table of Contents
1, the main contents of the instruction format design
1, CPU processing and functions
3) operation of the controller
FIG bus structure example of a multi-stage
Fourth, the input-output system
First, the instruction
1, the main contents of the instruction format design
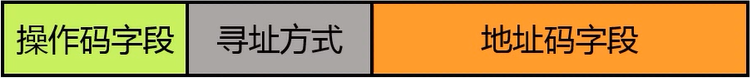
The required number of instructions and support opcode extension bits determining operation code field;
Determining the address field of the request operand number
The addressing requirements, determining the number of bits for each field addressing mode address code field
Determined using fixed length or variable length instruction command
example:

2, MIPS Instruction Summary

Feature
Simple Load / Store architecture
Easy-to-pipeline CPU design
Ease of compiler development
MIPS instruction addressing very simple, the operation of each instruction operation instruction is very simple
1), MIPS registers

Second, the central processor
1, CPU processing and functions

1) The main function

2) the main register

3) operation of the controller

3, data path
Path means performs data communication between

Data path and bus structures,

Single Bus

Dual Bus

Three bus

Third, the system bus
1, bus
It is an important part of the computer architecture, which may be connected through the computer system respective functional sections together to form a complete system.

effect

2, bus classification
Memory Bus
A short-range, high-speed bus, to match the characteristics of the memory, the maximum extent possible to increase the data bandwidth between the processor and memory, to optimize performance for data transmission Cache block.
System bus
An internal bus, also known as bus or board, the most important is the computer system bus, memory bus and also connected to I / O bus, intermediate bus.
I / O bus
Typically connected distant, relatively slow, for connecting various external devices, and is connected to the system bus or memory bus.
3, the bus connection
Single-bus structure

Dual bus architecture

Multilevel bus architecture

Bus Bridge
A connection means between the different rate of the bus, the speed signal from the buffer, a level shifter, the role of protocol conversion control.
FIG bus structure example of a multi-stage

Fourth, the input-output system
1 Overview
External device, the interface member, and the corresponding bus management computer software referred to as input / output system, referred to as the I / O system.
2. Features
Asynchrony
With respect to the peripheral device handler usually operate asynchronously
real-time
When the peripheral device interface with the processor, since different types of equipment, their work pace is different, the processor must transfer mode and the transmission rate required by the device to seize the opportunity to provide services according to different devices, which require real-time control.
And device independence
各种外部设备必须根据其特点和要求选择一种标准接口和处理器进行连接,他们之间的差别必须由设备本身的控制器通过硬件和软件填补;这样,处理器本身无须了解外设的具体细节,可以采用统一的硬件和软件对其管理。
3、输入输出过程
输入过程
CPU把一个地址值放在地址总线上,这一步将选择某一输入设备;
CPU等候输入设备的数据成为有效;
CPU从数据总线读入数据,并放在一个相应的寄存器中。
输出过程
CPU把一个地址值放在地址总线上,选择输出设备;
CPU把数据放在数据总线上;
输出设备认为数据有效,从而把数据取走。
