http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1541
Astronomers often examine star maps where stars are represented by points on a plane and each star has Cartesian coordinates. Let the level of a star be an amount of the stars that are not higher and not to the right of the given star. Astronomers want to know the distribution of the levels of the stars.
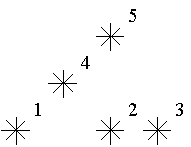
For example, look at the map shown on the figure above. Level of the star number 5 is equal to 3 (it's formed by three stars with a numbers 1, 2 and 4). And the levels of the stars numbered by 2 and 4 are 1. At this map there are only one star of the level 0, two stars of the level 1, one star of the level 2, and one star of the level 3.
You are to write a program that will count the amounts of the stars of each level on a given map.
Input
The first line of the input file contains a number of stars N (1<=N<=15000). The following N lines describe coordinates of stars (two integers X and Y per line separated by a space, 0<=X,Y<=32000). There can be only one star at one point of the plane. Stars are listed in ascending order of Y coordinate. Stars with equal Y coordinates are listed in ascending order of X coordinate.
Output
The output should contain N lines, one number per line. The first line contains amount of stars of the level 0, the second does amount of stars of the level 1 and so on, the last line contains amount of stars of the level N-1.
Sample Input
5 1 1 5 1 7 1 3 3 5 5
Sample Output
1 2 1 1 0
Hint
This problem has huge input data,use scanf() instead of cin to read data to avoid time limit exceed
题目大意:给出一些点的坐标,设在这个点的左下方(可以在同一水平线或同一竖直线上)的点有k个,则这个点的编号为k,输出n行,i行代表编号为i-1的点的个数。
思路:题目告诉我们点的坐标是这样给出的:先给出纵坐标小的,若纵坐标相等,则给出横坐标小的。因此纵坐标必定是非降序排列的,那么现在的点必定在前一个点的上方或者在同一水平线上,如果此时我们又能知道小于等于该点横坐标的点的个数k,那么该点的编号为k。(自身不算进去) 那么这个数据结构肯定要支持查询和修改,自然就想到了树状数组。一个点的编号确定以后,我们可以做一个add(x,1)操作(x为该点横坐标),这样通过查询query(x)得到的就是横坐标小于等于x的点的个数。注意本题的横坐标可能为0,因此读入横坐标后先做一个自增操作,且上界不是元素个数n,而是可能的最大的横坐标。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int maxn=32005;
int tree[maxn];
int flag[maxn];
inline int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int i,int v)
{
for(;i<=32001;i+=lowbit(i))
tree[i]+=v;
}
int query(int i)
{
int s=0;
for(;i;i-=lowbit(i))
s+=tree[i];
return s;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
memset(flag,0,sizeof(flag));
memset(tree,0,sizeof(tree));
int x,y;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
++x;
flag[query(x)]++;
update(x,1);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%d\n",flag[i]);
}
return 0;
}