Fix
Description
There are a few points on a plane, and some are fixed on the plane, some are not. We want to connect these points by some sticks so that all the points are fixed on the plane. Of course, we want to know the minimum length of the sum of the sticks.
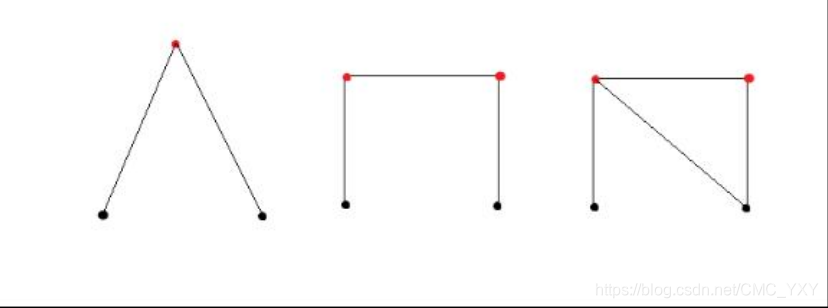
As in the images, the black points are fixed on the plane and red ones are not, which need to be fixed by sticks.
All the points in the left image have been fixed. But the middle one is not, which we need add one stick to fix those four points (the right image shows that stick). Triangle is steady, isn’t it?
Input
The input consists of multiply test cases. The first line of each test case contains one integer, n (1 <= n <= 18), which is the number of points. The next n lines, each line consists of three integers, x, y, c (0 <= x, y < 100). (x, y) indicate the coordinate of one point; c = 1 indicates this point is fixed; c = 0 indicates this point is not fixed. You can assume that no two points have the same coordinate.
The last test case is followed by a line containing one zero, which means the end of the input.
Output
Output the minimum length with six factional digits for each test case in a single line. If you cannot fix all the points, then output “No Solution”.
题面不给中文差评!
Sample Input
4
0 0 1
1 0 1
0 1 0
1 1 0
3
0 0 1
1 1 0
2 2 0
0
Sample Output
4.414214
No Solution
Hint
大概意思就是给你一些点,其中一些点是固定的,然后还有一些没有固定的,然后问你固定所有点所用的线段的最小长度是多少。
所谓固定,就是形如三角形的情况,就是两个固定的点向一个未固定的点连两条边,就能把未固定的点固定。
反思&题解
比赛思路: 懵……因为在花太久时间再其他题目上所以这题没有认真去想
正解思路: 状压DP,设
为固定状态为s时(1表示固定,0表示未固定)的最小长度,枚举状态,对于每个未固定的点找两个固定的点离它最小的距离,假设最小距离为tot,方程为:
反思: 突然发现状压DP好久没打了,要做几道题巩固巩固
CODE
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const double inf=100000000.0;
int c[21],n,gd,last,x[21],y[21];
double len[21],f[1<<21];
double getlen(int s,int k)
{
int cnt=0,i;
double mn1=inf,mn2=inf,sum;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if (s&(1<<i-1))
{
cnt++;
sum=sqrt(1.0*(x[i]-x[k])*(x[i]-x[k])+1.0*(y[i]-y[k])*(y[i]-y[k]));
if (sum<mn1)
{
mn2=mn1;
mn1=sum;
}
else if (sum<mn2) mn2=sum;
}
}
if (cnt<2) return -1;
return mn1+mn2;
}
int main()
{
while (1)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
if (n==0) break;
int i;
gd=0;
last=0;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&x[i],&y[i],&c[i]);
if (c[i]==1) gd|=1<<i-1;
last|=1<<i-1;
}
for (i=0;i<=last;i++)
f[i]=inf;
f[gd]=0;
int s;
for (s=gd;s<=last;s++)
{
if (f[s]!=inf)
{
int i;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if (!(s&(1<<i-1)))
{
double tot=getlen(s,i);
if (tot!=-1) f[s|(1<<i-1)]=min(f[s|(1<<i-1)],f[s]+tot);
}
}
}
}
if (f[last]==inf) printf("No Solution\n");
else printf("%.6lf\n",f[last]);
}
return 0;
}