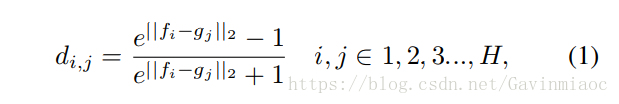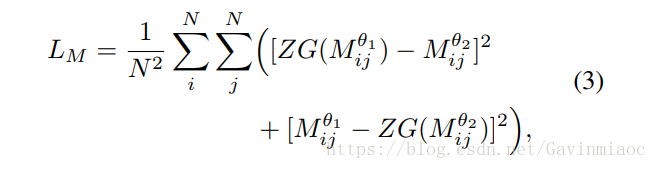研究背景
近年来受益于深度学习的发展,ReID 技术水平也得到了很大提升,在两个最为常用的ReID测试集Market1501和CUHK03上,首位命中率分别达到了89.9%和91.8%。不过,这个结果与人相比还是有一定的差距。实验表明,一个熟练的标注员在Market1501和CUHK03上的首位命中率分别可以达到93.5%和95.7%。
为了测试人类的ReID能力,研究者组织了10名专业的标注人员来进行测验。结果表明,一个熟练的标注员在Market1501和CUHK03上的首位命中率分别可以达到93.5%和95.7%。这个是现有的ReID方法无法企及的。
但不久前,旷视科技Face++在此项研究中取得了令人兴奋的进展:在旷视研究院团队发表的文章AlignedReID[1]中,作者提出了一种新方法,通过动态对准(Dynamic Alignment)和协同学习(Mutual Learning),然后再重新排序(Re-Ranking),使得机器在Market1501和CUHK03上的首位命中率达到了94.0%和96.1%,这也是首次机器在行人再识别问题上超越人类专家表现,创下了业界纪录。
1. an implicit alignment of local features can substantially improve global feature learning.
2.“The end-to-end learning with structure prior is more powerful than a “blindThe end-to-end learning “
Face++ 旷视科技最新的行人重识别论文 AlignedReID
刚读完这篇文章,用动态规划求最小路径进行特征对齐,很新奇,而且准确率很高。
让多个网络自动学习人体结构对齐,并彼此相互学习。
算法提到了两个创新点,动态对齐(Dynamic Alignment)和 协同学习(Mutual Learning),算法在Market1501和CUHK03上的Rank-1达到了94.0%和96.1%,首次在行人再识别问题上超越了人类表现。
论文整理
- 这篇文章作者提出了AlignedReID的方法,其亮点在于:在数据集Market1501与CUHK03上,该方法实现的rank-1 accuracy 首超人类,
- 作者认为:
- Traditional approaches have focused on low-level features such as colors, shapes, and local descriptors. With the renaissance of deep learning, the convolutional neural network (CNN) has dominated this field.
- 传统的方法大多采用CNN提取低级别的特征。
- Many CNN-based approaches learn a global feature, without considering the spatial structure of the person. This has a few major drawbacks:
- inaccurate person detection boxes might impact feature learning.
- the pose change or non-rigid body deformation makes the metric learning difficult.
- occluded parts of the human body might introduce irrelevant context into the learned feature.
- it is non-trivial to emphasis local differences in a global feature, especially when we have to distinguish two people with very similar apperances.
- 许多基于CNN的方法只学习了全局的特征,而没有考虑人体的空间结构,这会导致以下这些问题:
- 不准确的人物检测框可能会影响特征的学习;
- 姿势的改变和人体的变形可能会导致度量学习的困难;
- 人体的部分身体部位被遮挡可能会引入无关的上下文信息;
- 在全局特征上强调局部差异是非常重要的,尤其是在区分两个外貌非常相似的人的时候
-
- 为了解决以上问题,过去的研究将重心放在part-based, local feature learning。有些研究将整个身体分割为几个固定的部分,而不考虑这几个部分之间的对应关系。这样的话无法解决以上问题。还有研究使用pose estimation帮助人体几个部分的对齐,但这样需要额外的supervision and a pose estimation step。
- 所以,作者采用了AlignedReID的方法:
-
- In this paper, we propose a new approach, called AlignedReID, which still learns a global feature, but perform an automatic part alignment during the learning, without requring extra supervision or explicit pose estimation.
- 作者提出的方法中,仍然是学习全局的特征,但是能自动进行各部分的对齐,且这一操作不需要额外的supervision 和 explicit pose estimation.
- In the local branch, we align local parts by introducing a shortest path loss.
- 在局部特征的学习中,我们通过计算最短路径进行对齐操作。
- In the inference stage, we discard the local branch and only extract the global feature.
