目录
1. KMP算法介绍
- KMP是一个解决模式串在文本串是否出现过,如果出现过,最早出现的位置的经典算法
- Knuth-Morris-Pratt字符串查找算法,简称为“KMP算法”,常用于在一个文本串S内查找一个模式串P的出现位置,这个算法由Donald Knuth、Vaughan Pratt、James H. Morris三人于1977年联合发表,故取这3人的姓氏命名此算法.
- KMP方法算法就利用之前判断过信息,通过一个next数组, 保存模式串中前后最长公共子序列的长度,每次回溯时,通过next数组找到,前面匹配过的位置,省去了大量的计算时间
- 参考资料: https://www.cnblogs.com/ZuoAndFutureGirl/p/9028287.html
2. KMP算法最佳应用—字符串匹配问题
- 有一个字符串str1= "BBC ABCDAB ABCDABCDABDE",和一个子串str2="ABCDABD"
- 现在要判断str1是否含有str2,如果存在,就返回第一次出现的位置,如果没有,则返回-1
- 要求:使用KMP算法完成判断,不能使用简单的暴力匹配算法.
3. 思路
- 先得到子串的部分匹配表
“部分匹配值”就是”前缀”和”后缀”的最长的共有元素的长度。以”ABCDABD”为例,
- ”A”的前缀和后缀都为空集,共有元素的长度为0;
- ”AB”的前缀为[A],后缀为[B], 共有元素的长度为0;
- ”ABC”的前缀为[A, AB],后缀为[BC, C],共有元素的长度0;
- ”ABCD"的前缀为[A, AB, ABC],后缀为[BCD, CD,D],共有元素的长度为0;
- ”ABCDA"的前缀为[A, AB, ABC, ABCD], 后缀为[BCDA, CDA, DA,A], 共有元素为”A”,长度为1;
- ”ABCDAB”的前缀为[A, AB, ABC, ABCD, ABCDA],后缀为[BCDAB, CDAB, DAB, AB, B],共有元素为”AB",长度为2;
- ”ABCDABD"的前缀为[A, AB, ABC, ABCD, ABCDA, ABCDAB],后缀为[BCDABD, CDABD, DABD, ABD, BD, D],共有元素的长度为0。
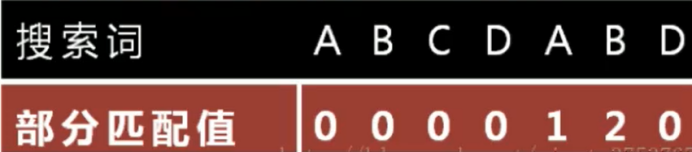
2. 使用部分匹配表完成KMP
4. 代码实现
4.1 KMP算法实现
package com.example.datastructureandalgorithm.violence;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author 浪子傑
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020/6/11
*/
public class KMPDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "BBC ABCDAB ABCDABCDABDE";
String str2 = "ABCDABD";
int[] next = kmpNext(str2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(next));
System.out.println(kmpSearch(str1, str2, next));
}
/**
* KMP算法查找
*
* @param str1
* @param str2
* @param next
* @return
*/
public static int kmpSearch(String str1, String str2, int[] next) {
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
// TODO 此处暂时无非理解~~
while (j > 0 && str1.charAt(i) != str2.charAt(j)) {
j = next[j - 1];
}
if (str1.charAt(i) == str2.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
if (j == str2.length()) {
return i - j + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 获取字符串的部分匹配表
*
* @param str
* @return
*/
public static int[] kmpNext(String str) {
// 创建返回的数组
int[] next = new int[str.length()];
next[0] = 0;
// 循环字符串进行比较
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
// TODO 此处暂时无非理解~~
while (j > 0 && str.charAt(i) != str.charAt(j)) {
j = next[j - 1];
}
if (str.charAt(i) == str.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
return next;
}
}
4.2 暴力匹配算法实现
package com.example.datastructureandalgorithm.violence;
/**
* @author 浪子傑
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020/6/10
*/
public class ViolenceMatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "我爱你中国亲爱的母亲,亲爱的母亲";
String s2 = "爱的母";
System.out.println(violenceMatch(s1,s2));
}
public static int violenceMatch(String str1, String str2) {
char[] s1 = str1.toCharArray();
char[] s2 = str2.toCharArray();
int s1Len = s1.length;
int s2Len = s2.length;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while (i < s1Len && j < s2Len) {
if (s1[i] == s2[j]) {
i++;
j++;
} else {
i = i - j + 1;
j = 0;
}
}
if (j == s2Len) {
return i - j;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}