图的邻接表存储 (图的遍历、拓扑排序、关键路径)
一、源代码
1、图的基本数据结构
//邻接表存储图
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
typedef struct ArcNode{
int adjvex; //该弧所指向的顶点位置
struct ArcNode* nextarc; //指向下一条弧的指针
int info; //权值
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode{
int data; //指向该边的终点
ArcNode *firstarc; //指向下一条边
}VNode;
typedef struct ALGraph{
int vexnum,arcnum; //图中当前顶点数和弧数
VNode* vertices; //包含顶点信息和指向第一条边的指针
}ALGraph;
2、基本操作
包括创建邻接表、销毁邻接表、获得邻接表的某个顶点、返回顶点v的第一个邻接顶点、返回邻接矩阵的下一个邻接顶点
//创建邻接表
void CreatGraph(ALGraph *Graph){
printf("输入顶点数:");
scanf("%d",&Graph->vexnum);
printf("输入弧数:");
scanf("%d",&Graph->arcnum);
Graph->vertices=(VNode*)malloc((Graph->vexnum+1)*sizeof(VNode)); //开辟数组(0号单元不用)
for(int i=1;i<=Graph->vexnum;i++){
printf("输入顶点信息:");
scanf("%d",&(Graph->vertices[i].data));
int j,first=1;
ArcNode *p,*q=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
printf("输入与%d顶点邻接的边:");
scanf("%d",&j);
if(j==-1) Graph->vertices[i].firstarc=nullptr;
while(j!=-1){
p=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
p->adjvex=j;
p->nextarc=nullptr;
printf("输入权值:");
scanf("%d",&(p->info));
if(first){
Graph->vertices[i].firstarc=p;
first=0;
}else{
q->nextarc=p;
}
q=p;
printf("输入与%d顶点邻接下一条的边:",Graph->vertices[i].data);
scanf("%d",&j);
}
}
}
//销毁邻接表
void ClearGraph_M(ALGraph *G)
{
(*G).vexnum = 0;
(*G).arcnum = 0;
