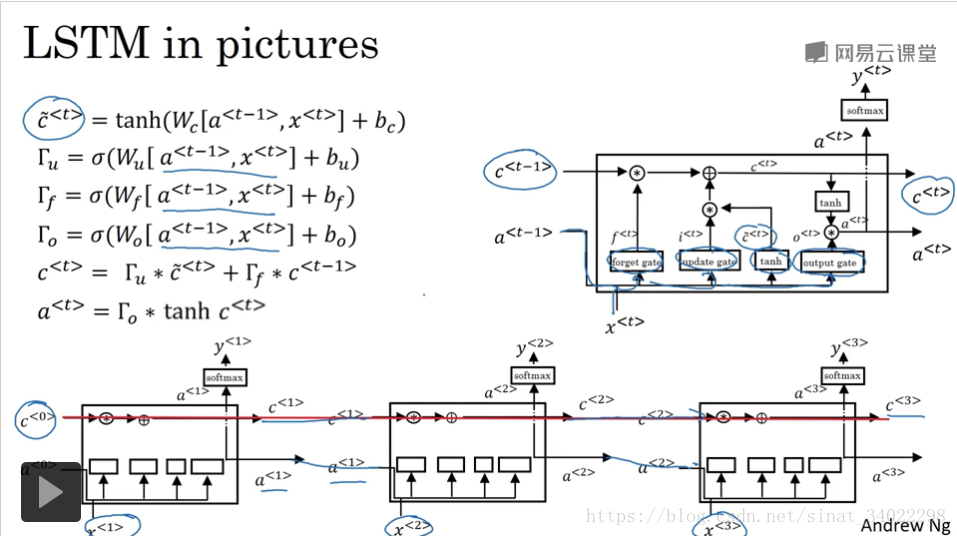
LSTM
程序Pycharm版
from __future__ import print_function
import IPython
import sys
from music21 import *
import numpy as np
from grammar import *
from qa import *
from preprocess import *
from music_utils import *
from data_utils import *
from keras.models import load_model, Model
from keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Dropout, Input, LSTM, Reshape, Lambda, RepeatVector
from keras.initializers import glorot_uniform
from keras.utils import to_categorical
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras import backend as K
def djmodel(Tx, n_a, n_values):
"""
Implement the model
Arguments:
Tx -- length of the sequence in a corpus
n_a -- the number of activations used in our model
n_values -- number of unique values in the music data
Returns:
model -- a keras model with the
"""
X = Input(shape=(Tx, n_values))
a0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='a0')
c0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='c0')
a = a0
c = c0
outputs = []
for t in range(Tx):
x = Lambda(lambda x: X[:,t,:])(X)
x = reshapor(x)
a, _, c = LSTM_cell(x, initial_state = [a, c])
out = densor(a)
outputs.append(out)
model = Model(inputs = [X, a0, c0], outputs = outputs)
return model
def music_inference_model(LSTM_cell, densor, n_values=78, n_a=64, Ty=100):
"""
Uses the trained "LSTM_cell" and "densor" from model() to generate a sequence of values.
Arguments:
LSTM_cell -- the trained "LSTM_cell" from model(), Keras layer object
densor -- the trained "densor" from model(), Keras layer object
n_values -- integer, umber of unique values
n_a -- number of units in the LSTM_cell
Ty -- integer, number of time steps to generate
Returns:
inference_model -- Keras model instance
"""
x0 = Input(shape=(1, n_values))
a0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='a0')
c0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='c0')
a = a0
c = c0
x = x0
outputs = []
for t in range(Ty):
a, _, c = LSTM_cell(x , initial_state = [a,c])
out = densor(a)
outputs.append(out)
x = Lambda(one_hot)(out)
inference_model = Model(inputs=[x0, a0, c0], outputs=outputs)
return inference_model
def predict_and_sample(inference_model, x_initializer=x_initializer, a_initializer=a_initializer,
c_initializer=c_initializer):
"""
Predicts the next value of values using the inference model.
Arguments:
inference_model -- Keras model instance for inference time
x_initializer -- numpy array of shape (1, 1, 78), one-hot vector initializing the values generation
a_initializer -- numpy array of shape (1, n_a), initializing the hidden state of the LSTM_cell
c_initializer -- numpy array of shape (1, n_a), initializing the cell state of the LSTM_cel
Returns:
results -- numpy-array of shape (Ty, 78), matrix of one-hot vectors representing the values generated
indices -- numpy-array of shape (Ty, 1), matrix of indices representing the values generated
"""
pred = inference_model.predict([x_initializer, a_initializer, c_initializer])
indices = np.argmax(pred, 2)
results = to_categorical(indices)
return results, indices
if __name__ == '__main__':
IPython.display.Audio('./data/30s_seq.mp3')
X, Y, n_values, indices_values = load_music_utils()
print('shape of X:', X.shape)
print('number of training examples:', X.shape[0])
print('Tx (length of sequence):', X.shape[1])
print('total # of unique values:', n_values)
print('Shape of Y:', Y.shape)
n_a = 64
reshapor = Reshape((1, 78))
LSTM_cell = LSTM(n_a, return_state=True)
densor = Dense(n_values, activation='softmax')
model = djmodel(Tx=30, n_a=64, n_values=78)
opt = Adam(lr=0.01, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999, decay=0.01)
model.compile(optimizer=opt, loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
m = 60
a0 = np.zeros((m, n_a))
c0 = np.zeros((m, n_a))
model.fit([X, a0, c0], list(Y), epochs=100)
inference_model = music_inference_model(LSTM_cell, densor, n_values=78, n_a=64, Ty=50)
x_initializer = np.zeros((1, 1, 78))
a_initializer = np.zeros((1, n_a))
c_initializer = np.zeros((1, n_a))
results, indices = predict_and_sample(inference_model, x_initializer, a_initializer, c_initializer)
print("np.argmax(results[12]) =", np.argmax(results[12]))
print("np.argmax(results[17]) =", np.argmax(results[17]))
print("list(indices[12:18]) =", list(indices[12:18]))
out_stream = generate_music(inference_model)
IPython.display.Audio('./data/30s_trained_model.mp3')
print("\nEND !!!")
参考
理解LSTM
