5.4 TensorFlow模型持久化
为了让训练结果可以复用,需要将训练得到的神经网络持久化。
5.4.1持久化代码实现
TensorFlow提供了tf.train.Saver类用来保存和还原一个神经网络模型。
以下代码给出了保存TensorFlow计算图的方法。
import tensorflow as tf;
# 声明两个变量并计算他们的和
v1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1]), name="v1")
v2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(2.0, shape=[1]), name="v2")
result = v1 + v2
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 声明tf.train.Saver类用于保存模型
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
saver.save(sess, "C:\Documents\TF_resource\model\model.ckpt")
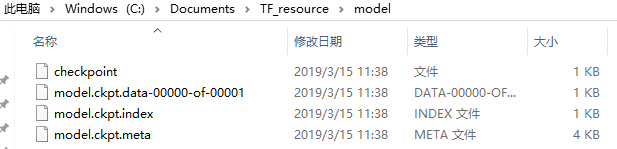
通过tf.train.Saver().save()方法,将model.ckpt保存到指定路径,虽然只指定了一个文件,但是保存后会有四个文件,这是因为TensorFlow会将计算图的结构和图上参数取值分别保存。
- model.ckpt.meta保存了计算图结构
- model.ckpt.index保存了参数索引
- model.ckpt.data保存了参数取值
- checkpoing保存了所有模型文件列表
可以用如下方式加载这个保存好的模型
import tensorflow as tf;
# 声明两个变量并计算他们的和
v1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1]), name="v1")
v2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(2.0, shape=[1]), name="v2")
result = v1 + v2
# 声明tf.train.Saver类用于保存模型
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver.restore(sess, "C:\Documents\TF_resource\model\model.ckpt")
print(sess.run(result))
# output
[3.]
加载模型的代码与保存模型的代码唯一不同的是,家在模型的代码没有运行变量的初始化过程,而是将变量的值通过已经保存的模型加载进来。如果不希望重复定义图上的运算,也可以直接加载已经持久化的图。
以下代码给出了一个样例
import tensorflow as tf;
# 声明tf.train.Saver类用于保存模型
saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph(
"C:\Documents\TF_resource\model\model.ckpt.meta"
)
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver.restore(sess, "C:\Documents\TF_resource\model\model.ckpt")
print(sess.run(tf.get_default_graph().get_tensor_by_name("add:0")))
# output
[3.]
可以通过类似saver = tf.train.Saver([v1])的方式加载部分变量。只加载v1,然后执行result会报错,变量v2没有被加载,在其初始化之前都是没有值的。
tf.train.Server类也支持在加载变量时给变量重命名。
v1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1]), name="other-v1")
v2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(2.0, shape=[1]), name="other-v2")
saver = tf.train.Saver({"v1":v1, "v2":v2})
通过上述类似字典的方式,就可以在加载模型时完成对变量的重命名。
如果在加载模型时直接将滑动平均模型的影子变量映射到变量自身,那么在使用训练好的模型就不需要再调用函数来获取变量的滑动平均值了。这样大大方便了滑动平均模型的使用。
以下代码给出了一个保存滑动平均模型的样例。
import tensorflow as tf;
v = tf.Variable(0, dtype=tf.float32, name="v")
# 在没有申明滑动平均模型时,只有一个变量v,所以以下语句只会输出“v:0”
for variables in tf.global_variables():
print(variables.name)
ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(0.99)
maintain_average_op = ema.apply(tf.global_variables())
# 在申明滑动平均模型之后,TensorFlow会自动生成一个影子变量
# v/ExponentialMovingAverage。于是以下语句会输出
# “v:0”和“v/ExponentialMovingAverage:0”
for variables in tf.global_variables():
print(variables.name)
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init_op)
sess.run(tf.assign(v, 10))
sess.run(maintain_average_op)
# 保存时,TensorFlow会将“v:0”和“v/ExponentialMovingAverage:0”两个变量都存下来
saver.save(sess, "C:\Documents\TF_resource\model\model.ckpt")
print(sess.run([v, ema.average(v)]))
# output
v:0
v:0
v/ExponentialMovingAverage:0
2019-03-15 15:24:39.672236: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:141] Your CPU supports instructions that this TensorFlow binary was not compiled to use: AVX2
[10.0, 0.099999905]
以下代码给出了如何通过变量重命名直接读取变量的滑动平均值。从下面程序的输出可以看出,读取的变量v的值实际上是上面代码中变量v的滑动平均值。
import tensorflow as tf;
v = tf.Variable(0, dtype=tf.float32, name="v")
saver = tf.train.Saver({"v/ExponentialMovingAverage":v})