}
//获得邻接表的某个顶点
int GetVex_M(ALGraph G, int order)
{
if(order>=1 && order<=G.vexnum)
return G.vertices[order].data;
else
return -1;
}
//返回顶点v的第一个邻接顶点
int FirstAdjVex_M(ALGraph G,int v)
{
if(G.vertices[v].firstarc)
return G.vertices[v].firstarc->adjvex;
else return -1;
}
//返回邻接矩阵的下一个邻接顶点
int NextAdjVex_M(ALGraph G, int v, int w) //v是顶点,w是当前顶点连接的顶点
{
int i=1;
ArcNode* p=G.vertices[v].firstarc;
for(i=1;;i++){
if(p&&p->adjvex==w)
if(p->nextarc)
return p->nextarc->adjvex;
if(p||p->nextarc) return -1;
p=p->nextarc;
}
}
3、已知邻接表求逆邻接表
//已知邻接表求逆邻接表
void Reverse(ALGraph A,ALGraph *B){
//逆邻接表
int i,k;
ArcNode *p1,*p2;
B->vexnum=A.vexnum;
B->arcnum=A.arcnum;
for(i=1;i<=A.vexnum;i++){ //逆邻接表初始化
B->vertices=(VNode*)malloc((B->vexnum+1)*sizeof(VNode)); //开辟数组(0号单元不用)
B->vertices[i].data=A.vertices[i].data;
B->vertices[i].firstarc=nullptr;
}
for(i=1;i<=A.vexnum;i++){
p1=A.vertices[i].firstarc;
while(p1){
k=p1->adjvex;
p2=(ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
p2->adjvex=i;
p2->nextarc= nullptr;
p2->info=p1->info;
//将逆邻接表的元素接上
ArcNode *q=(ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
q=B->vertices[k].firstarc;
ArcNode *t=(ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
if(!B->vertices[k].firstarc)
B->vertices[k].firstarc=p2;
else{
for(;q;t=q,q=q->nextarc); //t指向非空的前一个节点
t->nextarc=p2;
}
