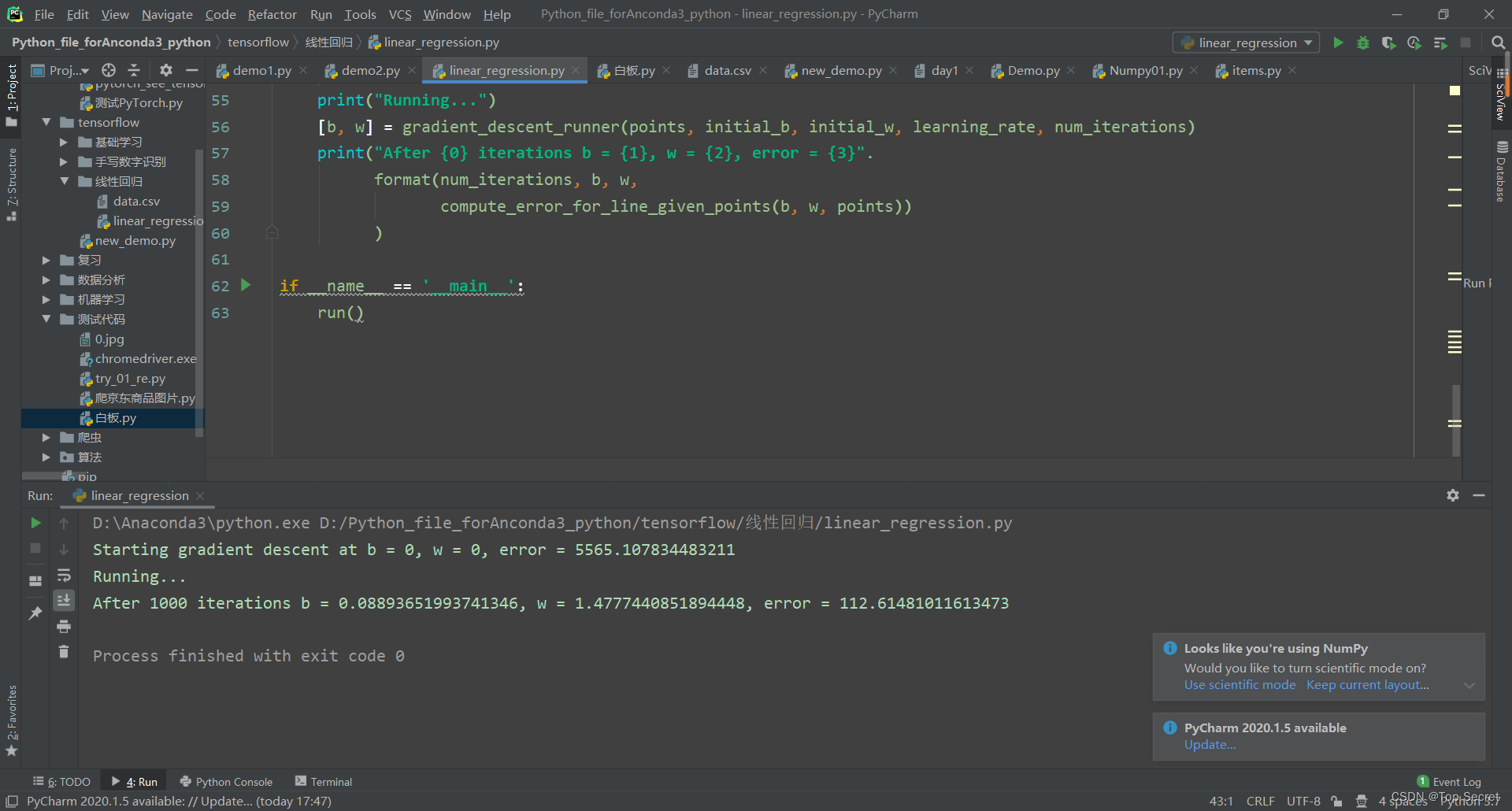
1. 实现一个线性回归的问题
# 实现一个线性回归的问题 # y = wx + b
step1: 计算损失函数loss的值

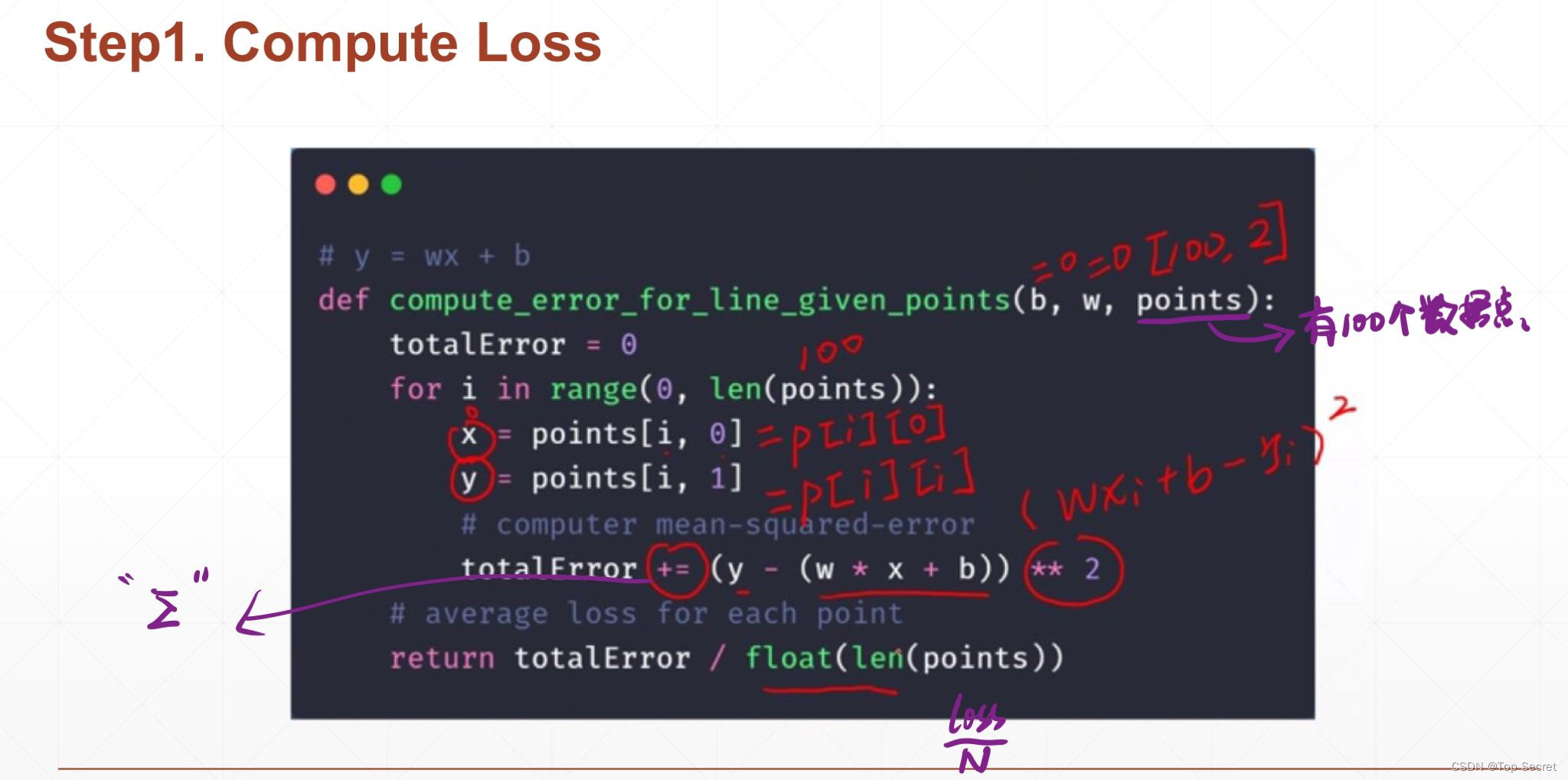
# 实现一个线性回归的问题
# y = wx + b
# step1: 计算损失函数loss的值
def compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, w, points): #points表示数据的数量
totalError = 0 #初始化损失函数的值
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
# computer mean-squared-error
totalError += (y - (w * x + b)) ** 2 #求loss的累积和
# average loss for each point
return totalError / float(len(points))step2:计算梯度与更新
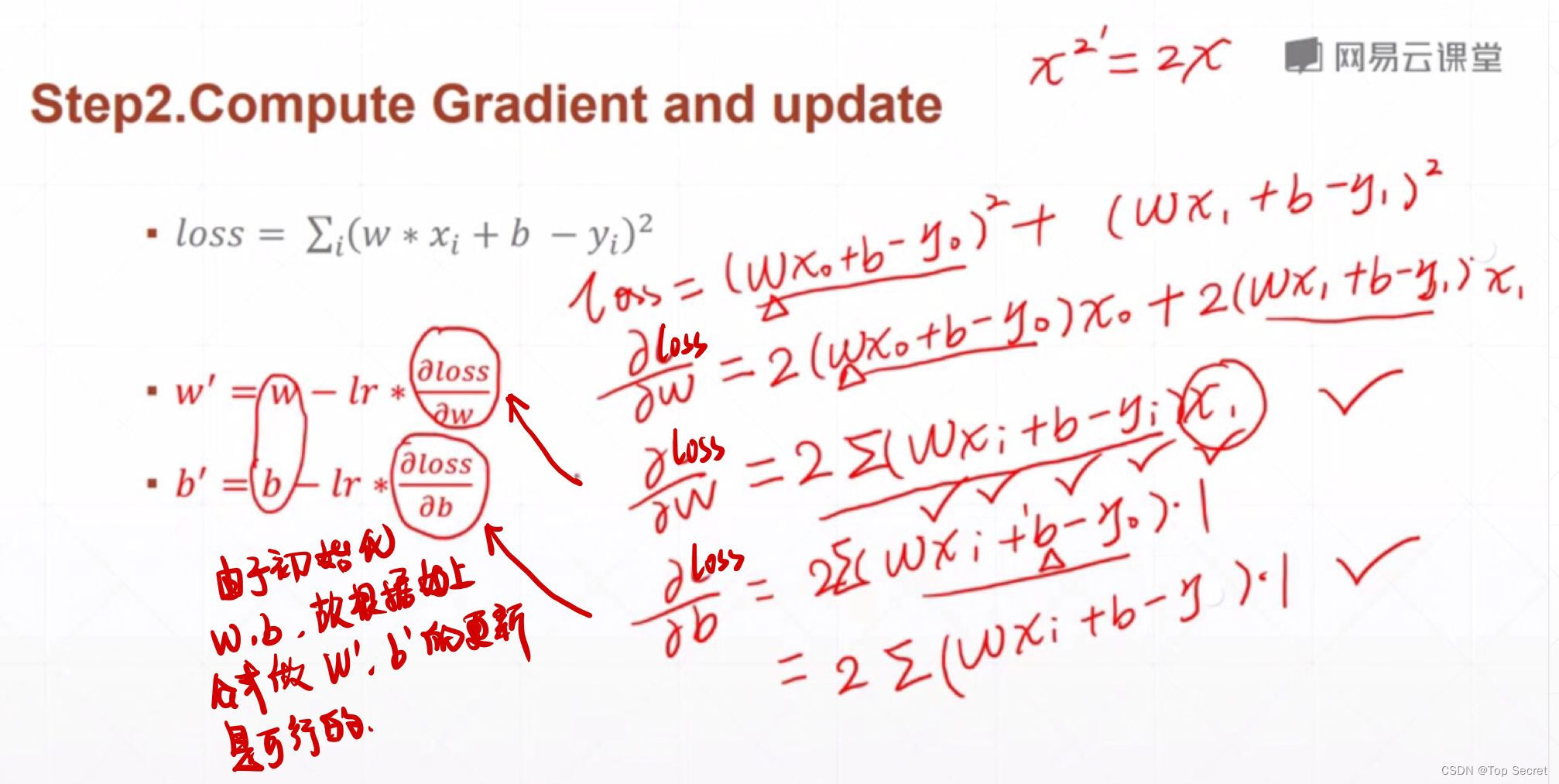
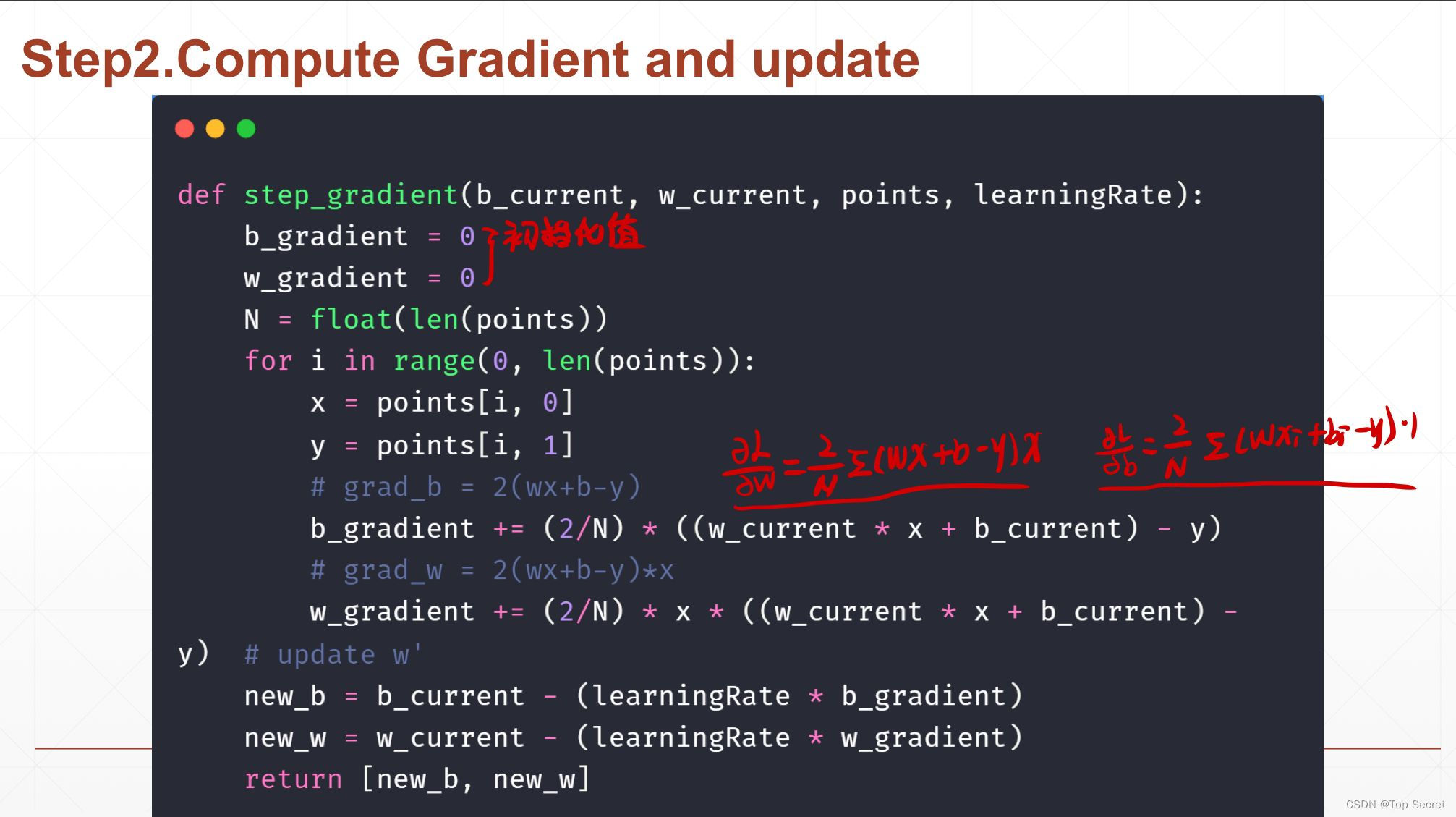
# step2:计算梯度与更新
def step_gradient(b_current, w_current, points, learningRate):
b_gradient = 0
w_gradient = 0
N = float(len(points))
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
