1、Introduction
(1)神经网络的几个优化方向:prune redundant connection, use low-precision or quantized weights, use more efficient architectures
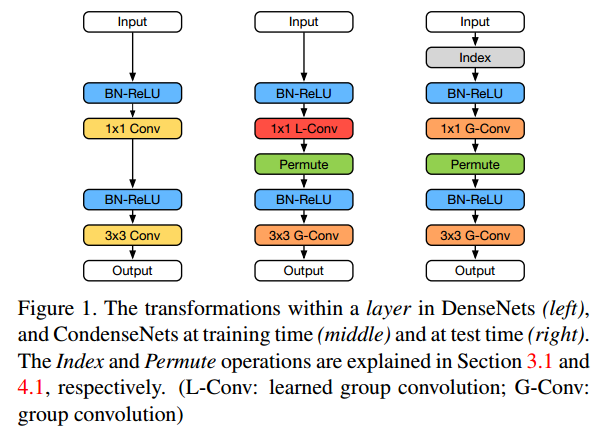
(2)神经网络中的redundancy :layer-by-layer的连接模式迫使网络在整个网络中复制来自早期层的特性,DenseNet架构通过直接将每一层和它前面的层相连接来alleviates the need for feature replication 。尽管更加efficient,但当早期的feature在后来的层中不需要时,密集的连接会导致冗余。
(3)与之前的剪枝方法相比,本文的方法在训练过程中自动学习一个稀疏化的网络,并生成一个规则连接模式,该模式可以使用组卷积有效地实现。
2、Related work and background
2.1. Related work
(1)weights pruning and quantization:细粒度(Fine-grained) 的pruning可以取得更高的稀疏性,但是它需要存储很多索引,并且依赖专门的硬件加速;粗粒度(coarse-grained)的剪枝,比如filter-level剪枝,取得的稀疏性比较低,但是最终的网络结构更加规整,便于高效地实现。CondenseNets在训练的最初阶段就进行weight pruning,相比于filter-level级的剪枝方法可以达到更高的稀疏性,因此在sparsity和regularity之间达到一个sweet spot。
(2)Efficient network architectures:MobileNet、ShuffleNet等,主要特点是使用了depth-wise separable卷积,这些网络的一个实际缺点是深度可分卷积在大多数深度平台上还没有得到有效的实现(A practical downside of these networks is depth-wise separable convolutions are not (yet) efficiently implemented in most deeplearning platforms.)。CondenseNet 使用well-supported 分组卷积,可以在实际中取得更高的计算效率。
2.2. DenseNet
(1)每一层产生k个特征,其中k被称为网络的增长率。DenseNets的独特之处在于,the input of each layer is a concatenation of all feature maps generated by all preceding layers within the same dense block 每个层执行一系列连续的转换:先用1*1卷积降通道,再用3*3卷积生成k个通道 。