p1=p1->nextarc;
}
}
}
4、遍历算法(深度优先,广度优先)
//深度优先遍历
int visited[100]; //标志数组,0表示未被访问,1表示已访问
void DFS(ALGraph G,int v);
void DFSTraverse(ALGraph G){ //对图G做深度优先遍历
int v;
for(v=1;v<=G.vexnum;v++) //标志数组初始化
visited[v]=0;
for(v=1;v<=G.vexnum;v++)
if(!visited[v]) DFS(G,v);
}
void DFS(ALGraph G,int v){
//从第v个顶点出发递归地深度优先遍历图G
int w;
visited[v]=1;
printf("%d",G.vertices[v].data); //访问第v个顶点
for(w=FirstAdjVex_M(G,v);w!=-1;w=NextAdjVex_M(G,v,w))
if(!visited[w]) DFS(G,w); //对v的尚未访问的邻接顶点w递归调用DFS
}
//广度优先遍历算法
void BFSTraverse(ALGraph G){
//按广度优先非递归遍历图G,使用辅助队列Q和标志访问数组
int v;
for(v=1;v<=G.vexnum;v++) //标志数组初始化
visited[v]=0;
queue<int> Q; //辅助队列
for(v=1;v<=G.vexnum;v++){
if(!visited[v]){
visited[v]=1;
printf("%d",G.vertices[v].data);
Q.push(v);
while(!Q.empty()){
int u=Q.front(); //队头元素出队并置位 Q
Q.pop();
for(int w=FirstAdjVex_M(G,u);w!=-1;w=NextAdjVex_M(G,u,w)){
if(!visited[w]){ //w为u的尚未访问的邻接顶点
visited[w]=1;
printf("%d",G.vertices[w].data);
Q.push(w);
}
}
}
}
}
}
*5、生成树
//无向图的连通分量和生成树(深度优先生成树)
typedef struct CS{
int data;
struct CS *firstchild,*nextsibling;
}CSNode,*CSTree;
void DFSTree(ALGraph G,int v,CSTree *T);
void DFSForest(ALGraph G,CSTree *T,int *c){
//建立无向图G的深度优先生成森林的孩子兄弟链表
*T= nullptr;
CSTree p,q;
q=(CSTree)malloc(sizeof(CSNode));
int v,count=0; //count为连通分量个数
for(v=1;v<=G.vexnum;v++) //标志数组初始化
visited[v]=0;
for(v=1;v<=G.vexnum;v++)
