一、Github项目地址
https://github.com/taskArithmetic/arithmetic
结对项目成员:张博愉 3118005074;林梓琦 3118005062
二、PSP表格
| PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
| Planning |
计划 |
60 |
|
| · Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
30 |
|
| Development |
开发 |
1530 |
|
| · Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
120 |
|
| · Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
60 |
|
| · Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
30 |
|
| · Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
20 |
|
| · Design |
· 具体设计 |
60 |
|
| · Coding |
· 具体编码 |
1000 |
|
| · Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
120 |
|
| · Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
120 |
|
| Reporting |
报告 |
|
|
| · Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 |
|
| · Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
15 |
|
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
120 |
|
| 合计 |
|
1785 |
|
三、效能分析
我们对程序进行了生成1万道题目时的效能分析,类的调用情况如图
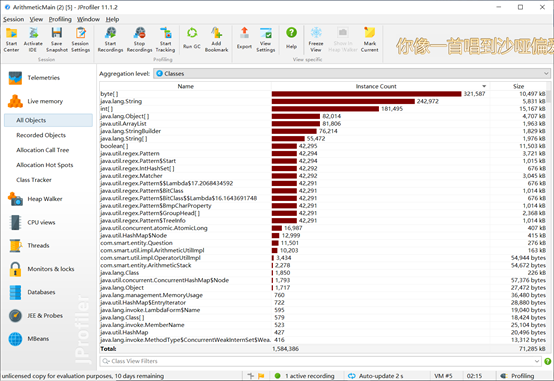
在没有优化前,我们的查重函数耗能最多。在对查重函数进行改进后,可以看到对查重函数所在类的调用已不在前列,大大减少了耗能。
四、设计实现过程
本程序的结构如下
Main函数
entity 实体类:ArithmeticStack, Question
/** * 四则运算实现栈 */ public class ArithmeticStack { String[] data; int maxsize; int top; public ArithmeticStack(int maxsize) { this.maxsize = maxsize; data = new String[maxsize]; top = 0; } // 将数据压入栈中 public void push(String s) { data[top++] = s; } // 弹出栈中的一个值 public String pop() { if (top == 0) { return null; } else { return data[--top]; } } @Override public String toString() { return "ArithmeticStack{" + "data=" + Arrays.toString(data) + '}'; } }
/** * Question 实体类:包含问题本身和它对于的答案 */ public class Question implements Serializable { private String suffixQuestion; private String infixQuestion; private String answer; public Question(String suffixQuestion) { this.suffixQuestion = suffixQuestion; } public Question() { } public String getSuffixQuestion() { return suffixQuestion; } public void setSuffixQuestion(String suffixQuestion) { this.suffixQuestion = suffixQuestion; } public String getInfixQuestion() { return infixQuestion; } public void setInfixQuestion(String infixQuestion) { this.infixQuestion = infixQuestion; } public String getAnswer() { return answer; } public void setAnswer(String answer) { this.answer = answer; } @Override public String toString() { return "Question{" + "suffixQuestion= " + suffixQuestion + ' ' + ", infixQuestion= " + infixQuestion + ' ' + ", answer= " + answer + ' ' + '}'; } }
util(impl) 工具类接口及其实现类:ArithmeticUtil, IIOUtil, IOperatorUtil, IOperandUtil, IParamsUtil, IProduceQuestionUtil
gui 图形界面:ArithmeticFrame
本程序主要函数调用关系如图

五、代码说明
生成随机操作数数函数randomOperand
public static String randomOperand(int r) { int numerator; // 分子 int denominator; // 分母 Random ran = new Random(); denominator = ran.nextInt(15) + 1; numerator = ran.nextInt(denominator * r); String fraction = numerator + "/" + denominator; ArithmeticUtilImpl arithmeticUtil = new ArithmeticUtilImpl(); return arithmeticUtil.simplify(fraction); }
生成随机操作符函数randomOperator
public static String randomOperator() { String[] operators = {"+", "-", "*", "÷"}; Random random = new Random(); int i = random.nextInt(4); return operators[i]; }
题目生成函数produce
/** * 生成问题,将问题返回,问题包括:中缀表达式,后缀表达式,答案 * * @param r 该参数是用户指定的操作数的最大值 */ public List<Question> produce(int n, int r) { // 存放要返回的question列表 List<Question> questions = new ArrayList<>(); Random random = new Random(); IArithmeticUtil arithmeticUtil = new ArithmeticUtilImpl(); Map<Question, String> questionStringMap = new HashMap<>(); boolean flag; while (questions.size() < n) { flag = true; Question question = new Question(); // 操作符最多有3个,则操作数最多有四个、最少有两个 int count = random.nextInt(3) + 2; int operandCount = 0; int operatorCount = 0; String suffixQuestion = ""; while (operatorCount != operandCount - 1 || operandCount < count) { if (operandCount == count) { suffixQuestion += OperatorUtilImpl.randomOperator() + " "; operatorCount++; continue; } if (operandCount - operatorCount > 1) { switch (random.nextInt(2)) { case 0: suffixQuestion += OperandUtilImpl.randomOperand(r) + " "; operandCount++; break; case 1: suffixQuestion += OperatorUtilImpl.randomOperator() + " "; operatorCount++; break; } } else { suffixQuestion += OperandUtilImpl.randomOperand(r) + " "; operandCount++; } } // 将中缀表达式,后缀表达式,答案封装进question中 question.setSuffixQuestion(suffixQuestion); question.setInfixQuestion(suffixToInfix(suffixQuestion)); if (!arithmeticUtil.operate(question)) { continue; } if (questionStringMap.containsValue(question.getAnswer())) { for (Map.Entry<Question, String> entry : questionStringMap.entrySet()) { // 当答案一样时,进行栈比较,如果栈比较返回的结果为“重复”,将flag设为false if (entry.getValue().equals(question.getAnswer()) && compareSuffix(entry.getKey(), question)) { flag = false; } } } if (flag) { questionStringMap.put(question, question.getAnswer()); questions.add(question); } } return questions; }
查重函数compareSuffix
/** * 对两个表达式进行查重,方法: * 首先判断两个表达式是否完全相同,如果完全相同,返回true,否则继续执行方法 * * @return 如果题目重复返回true,不重复返回false */ public boolean compareSuffix(Question q1, Question q2) { String suffix1 = q1.getSuffixQuestion(); String suffix2 = q2.getSuffixQuestion(); if (suffix1.length() != suffix2.length()) { return false; } if (suffix1.equals(suffix2)) { return true; } ArithmeticStack stack1 = new ArithmeticStack(suffix1.length()); ArithmeticStack stack2 = new ArithmeticStack(suffix2.length()); String[] params1 = suffix1.split(" "); String[] params2 = suffix2.split(" "); int j = 0; for (String s : params1) { if (s.matches("[+\\-*÷]")) { String s1_1 = stack1.pop(); String s1_2 = stack1.pop(); while (!params2[j].matches("[+\\-*÷]")) { stack2.push(params2[j]); j++; } if (!s.equals(params2[j])) { return false; } String s2_1 = stack2.pop(); String s2_2 = stack2.pop(); IOperatorUtil operatorUtil = new OperatorUtilImpl(); // 判断s1_1和s1_2是否为运算式 if (operatorUtil.hasOperator(s1_1) || operatorUtil.hasOperator(s1_2)) { if (!operatorUtil.hasOperator(s2_1) && !operatorUtil.hasOperator(s2_2)) { return false; } if (operatorUtil.hasOperator(s1_1)) { if (operatorUtil.hasOperator(s2_1)) { if (!s1_2.equals(s2_2)) { return false; } } else { if (!s1_2.equals(s2_1)) { return false; } } } else { if (operatorUtil.hasOperator(s2_1)) { if (!s1_1.equals(s2_2)) { return false; } } else { if (!s1_1.equals(s2_1)) { return false; } } } } else { if (!((s1_1.equals(s2_1) && s1_2.equals(s2_2)) || (s1_1.equals(s2_2) && s1_2.equals(s2_1)))) { return false; } } stack1.push("(" + s1_2 + s + s1_1 + ")"); stack2.push("(" + s2_2 + s + s2_1 + ")"); j++; } else if (!s.matches("[+\\-*÷]") && !s.equals(" ")) { stack1.push(s); } } return true; }
计算答案函数operate。其中,我们把式子分解成不可分的表达式,利用compute计算
public boolean operate(Question question) { String suffix = question.getSuffixQuestion(); String[] params = suffix.split(" "); String result; // 存放中间结果 ArithmeticStack stack = new ArithmeticStack(suffix.length()); for (String param : params) { if (param.matches("[+\\-*÷]")) { // 遇到操作符,弹出两个操作数计算并进栈 String operand1 = stack.pop(); String operand2 = stack.pop(); result = compute(operand1, operand2, param); if (result == null) { return false; } stack.push(result); } else { // 遇到数字直接进栈 stack.push(param); } } result = simplify(stack.pop()); question.setAnswer(result); return true; } public String compute(String number1, String number2, String operator) { String result = null; int[] numerator = new int[2]; // 两个操作数的分子 int[] denominator = new int[2]; // 两个操作数的分母 String[] operand1 = number1.split("/"); String[] operand2 = number2.split("/"); if (operand1.length == 1) { // 判断是否为分数 numerator[1] = Integer.parseInt(operand1[0]); denominator[1] = 1; } else { denominator[1] = Integer.parseInt(operand1[1]); if (operand1[0].contains("'")) { // 判断是否为带分数 String[] num = operand1[0].split("'"); numerator[1] = Integer.parseInt(num[0]) * denominator[1] + Integer.parseInt(num[1]); } else { numerator[1] = Integer.parseInt(operand1[0]); } } if (operand2.length == 1) { // 判断是否为分数 numerator[0] = Integer.parseInt(operand2[0]); denominator[0] = 1; } else { denominator[0] = Integer.parseInt(operand2[1]); if (operand2[0].contains("'")) { // 判断是否为带分数 String[] num = operand2[0].split("'"); numerator[0] = Integer.parseInt(num[0]) * denominator[0] + Integer.parseInt(num[1]); } else { numerator[0] = Integer.parseInt(operand2[0]); } } switch (operator) { case "+": result = (numerator[0] * denominator[1] + numerator[1] * denominator[0]) + "/" + (denominator[0] * denominator[1]); break; case "-": int i = numerator[0] * denominator[1] - numerator[1] * denominator[0]; if (i < 0) { return null; } result = i + "/" + (denominator[0] * denominator[1]); break; case "*": result = (numerator[0] * numerator[1]) + "/" + (denominator[0] * denominator[1]); break; case "÷": if (numerator[0] * denominator[1] > numerator[1] * denominator[0]) { return null; } if (numerator[1] * denominator[0] == 0) { return null; } result = (numerator[0] * denominator[1]) + "/" + (numerator[1] * denominator[0]); break; } return result; }
比较答案函数checkAnswer
public void checkAnswer(String answerFilePath, String taskFilePath) throws IOException { File answerFile = new File(answerFilePath); File taskFile = new File(taskFilePath); if (!answerFile.exists() || !taskFile.exists()) { String s = ""; s += answerFile.exists() ? "" : (" " + answerFilePath); s += taskFile.exists() ? "" : (" " + taskFilePath + " "); System.out.println("选择的文件" + s + "不存在!"); return; } BufferedReader answerReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(answerFile)); BufferedReader taskReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(taskFile)); String answer, task; List<Integer> wrongQuestions = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> rightQuestions = new ArrayList<>(); int count = 0; while ((answer = answerReader.readLine()) != null && (task = taskReader.readLine()) != null) { count++; answer = answer.replaceAll(" ", ""); task = task.replaceAll(" ", ""); String[] answerParams = answer.split("="); String[] taskParams = task.split("="); if (!answerParams[1].equals(taskParams[1])) { wrongQuestions.add(count); } else { rightQuestions.add(count); } } answerReader.close(); taskReader.close(); String answerFileName = answerFile.getName(); String taskFileName = taskFile.getName(); File gradeFile = new File("grades/" + answerFileName.substring(0, answerFileName.indexOf(".")) + "_" + taskFileName.substring(0, taskFileName.indexOf(".")) + "_" + "grade.txt"); if (gradeFile.exists()) { gradeFile.delete(); } gradeFile.createNewFile(); BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(gradeFile)); writer.write("Correct:" + rightQuestions.size() + "\n( "); for (Integer i : rightQuestions) { writer.write(i + " "); } writer.write(")\n\n"); writer.write("Wrong:" + wrongQuestions.size() + "\n( "); for (Integer i : wrongQuestions) { writer.write(i + " "); } writer.write(")"); writer.close(); }
六、测试运行
生成10000道题目
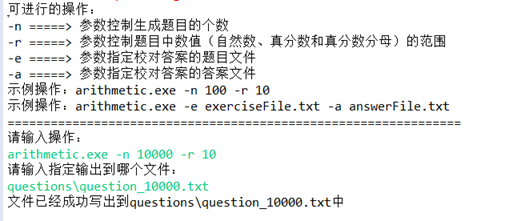
问题文件


答案文件

答案校对

图形界面
七、开发实际时间
| PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
| Planning |
计划 |
60 |
50 |
| · Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
30 |
25 |
| Development |
开发 |
1530 |
1880 |
| · Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
120 |
150 |
| · Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
60 |
60 |
| · Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
30 |
40 |
| · Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
20 |
20 |
| · Design |
· 具体设计 |
60 |
70 |
| · Coding |
· 具体编码 |
1000 |
1200 |
| · Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
120 |
100 |
| · Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
120 |
240 |
| Reporting |
报告 |
|
|
| · Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 |
25 |
| · Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
15 |
10 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
120 |
90 |
| 合计 |
|
1785 |
2080 |
八、项目小结
对于我们来说,这次的结对项目作业是一个很难得的学习经验。我们在开始作业前就进行了一次简短的讨论,把初步的项目结构给
制定了下来,这也为我们的开发提供了不少便利。在这次项目开发过程中,我们多次积极讨论,同步更新代码,学会了如何作为一个
团队去进行开发工作。
遇到的困难:由于我们事前便详细的进行了项目的需求分析,在开发过程中我们并没有遇到太多意料之外的困难。唯一卡住我们的地方
便是在进行减法或除法判断时如何同时更改表达式。这个问题困扰了我们一段时间,最终我们选择妥协方案:遇到不符合的表达式便重
新生成而不是进行调整。
结对项目共同感受:良好的代码习惯能更有助于团队开发。团队的沟通能有效减少开发困难
张博愉的闪光点:善于交流沟通、对于算法实现有着独特想法
林梓琦的闪光点:打码能力强、做事效率高。本程序的大部分代码均有梓琦同学完成。代码习惯良好,可读性强。有自己独特的想法
