此处介绍四种线性回归算法的衡量指标。
第一种:MSE(均方误差)
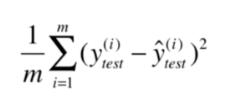
第二种:RMSE(均方根误差)
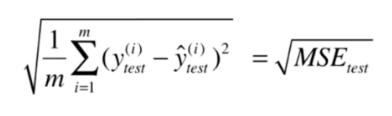
使用RMSE,采用同样的量纲的话,误差背后的意义更加明显。
量纲,又叫作因次,是表示一个物理量由基本量组成的情况。确定若干个基本量后,每个导出量都可以表示为基本量的幂的乘积的形式。引入量纲这一概念可以进行量纲分析,这既是物理学的基础,又有着很多重要应用。——维基百科
第三种:MAE(平均绝对误差)
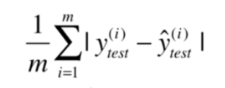
第四种:R Squared(决定系数)
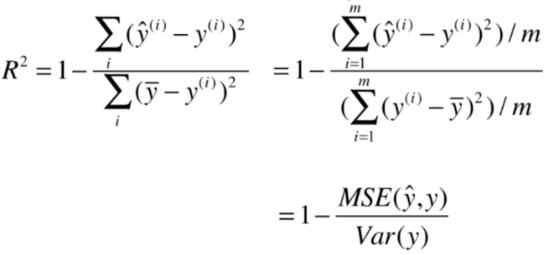
首先在PlayML文件夹中写一个model_selection模块,用于分割数据集:
import numpy as np
def train_test_split(X, y, test_ratio=0.2, seed=None):
if seed:
np.random.seed(seed)
shuffled_indexes = np.random.permutation(len(X))
test_size = int(len(X) * test_ratio)
test_indexes = shuffled_indexes[:test_size]
train_indexes = shuffled_indexes[test_size:]
X_train = X[train_indexes]
y_train = y[train_indexes]
X_test = X[test_indexes]
y_test = y[test_indexes]
return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
然后使用线性回归模型拟合波士顿房产数据:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
boston = datasets.load_boston()
x = boston.data[:,5] # 只取出第5列(房间数量这一特征)
y = boston.target
x = x[y < 50.0] # 剔除超过50的点(因为有可能有超过50的,但是在图中只显示50)
y = y[y < 50.0]
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
Output:
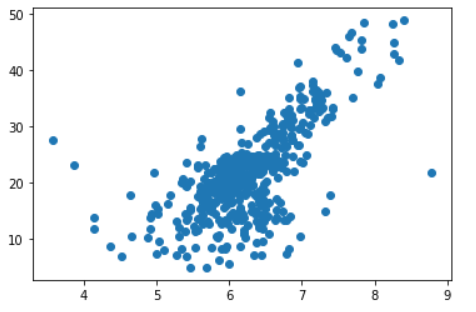
from playML.model_selection import train_test_split # 分割数据集
from playML.SimpleLinearRegression import SimpleLinearRegression2
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, seed=666)
reg = SimpleLinearRegression2()
reg.fit(x_train, y_train)
plt.scatter(x_train, y_train)
plt.plot(x_train, reg.predict(x_train), color='r')
plt.show()
Output:
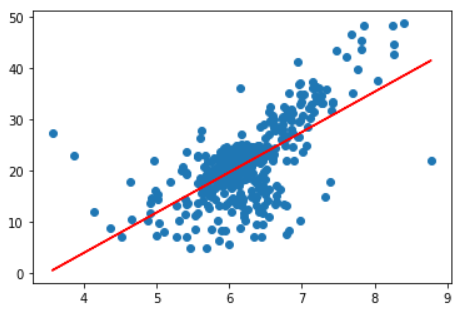
接下来使用上述指标衡量我们的模型:
y_predict = reg.predict(x_test)
MSE(均方误差):
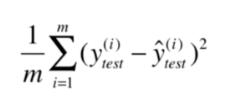
mse_test = np.sum((y_predict - y_test)**2) / len(y_test)
print(mse_test)
Output:

RMSE(均方根误差):
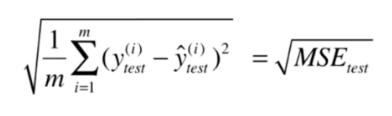
from math import sqrt
rmse_test = sqrt(mse_test)
print(rmse_test)

MAE(平均绝对误差):
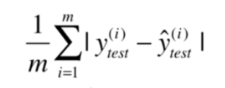
mae_test = np.sum(np.absolute(y_predict - y_test)) / len(y_test)
print(mae_test)

R Squared(决定系数):
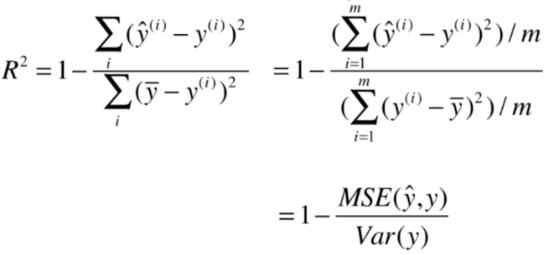
print(1 - mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict) / np.var(y_test))

计算上面指标的算法可以封装成一个模块
参考资料:bobo老师机器学习教程
