codeforces上的代码是开放的,常常就能看到本渣与大神们的差距
比如二分查找。。。
1.在数组中,找出第一个4所在位置
输入:
14 4
1 2 2 3 4 4 4 4 5 6 7 9 9 10这是本鶸代码。。。。。。。
#include <stdio.h>
int a[1010],n;
int main(){
int i,l,r,mid,b;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&b);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
l=0,r=n;
while(l+1<r){
mid=(l+r)/2;
if(a[mid]<b)l=mid;
else r=mid;//a[mid]>=b
}
if(a[r]==b)printf("%d\n",r);//找数字b出现在最左侧
else printf("NO\n");
return 0;
}输出:
5
然而大神是这样写的:
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[1010],n;
int main(){
int i,b,pos;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&b);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
pos=lower_bound(a+1,a+1+n,b)-a;//找数字b出现在最左侧
if(pos==n+1||a[pos]!=b)printf("NO\n");
else printf("%d\n",pos);//a[pos]==b;
return 0;
}2.在数组中,找出最后一个4所在位置
输入:
14 4
1 2 2 3 4 4 4 4 5 6 7 9 9 10这是本鶸代码。。。。。。。
#include <stdio.h>
int a[1010],n;
int main(){
int i,l,r,mid,b;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&b);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
l=1,r=n+1;
while(l+1<r){
mid=(l+r)/2;
if(a[mid]<=b)l=mid;
else r=mid;
}
if(a[l]==b)printf("%d\n",l);//找数字b出现在最右侧
else printf("NO\n");
return 0;
}然而大神是这样写的:
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[1010],n;
int main(){
int i,b,pos;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&b);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&a[i]);
pos=upper_bound(a+1,a+1+n,b)-a;//找数字b出现在最右侧
if(pos==n+1||a[pos-1]!=b)printf("NO\n");
else printf("%d\n",pos-1);//a[pos-1]==b;
return 0;
}3.用法
头文件:#include <algorithm>
时间复杂度:一次查询O(log n),n为数组长度。
图示:
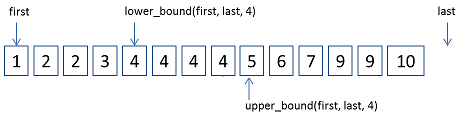
lower_bound:
功能:查找非递减序列[first,last) 内第一个大于或等于某个元素的位置。
返回值:如果找到返回找到元素的地址否则返回last的地址。(这样不注意的话会越界,小心)
用法:int t=lower_bound(a+l,a+r,key)-a;(a是数组)。
upper_bound:
功能:查找非递减序列[first,last) 内第一个大于某个元素的位置。
返回值:如果找到返回找到元素的地址否则返回last的地址。(同样这样不注意的话会越界,小心)
用法:int t=upper_bound(a+l,a+r,key)-a;(a是数组)。
