一元线性回归
方法1:numpy
import numpy as np, matplotlib.pyplot as mp
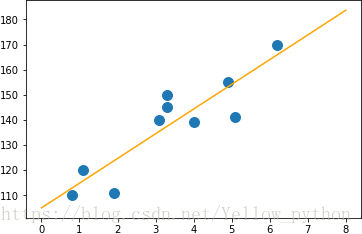
xp = [0.8, 1.1, 1.9, 3.1, 3.3, 3.3, 4.0, 5.1, 4.9, 6.2]
yp = [110, 120, 111, 140, 150, 145, 139, 141, 155, 170]
k, b = np.polyfit(xp, yp, 1)
print(k, b)
xl = np.linspace(0, 8, 3)
yl = xl * k + b
mp.scatter(xp, yp, s=99)
mp.plot(xl, yl, color='orange')
mp.show()
方法2:sklearn
from sklearn import linear_model
import numpy as np, matplotlib.pyplot as mp
x = [0.8, 1.1, 1.9, 3.1, 3.3, 3.3, 4.0, 5.1, 4.9, 6.2]
y = [110, 120, 111, 140, 150, 145, 139, 141, 155, 170]
x = np.array(x).reshape(-1, 1)
print(x)
model = linear_model.LinearRegression()
model.fit(x, y)
print(model.coef_, model.intercept_)
xl = np.array([0, 7]).reshape(-1, 1)
yl = model.predict(xl)
mp.scatter(x, y)
mp.plot(xl, yl, color='orange')
mp.show()

多元线性回归
import requests, re, pandas as pd, numpy as np, matplotlib.pyplot as mp
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
from sklearn import linear_model
def download():
url = 'https://blog.csdn.net/Yellow_python/article/details/81224614'
header = {'User-Agent': 'Opera/8.0 (Windows NT 5.1; U; en)'}
r = requests.get(url, headers=header)
data = re.findall('<pre><code>([\s\S]+?)</code></pre>', r.text)[0].strip()
df = pd.DataFrame([i.split(',') for i in data.split()], columns=['x1', 'x2', 'y'])
df['x1'] = pd.to_numeric(df['x1'])
df['x2'] = pd.to_numeric(df['x2'])
df['y'] = pd.to_numeric(df['y'])
return df
df = download()
model = linear_model.LinearRegression()
model.fit(df[['x1', 'x2']], df.y)
k, b = model.coef_, model.intercept_
print(k, b)
predict_x = pd.DataFrame([[0, 0], [0, 11], [11, 0], [11, 11]])
predict_y = predict_x[0] * k[0] + predict_x[1] * k[1] + b
x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(predict_x[0], predict_x[1])
y = x1 * k[0] + x2 * k[1] + b
fig = mp.figure()
ax = mplot3d.Axes3D(fig)
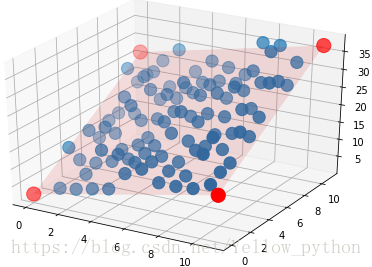
ax.scatter(df.x1, df.x2, df.y, s=150)
ax.scatter(predict_x[0], predict_x[1], predict_y, color='red', s=200)
ax.plot_surface(x1, x2, y, alpha=0.04, color='red')
mp.show()
附录:数据源
1,1,3.29
2,1,4.03
3,1,5.12
4,1,6.09
5,1,11.50
6,1,13.74
7,1,10.88
8,1,10.85
9,1,11.24
10,1,13.37
1,2,13.43
2,2,6.68
3,2,14.55
4,2,14.33
5,2,12.97
6,2,14.12
7,2,12.48
8,2,12.08
9,2,19.16
10,2,15.11
1,3,8.23
2,3,8.22
3,3,9.68
4,3,11.33
5,3,13.93
6,3,14.05
7,3,13.34
8,3,17.64
9,3,22.11
10,3,16.00
1,4,15.08
2,4,16.95
3,4,11.46
4,4,13.69
5,4,14.43
6,4,18.91
7,4,17.64
8,4,17.11
9,4,17.15
10,4,22.94
1,5,11.39
2,5,13.58
3,5,22.40
4,5,14.18
5,5,19.62
6,5,23.35
7,5,21.42
8,5,18.73
9,5,20.04
10,5,20.07
1,6,14.77
2,6,22.42
3,6,16.63
4,6,17.98
5,6,20.95
6,6,20.53
7,6,22.16
8,6,22.19
9,6,25.10
10,6,23.90
1,7,15.43
2,7,16.10
3,7,23.87
4,7,23.38
5,7,27.56
6,7,24.89
7,7,26.38
8,7,28.94
9,7,23.83
10,7,31.77
1,8,26.67
2,8,25.21
3,8,19.63
4,8,20.75
5,8,23.24
6,8,26.34
7,8,23.44
8,8,26.45
9,8,29.54
10,8,30.71
1,9,21.37
2,9,25.12
3,9,21.68
4,9,22.28
5,9,24.68
6,9,25.91
7,9,26.09
8,9,30.43
9,9,36.57
10,9,28.16
1,10,21.95
2,10,26.82
3,10,30.76
4,10,25.43
5,10,29.23
6,10,28.23
7,10,27.10
8,10,36.81
9,10,36.86
10,10,33.03


