版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/mr_muli/article/details/82979604
- 新建MeanShift.py文件
import numpy as np
# 定义 预先设定 的阈值
STOP_THRESHOLD = 1e-4
CLUSTER_THRESHOLD = 1e-1
# 定义度量函数
def distance(a, b):
return np.linalg.norm(np.array(a) - np.array(b))
# 定义高斯核函数
def gaussian_kernel(distance, bandwidth):
return (1 / (bandwidth * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi))) * np.exp(-0.5 * ((distance / bandwidth)) ** 2)
# mean_shift类
class mean_shift(object):
def __init__(self, kernel=gaussian_kernel):
self.kernel = kernel
def fit(self, points, kernel_bandwidth):
shift_points = np.array(points)
shifting = [True] * points.shape[0]
while True:
max_dist = 0
for i in range(0, len(shift_points)):
if not shifting[i]:
continue
p_shift_init = shift_points[i].copy()
shift_points[i] = self._shift_point(shift_points[i], points, kernel_bandwidth)
dist = distance(shift_points[i], p_shift_init)
max_dist = max(max_dist, dist)
shifting[i] = dist > STOP_THRESHOLD
if(max_dist < STOP_THRESHOLD):
break
cluster_ids = self._cluster_points(shift_points.tolist())
return shift_points, cluster_ids
def _shift_point(self, point, points, kernel_bandwidth):
shift_x = 0.0
shift_y = 0.0
scale = 0.0
for p in points:
dist = distance(point, p)
weight = self.kernel(dist, kernel_bandwidth)
shift_x += p[0] * weight
shift_y += p[1] * weight
scale += weight
shift_x = shift_x / scale
shift_y = shift_y / scale
return [shift_x, shift_y]
def _cluster_points(self, points):
cluster_ids = []
cluster_idx = 0
cluster_centers = []
for i, point in enumerate(points):
if(len(cluster_ids) == 0):
cluster_ids.append(cluster_idx)
cluster_centers.append(point)
cluster_idx += 1
else:
for center in cluster_centers:
dist = distance(point, center)
if(dist < CLUSTER_THRESHOLD):
cluster_ids.append(cluster_centers.index(center))
if(len(cluster_ids) < i + 1):
cluster_ids.append(cluster_idx)
cluster_centers.append(point)
cluster_idx += 1
return cluster_ids
- 调用上述py文件
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Oct 09 11:02:08 2018
@author: muli
"""
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import numpy as np
import MeanShift
def colors(n):
ret = []
for i in range(n):
ret.append((random.uniform(0, 1), random.uniform(0, 1), random.uniform(0, 1)))
return ret
def main():
centers = [[-1, -1], [-1, 1], [1, -1], [1, 1]]
X, _ = make_blobs(n_samples=300, centers=centers, cluster_std=0.4)
mean_shifter = MeanShift.mean_shift()
_, mean_shift_result = mean_shifter.fit(X, kernel_bandwidth=0.5)
np.set_printoptions(precision=3)
print('input: {}'.format(X))
print('assined clusters: {}'.format(mean_shift_result))
color = colors(np.unique(mean_shift_result).size)
for i in range(len(mean_shift_result)):
plt.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], color = color[mean_shift_result[i]])
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
-
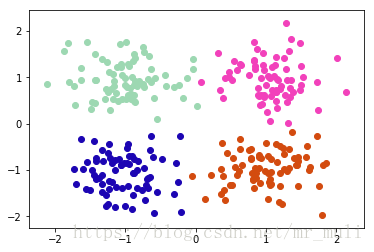
结果如图所示:
-
参考链接:https://github.com/zziz/mean-shift