if(!visited[v]){ //第V个顶点为新的生成树的根节点
p=(CSTree)malloc(sizeof(CSNode)); //分配根节点
p->data=GetVex_M(G,v); //给根节点赋值
p->firstchild=nullptr;
p->nextsibling=nullptr;
if(!(*T))
(*T)=p; //是第一棵生成树的根
else q->nextsibling=p; //是其他生成树的根(前一棵根的兄弟)
q=p; //q指示当前生成树的树根
DFSTree(G,v,&p); //建立以p为根的生成树
count++;
}
*c=count;
}
void DFSTree(ALGraph G,int v,CSTree *T){
//从第v个顶点出发深度优先遍历图G,建立以T为根的生成树
CSTree p,q;
int first=1;
visited[v]=1;
for(int w=FirstAdjVex_M(G,v);w!=-1;w=NextAdjVex_M(G,v,w)){
if(!visited[w]){
p=(CSTree)malloc(sizeof(CSNode)); //分配孩子节点
p->data=GetVex_M(G,w);
p->nextsibling=nullptr;
p->firstchild=nullptr;
if(first){ //w是v的第一个未被访问的邻接顶点
(*T)->firstchild=p; //是根的左孩子结点
first=0;
}else{ //w是v的其他未被访问过的邻接顶点
q->nextsibling=p; //是上一邻接顶点的右兄弟结点
}
q=p;
DFSTree(G,w,&q); //从第w个顶点出发深度优先遍历图G,建立子生成树
}
}
}
//验证生成树
void LevelTraverse(CSTree T) { //孩子兄弟链表的层次遍历算法
CSTree P = T;
CSTree K ;
queue<CSTree> sqQueue; //声明一个队列
while (P) //这里的 P 是指森林中可能有多棵子树,指向每棵子树的根节点
{
K = P; //利用 K 来遍历以 P 为根节点子树中的节点
sqQueue.push(K); //先将根节点入队
while (!sqQueue.empty()) { //只要队列不为空,则依次出队,直到队空
printf("%d",sqQueue.front()->data); //打印该元素
K=sqQueue.front();
sqQueue.pop(); //出队
if (K->firstchild) { //如果该节点不是森林中的叶节点,则进入下一层
K = K->firstchild; //将 K 指向 K 最左边的孩子
sqQueue.push(K); //入队
while (K->nextsibling) { //判断它是否有兄弟节点
K = K->nextsibling;
sqQueue.push(K);;//入队它的兄弟节点(在同一层上)
