归并排序:
核心:分而治之,递归
思想:先分再合
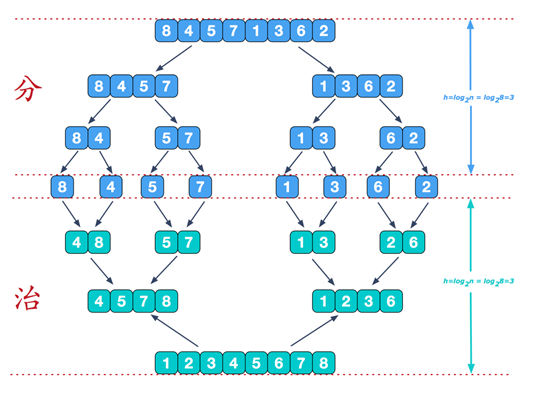
分的代码实现:
/*
* 归并排序
*/
public static void merge_sort(int[] str, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left < right) {
int mad = (left + right) / 2;
merge_sort(str, left, mad, temp);
merge_sort(str, mad + 1, right, temp);
merge(str, left, right, temp);
}
* 归并排序
*/
public static void merge_sort(int[] str, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left < right) {
int mad = (left + right) / 2;
merge_sort(str, left, mad, temp);
merge_sort(str, mad + 1, right, temp);
merge(str, left, right, temp);
}
}
合的代码实现:
// left 和 right 定义操作str数组中的一段数组
public static void merge(int[] str, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
// 操作str的一段数组
// 把数组从中间切成两段 第一段从l=left 到 mad-1 第二段从r=mad到right
int mad = (left + right) / 2;
int l = left;
int r = mad + 1;
int i = 0;
// 把两段数组按大小排序 存放到temp数组中;
// 当其中一断数组越界 退出
// 越界 :段数据的左边超过的右边
while (l <= mad && r <= right) {// 不越界 继续比较
if (str[l] <= str[r]) {
temp[i] = str[l];
l++;
i++;
} else {
temp[i] = str[r];
r++;
i++;
}
}
// 当越界退出时,得考虑未比较完的那一段
// 因为每段都是有序的 所以直接加在temp【】后面
// 左段越界
if (l > mad) {
// 把右边剩余加入
while (r <= right) {
temp[i] = str[r];
i++;
r++;
}
}
// 右边越界
if (r > right) {
// 把左边剩余加入
while (l <= mad) {
temp[i] = str[l];
i++;
l++;
}
public static void merge(int[] str, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
// 操作str的一段数组
// 把数组从中间切成两段 第一段从l=left 到 mad-1 第二段从r=mad到right
int mad = (left + right) / 2;
int l = left;
int r = mad + 1;
int i = 0;
// 把两段数组按大小排序 存放到temp数组中;
// 当其中一断数组越界 退出
// 越界 :段数据的左边超过的右边
while (l <= mad && r <= right) {// 不越界 继续比较
if (str[l] <= str[r]) {
temp[i] = str[l];
l++;
i++;
} else {
temp[i] = str[r];
r++;
i++;
}
}
// 当越界退出时,得考虑未比较完的那一段
// 因为每段都是有序的 所以直接加在temp【】后面
// 左段越界
if (l > mad) {
// 把右边剩余加入
while (r <= right) {
temp[i] = str[r];
i++;
r++;
}
}
// 右边越界
if (r > right) {
// 把左边剩余加入
while (l <= mad) {
temp[i] = str[l];
i++;
l++;
}
}
System.out.println("temp: " + Arrays.toString(temp));
// 把temp数组存的数转到原来的str[]数组对应操作的那段数据
int j = left;
int k = 0;
while (j <= right) {
str[j] = temp[k];
j++;
k++;
}
}
System.out.println("temp: " + Arrays.toString(temp));
// 把temp数组存的数转到原来的str[]数组对应操作的那段数据
int j = left;
int k = 0;
while (j <= right) {
str[j] = temp[k];
j++;
k++;
}
}