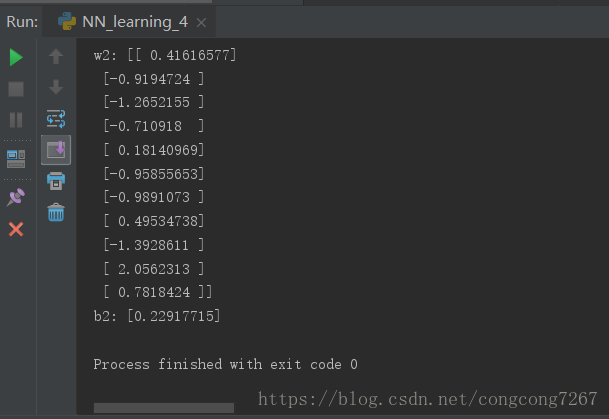
print("w1:",sess.run(w1))
print("b1:",sess.run(b1))
print("w2:",sess.run(w2))
print("b2:",sess.run(b2))
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c = np.squeeze(Y_c))
plt.contour(xx,yy,probs,levels=[.5]) #plt.contour(x轴坐标值,y轴坐标值,该点的高度,levels=[等高线的高度]) 通过x轴坐标,y轴坐标和各点的高度,将指定高度的点描上颜色
plt.show()
运行截图
下面是损失函数为loss_mse是的截图
下面是损失函数为loss_total的运行截图
可以有图像直观看出来,正则化了的损失函数效果更好