- 在预测阶段,只使用了全局特征而没有采用局部特征。
- In other words, the global feature itself, with the aid of local features learning, can greatly address the drawbacks we mentioned above, in our new joint learning framework.
- 换句话说,在基于局部特征学习得到的全局特征能够解决基于CNN方法遇到的那四个问题。
- In addition, the form of global feature keeps our approach attractive for the deployment of a large ReID system, without costly local features matching.
- 作者还说,全局特征的形式使得他们的方法在大型的人物重识别中仍然能够很好的工作,而不需采用消耗巨大的局部特征匹配。
- We also adopt a mutual learning approach in the metric learning setting, to allow two models to learn better representations from each other.
- 对于度量学习,作者采用的是mutual learning 的方法,并取得了很好的结果
-
- Metric Learning:Deep metric learning methods transform raw images into embedding feature, then compute the feature distances as their similarities. Usually, two images of the same person are defined as a positive pair, whereas two images of different persons are a negative pair. Triplet loss is motivatived by the margin enforced between positive and negative pairs. Selecting suitable samples for the training model through hard mining has been shown to be effective. Combining softmax loss with metric learning loss to speed up the convergence is also a popular method.
- Feature Alignments: Consider the spatial local information when learning features.
- Mutual Learning: presents a deep mutual learning strategy where an ensemble of students learn collaboratively and teach each other throughout the training process.
- Re-Ranking: After obtaining the image features, most current works choose the L2 Euclidean distance to compute a similarity score for a ranking or retrieval task.