}
}
}
P = P->nextsibling; //指向下一棵树的根节点
}
}
6、拓扑排序
//拓扑排序
void TopologicalSort(ALGraph G){
int k;
int indegree[G.vexnum+1];
for(int i=1;i<=G.vexnum;i++){ //求各顶点的入度并放入indegree数组中
k=0;
for(int j=1;j<=G.vexnum;j++){ //遍历整个邻接表
ArcNode* p=G.vertices[j].firstarc;
while(p){
if(p->adjvex==i)
k++;
p=p->nextarc;
}
}
indegree[i]=k;
}
queue<int> S;
for(int i=1;i<=G.vexnum;i++){
if(!indegree[i])
S.push(i); //入度为0则进队列
}
int count=0; //对输出顶点计数
while(!S.empty()){
printf("%d",G.vertices[S.front()].data);
int i=S.front();
count++; //输出i号顶点并计数
S.pop();
ArcNode *p;
for(p=G.vertices[i].firstarc;p;p=p->nextarc){
int s=p->adjvex; //对i号顶点的每个邻接点的度数减1
if(!(--indegree[s]))
S.push(s); //若入度减为0,则入队
}
}
if(count<G.vexnum) printf("有回路"); //异常处理,也可判断有无回路
}
7、关键路径
//关键路径
//求事件的最早发生时间,依赖于拓扑排序
stack<int> I; //栈I返回图G的一个拓扑序列,全局变量
int ve[100]={0}; //事件的最早发生时间,全局变量
int vl[100]; //顶点事件的最迟发生时间,全局变量
void TopologicalSortve(ALGraph G){ //栈I返回图G的一个拓扑序列,为了后面求最迟发生时间
int k;
int indegree[G.vexnum+1];
for(int i=1;i<=G.vexnum;i++){ //求各顶点的入度并放入indegree数组中
k=0;
for(int j=1;j<=G.vexnum;j++){ //遍历整个邻接表
ArcNode* p=G.vertices[j].firstarc;
while(p){
if(p->adjvex==i)
k++;
p=p->nextarc;
}
}
indegree[i]=k;
}
queue<int> S;
for(int i=1;i<=G.vexnum;i++){
if(!indegree[i]) {
S.push(i); //入度为0则进队列
I.push(i);
}
}
int count=0; //对输出顶点计数
while(!S.empty()){