# grad_b = 2(wx+b-y)
b_gradient += (2/N) * ((w_current * x + b_current) - y)
# grad_w = 2(wx+b-y)*x
w_gradient += (2/N) * x * ((w_current * x + b_current) - y)
# update w'
new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient)
new_w = w_current - (learningRate * w_gradient)
return [new_b, new_w]step3:更新权值w


#更新权值w
def gradient_descent_runner(points, starting_b, starting_w, learning_rate, num_iterations):
b = starting_b
w = starting_w
# update for several times
for i in range(num_iterations):
b, w = step_gradient(b, w, np.array(points), learning_rate)
return [b, w]
step4:主函数
def run():
points = np.genfromtxt("data.csv", delimiter=",") #读取数据
learning_rate = 0.0001 #学习率
initial_b = 0 # initial y-intercept guess
initial_w = 0 # initial slope guess
num_iterations = 1000
print("Starting gradient descent at b = {0}, w = {1}, error = {2}"
.format(initial_b, initial_w,
compute_error_for_line_given_points(initial_b, initial_w, points))
)
print("Running...")
[b, w] = gradient_descent_runner(points, initial_b, initial_w, learning_rate, num_iterations)
print("After {0} iterations b = {1}, w = {2}, error = {3}".
format(num_iterations, b, w,
compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, w, points))
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()线性回归问题的全部代码:
import numpy as np
# 实现一个线性回归的问题
# y = wx + b
# step1: 计算损失函数loss的值
def compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, w, points): #points表示数据的数量
totalError = 0 #初始化损失函数的值
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