- 下面对AlignedReID的原理进行更深的一步介绍:
- In AlignedReID, we generate a single global feature as the final output of the input image, and use the L2 distance as the similarity metric. However, the global feature is learned jointly with local features in the learning stage.
- Re-ID一般分为两步:一是提取特征,二是进行度量学习。在AlignedReID中,每张输入图片的最终输出是单一的全局特征,而该全局特征是与局部特征联合训练得来的。
- A global feature(a C-d vector) is extracted by directly applying global pooling on the feature map.
- 对于全局特征的提取,便是用global pooling在feature map上滑动提取特征。
- For the local features, a horizontal pooling, which is a global pooling in the horizontal direction, is first applied to extract a local feature for each row, and a 1X1 convolution is then applied to reduce the channel number from C to c. In this way, each local feature(a c-d vector) represents a horizontal part of image for a person.
- 对于局部特征提取,便是用horizontal pooling对feature map进行逐行提取,然后再进行1x1的卷积操作。这样得到的特征代表人体的水平部分。
- As a result, a person image is represented by a global feature and H local features.
- 最后,一张图像就可以用一个全局特征和多个局部特征代替。
- The distance of two person images is the summation of their global and local distances.
- 两张图片的距离是全局特征距离与局部特征距离之和。
- The global distance is simply the L2 distance of the global features.
- 全局特征距离是指全局特征之间的L2距离。
- For the local distance, we dynamically match the local parts from top to bottom to find the alignment of local feature with the minimum total distance.
- 局部特征距离是指通过动态规划的方法求出的最短路径,并通过该最短距离找到对齐的局部特征。