# 等价于 saver = tf.train.Saver(ema.variables_to_restore())
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver.restore(sess, "C:\Documents\TF_resource\model\model.ckpt")
print(sess.run(v))
# output
0.099999905
TensorFlow提供了convert_variables_to_constants函数,通过这个函数可以将计算图中的变量及其取值通过常量的方式保存眯着眼整个TensorFlow计算图可以统一存放在一个文件中。
import tensorflow as tf;
from tensorflow.python.framework import graph_util;
v1 = tf.Variable(1, dtype=tf.float32, name="v1")
v2 = tf.Variable(2, dtype=tf.float32, name="v2")
result = v1 + v2
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
# 导出当前计算图的GraphDef部分,只需要这一部分就可以完成从输入层到输出层的计算过程
graph_def = tf.get_default_graph().as_graph_def()
# 将图中的变量及其取值转化为常量,同时将图中不必要的节点去掉。
output_graph_def = graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(
sess, graph_def, ['add']
)
# 将导出的模型存入文件
with tf.gfile.GFile("C:\Documents\TF_resource\model\combined_model.pb", "wb") as f:
f.write(output_graph_def.SerializeToString())
from tensorflow.python.platform import gfile;
with tf.Session() as sess:
model_filename = "C:\Documents\TF_resource\model\combined_model.pb"
# 读取保存的模型文件,并将文件解析成对应的GraphDef Protocol Buffer
with gfile.FastGFile(model_filename, 'rb') as f:
graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
# 将graph_def中保存的图加载到当前的图中。return_elements={"add:0"}给出了返回
# 的张量名称。在保存的时间给出的是计算节点的名称,为“add”。加载时给出的是张
# 量名,所以是“add:0”
result = tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, return_elements=["add:0"])
print(sess.run(result))
# output
[3.0]
5.4.2 持久化原理及数据格式
TensorFlow通过元图(MetaGraph)来记录计算图中节点的信息以及运行计算图中节点所需要的元数据。TensorFlow中元图是由MetaGraphDef Protocol Buffer 定义的。MetaGraphDef中的内容(计算图结构)就构成了TensorFlow持久化时的第一个文件(model.cpkt.meta)。
message MetaGraphDef {
MetaInfoDef meta_info_def = 1;
GraphDef graph_def = 2;
SaverDef saver_def = 3;
map<string, CollectionDef> collection_def = 4;
map<string, SignatureDef> signature_def = 5;
repeated AssetFileDef asset_file_def = 6;
}
meta文件是无法直接打开的,为了方便测试,TensorFlow提供了export_meta_graph函数,这个函数支持以json格式导出MetaGraphDef Protocol Buffer。
import tensorflow as tf;
# 定义变量相加的计算
v1 = tf.Variable(1, dtype=tf.float32, name="v1")
v2 = tf.Variable(2, dtype=tf.float32, name="v2")
result = v1 + v2
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.export_meta_graph("C:\Documents\TF_resource\model\model.ckpt.meda.json", as_text=True)
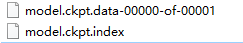
上图两个文件保存了所有变量的取值。其中model.ckpt.data文件是通过SSTable格式存储的,可以大致理解为就是一个(key,value)列表。TensorFlow提供了tf.train.NewCheckpointReader类来查看保存的变量信息。
reader = tf.train.NewCheckpointReader("C:\Documents\TF_resource\model\model.ckpt")
# 获取所有变量列表。这个是一个从变量名到变量维度的字典
global_variables = reader.get_variable_to_shape_map()
for variable_name in global_variables:
print(variable_name, global_variables[variable_name])
# 获取名称为v1的变量的取值
print("Value for variable v1 is ", reader.get_tensor("v1"))
# output
v1 [1]
v2 [1]
Value for variable v1 is [1.]
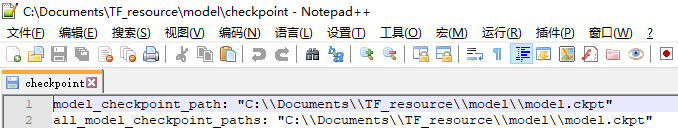
最后一个文件名字是固定的,叫checkpoint。这个文件时tf.train.Saver类自动生成并自动维护的。在checkpoint文件中维护了由一个tf.train.Saver类持久化的所有TensorFlow模型文件的文件名。当某个保存的TensorFlow模型文件被删除时,这个模型所对应的文件名也会从checkpoint文件中删除。checkpoint中内容的格式为CheckpointState Protocol Buffer。
message CheckpointState {
string model_checkpoint_path = 1;
repeated string all_model_checkpoint_paths = 2;
}
- model_checkpoint_path中保存了最新的TensorFlow模型文件的文件名。
- all_model_checkpoint_paths中列出了当前还没有被删除的TensorFlow模型文件的文件名