# computer mean-squared-error
totalError += (y - (w * x + b)) ** 2 #求loss的累积和
# average loss for each point
return totalError / float(len(points))
# step2:计算梯度与更新
def step_gradient(b_current, w_current, points, learningRate):
b_gradient = 0
w_gradient = 0
N = float(len(points))
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
# grad_b = 2(wx+b-y)
b_gradient += (2/N) * ((w_current * x + b_current) - y)
# grad_w = 2(wx+b-y)*x
w_gradient += (2/N) * x * ((w_current * x + b_current) - y)
# update w'
new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient)
new_w = w_current - (learningRate * w_gradient)
return [new_b, new_w]
#更新权值w
def gradient_descent_runner(points, starting_b, starting_w, learning_rate, num_iterations):
b = starting_b
w = starting_w
# update for several times
for i in range(num_iterations):
b, w = step_gradient(b, w, np.array(points), learning_rate)
return [b, w]
def run():
points = np.genfromtxt("data.csv", delimiter=",") #读取数据
learning_rate = 0.0001 #学习率
initial_b = 0 # initial y-intercept guess
initial_w = 0 # initial slope guess
num_iterations = 1000
print("Starting gradient descent at b = {0}, w = {1}, error = {2}"
.format(initial_b, initial_w,
compute_error_for_line_given_points(initial_b, initial_w, points))
)
print("Running...")
[b, w] = gradient_descent_runner(points, initial_b, initial_w, learning_rate, num_iterations)
print("After {0} iterations b = {1}, w = {2}, error = {3}".
format(num_iterations, b, w,
compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, w, points))
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()