- This is based on a simple assumption that, for two images of the same person, the local feature from one body part of the first image is more similar to the semantically corresponding body part of the other image.
- 当然这一度量学习是基于假设:对于同一个人的同一部位在不同的图片中具有较高的相似度。
算法描述
和其他基于深度学习的ReID方法类似,作者同样是用深度卷积神经网络去提取特征,用Hard Sample Mining后的Triplet Loss做损失函数,把特征的欧式距离作为两张图片的相似度。
不同之处在于,作者在学习图像相似度的时候考虑了人体结构的对齐。虽然此前有人考虑过这一点,比如简单的,把人的头、身、腿分成三部分;还有精细一点的,先通过人体骨架估计,然后再通过骨架信息来对齐。但后一种方法,引入了另一个困难的问题或要求额外的标注工作。AlignedReID作者的思路是引入端到端的方法,让网络自动去学习人体对齐,从而提高性能。
在AlignedReID中,深度卷积神经网络不仅提取全局特征,同时也对各局部提取局部信息。对于两张图片中任意一对局部信息,计算它们之间的距离,构成一个距离矩阵。再通过动态规划,计算一条从矩阵左上角到右下角的最短路径。这条最短路径中的一条边就对应了一对局部特征的匹配,它给出了一种人体对齐的方式,在保证身体个部分相对顺序的情况下,这种对齐方式的总距离是最短的。在训练的时候,最短路径的长度被加入到损失函数,辅助学习行人的整体特征。
最关键的 Aligned ReID 框架图,下图是不包含 Mutual Learning 的情况:
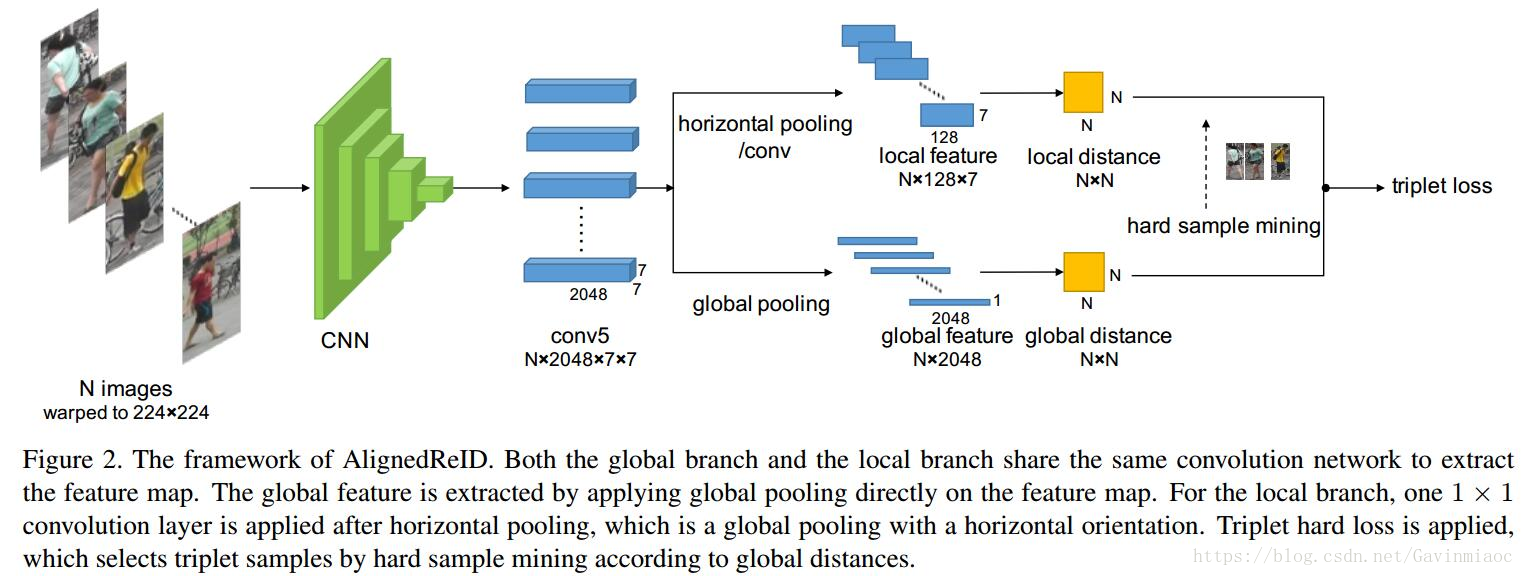
这里面 N 为一个Batch(论文中N=128),通过一个共享的特征提取层后,分别提取局部特征和全局特征,通过N*N的距离矩阵描述,计算triplet loss。
在一个min-batch中,通过global distance计算距离,选择 相同标签差异最大、不同标签差异最小的input构造hard samples。实验中Triplet margin设为0.3。
动态规划
如图所示,乍一看,这条最短路径上有一些边是冗余的,例如图中的第一条边。为什么不只寻找那些匹配的边呢?作者给出的解释是这样的:局部信息不仅要自我匹配,也要考虑到整个人体对齐的进程。为了使匹配能够从头到脚按顺序进行,那么有一些冗余的匹配是必须的。另外,通过设计局部距离函数,这些冗余匹配在整个最短路径的长度中贡献很小。
动态规划实际是为了解决两幅图像之间的 Part对齐问题,如图 [part1]<->[part4]
1)Part model能够对目标特征进行细粒度刻画,是非常必要的
2)最短路径包含非相关特征(如part1<->part1),这非但不会对结果造成影响,而且还会对维护垂直方向对齐的次序起着至关重要的作用。
即 路径规划本身隐含了自上而下的顺序。
注:非相关特征距离d比较大,其梯度接近于0,因此对于最短路径的贡献是比较小的。
有兴趣的同学可以参考下面的公式证明一下。
3)路径规划过程
先来看part距离公式(H表示水平划分,文中已验证最好的H=6):
规划从(1,1)到(H,H)的最短路径,参考公式:
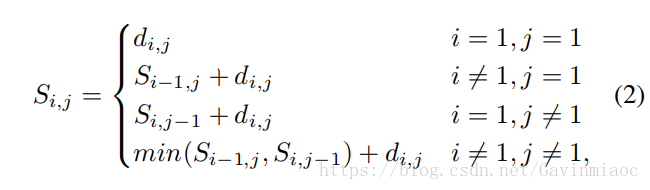
协同学习
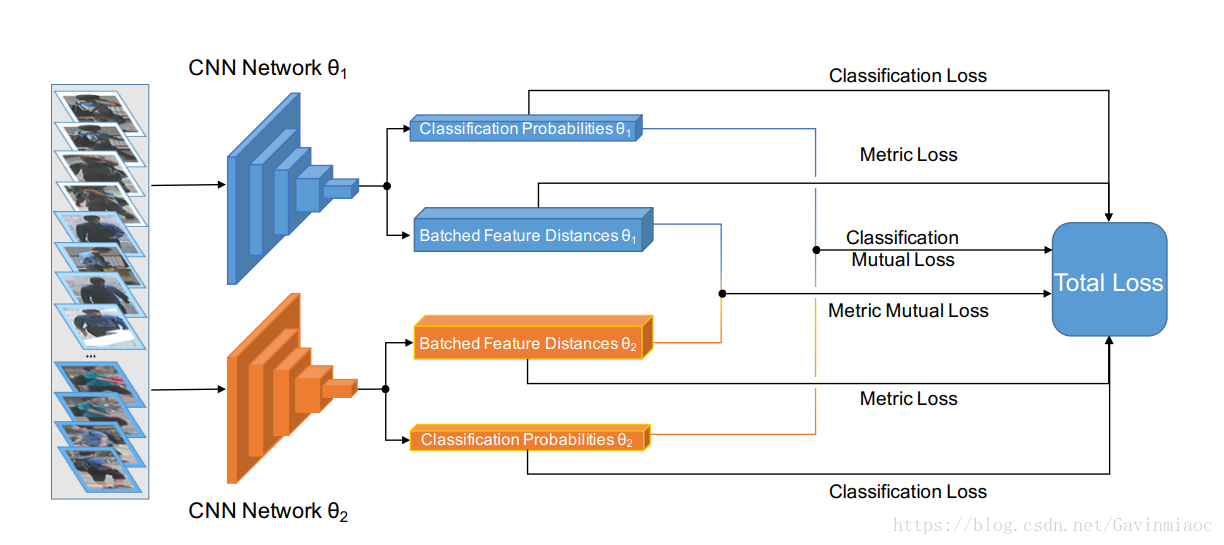
除了在训练过程中让人体结构自动对齐外,作者还提到了同时训练两个网络并使它们互相学习,可以有效提高模型的精度。这个训练方法在分类问题中已经比较常见,作者做了一些改进让它能够应用于度量学习(Metric Learning)。
协同学习的框架:
在上图所示的训练过程中:同时训练的两个网络都包含一个分支做分类,一个分支做度量学习。两个做分类的分支通过KL divergence互相学习;两个做度量学习的分支通过作者提出的metric mutual loss互相学习。而如前所述,度量学习的分支又包括两个子分支,一个是全局特征的分支,一个是局部特征的分支。比较有趣的是,一旦训练完成,分类分支和局部特征分支都被丢弃,只保留了全局特征分支做ReID。也就是说,无论是训练行人分类,还是通过人体对齐学习局部特征,都是为了更好的得到图像的全局特征。
1) 通过两个网络(上图θ1和θ2)实现 Mutual Learning
每个网络又包含 Classification Learning和 Metric Learning,用于分类和距离度量。通过 Classification Mutual Loss 和 Metric Mutual Loss 实现协同学习。
注:两个网络相互学习,没有主次之分。
2)预测阶段,只用到了全局特征,没有采用局部特征
原因在于,通过协同学习,提取的全局特征在局部特征影响下,已经能够准确描述图像,和局部特征并无区别,作者通过实验验证(仅在小gallery上Rank-1有所提升,0.3-0.5%)。
当然还有一个原因,就是全局特征的提取更快,一致性描述更强。
3)Batch解构
对于一个Batch内N幅图像,通过global distance计算两两之间的距离,得到N*N的距离矩阵M,其中Mi,j表示图像(i,j)之间的距离,Mutual LearningLoss定义为:
实验结果
算法在测试过程中已经超过了人类的认知,在典型数据集上表现也非常不错。和state-of-the-art 方法的对比:
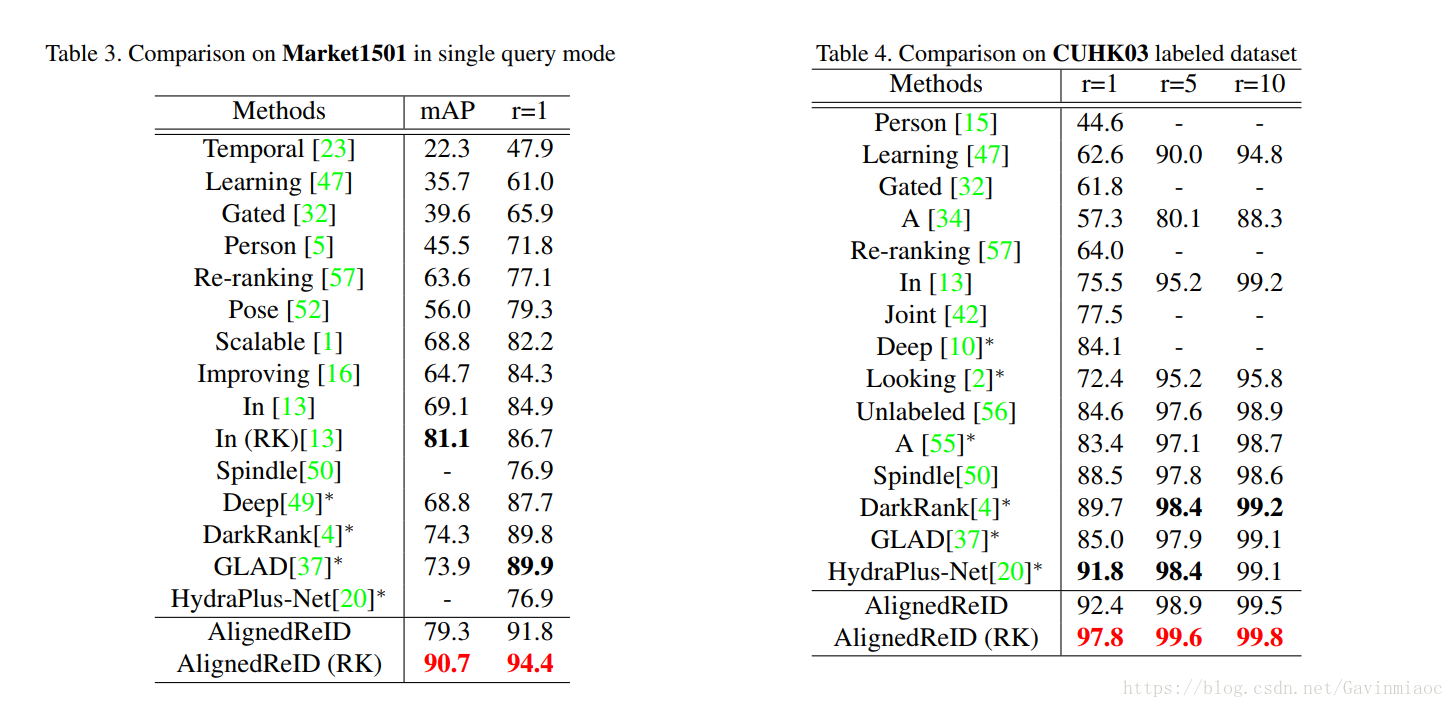
此文所展示的方法让ReID技术在实验结果的表现中上了全新的台阶。不过文章的最后也指出,虽然机器在两个常用数据集上超过了人类的水平,但还不能说行人再识别(ReID)任务已经被很好地解决了。在实际的应用中,人类,尤其是经过专业训练的人,可以通过经验、直觉,并利用环境、上下文等综合信息,在拥挤,模糊,昏暗等情况下进行更深入的分析,所以在开放和极端条件下的环境中,人和机器相比仍具有很大的优势。在未来的实践中,行人再识别(ReID)的解决和应用还需要更多努力。
AlignedReID文章作者之一张弛表示:“我们从2016年开始研究ReID,当时Top1的精度达到60%就可以说是state of the art了。但是业务要求至少达到90%以上,甚至更高。现在我们已经在两个常用数据集上做到超过人类水平,到这也只是迈出了实用化的第一步,在实战场景中还有更多的挑战要应对。希望ReID技术的进一步成熟,能让我们的社会更安全,更便捷。”
网友的一个复现代码分享:
https://github.com/huanghoujing/AlignedReID-Re-Production-Pytorch
论文翻译
参考文献:
1.https://blog.csdn.net/linwh8/article/details/78808810
2.https://blog.csdn.net/wayne2019/article/details/78898253
3.https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/32603701
4.https://www.zhihu.com/question/68784718
5.http://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1585374141113162948&wfr=spider&for=pc