printf("%d",G.vertices[S.front()].data);
int i=S.front();
count++; //输出i号顶点并计数
S.pop();
ArcNode *p;
for(p=G.vertices[i].firstarc;p;p=p->nextarc){
int s=p->adjvex; //对i号顶点的每个邻接点的度数减1
if(!(--indegree[s])) {
S.push(s); //若入度减为0,则入队
I.push(s);
}
if(ve[i]+p->info>ve[s]) //关键步骤,取大
ve[s]=ve[i]+p->info;
}
}
if(count<G.vexnum) printf("有回路"); //异常处理,也可判断有无回路
}
//求顶点事件的最迟发生时间,输出G 的各项关键活动
void CriticalPath(ALGraph G){
// while(!I.empty()){
// printf("%d ",I.top());
// I.pop();
// }
ArcNode* p;
ALGraph B; //G的逆邻接表
void Reverse(ALGraph A,ALGraph* B);
Reverse(G,&B);
for(int i=1;i<=G.vexnum;i++)
vl[i]=ve[G.vexnum]; //初始化顶点事件的最迟发生时间,都为最后一个事件的最早发生时间
while(!I.empty()){ //按拓扑逆序列求各顶点的vl值
int j=I.top();
I.pop();
p=B.vertices[j].firstarc;
while(p){
int k=p->adjvex;
int dut=p->info;
if(vl[j]-dut<vl[k])
vl[k]=vl[j]-dut; //取小
p=p->nextarc;
}
}
//求关键活动
printf("\n");
printf("关键活动为:\n");
for(int j=1;j<=G.vexnum;j++)
if(ve[j]==vl[j])
printf("%d",G.vertices[j].data);
}
//打印ve和vl
void print(ALGraph G){
printf("\n");
printf("最早发生时间ve:\n");
for(int i=1;i<=G.vexnum;i++)
printf("%d ",ve[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("最迟发生时间vl:\n");
for(int i=1;i<=G.vexnum;i++)
printf("%d ",vl[i]);
}
二、图解
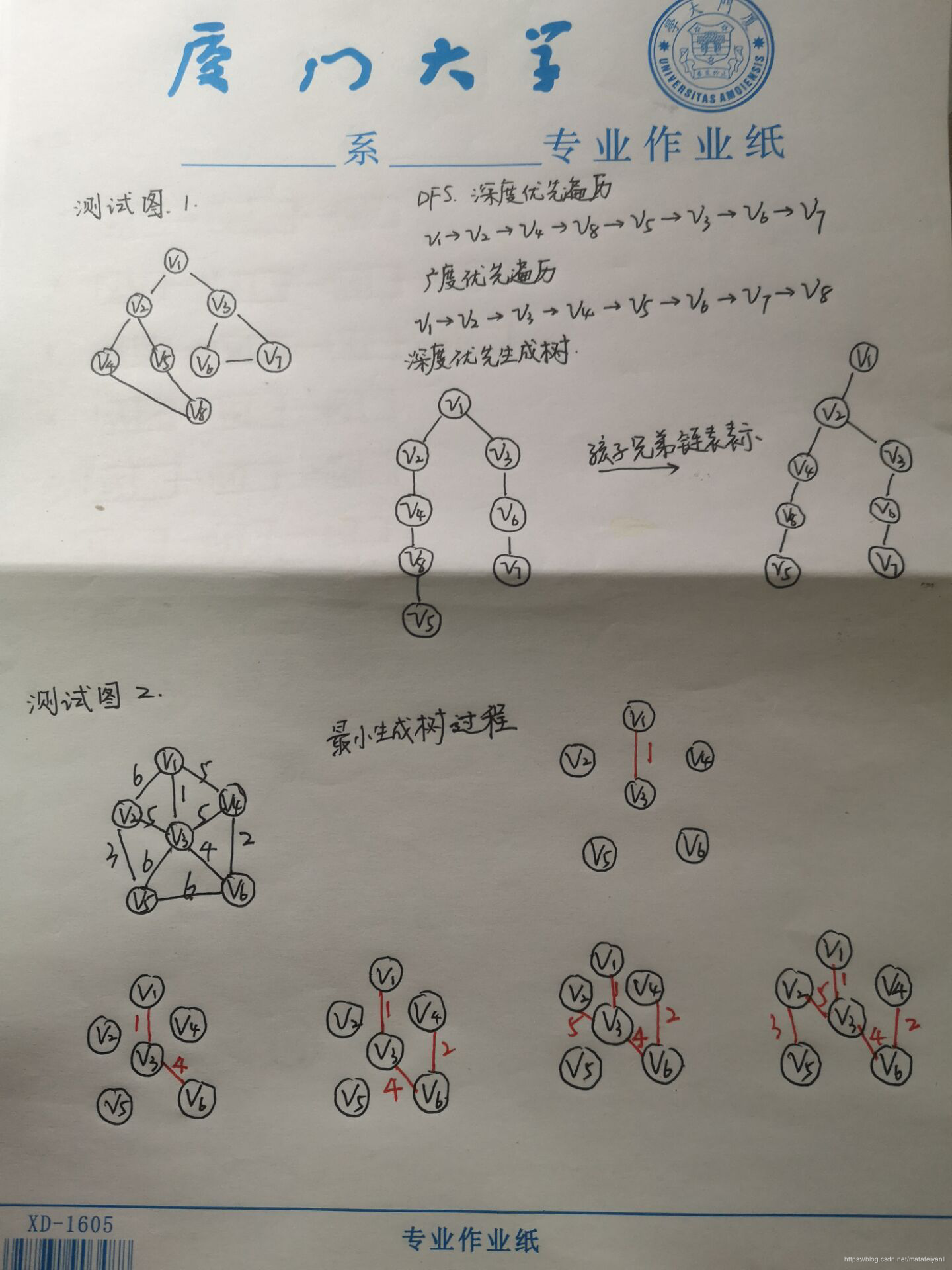
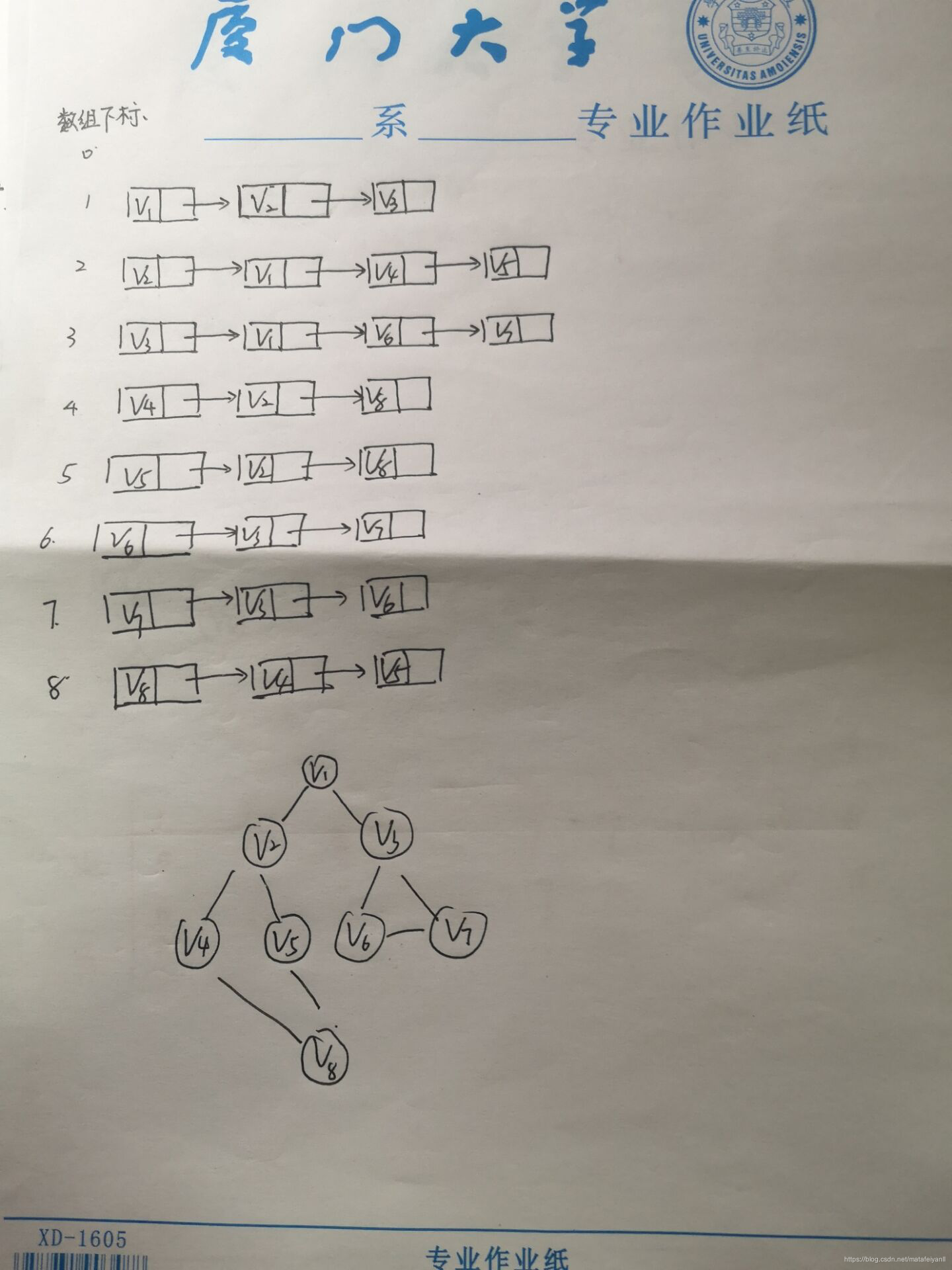
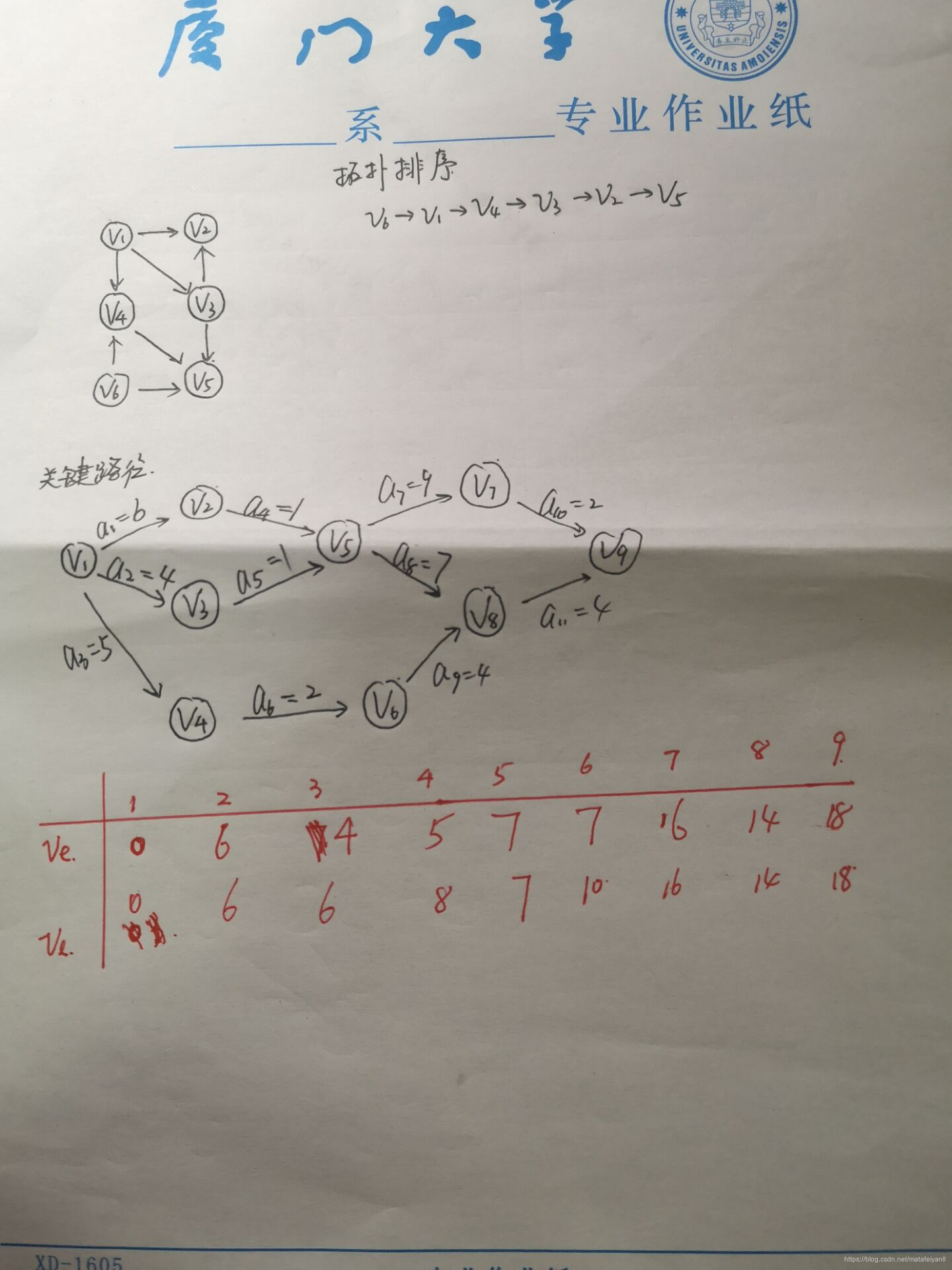 三、测试
三、测试
1、测试函数
//测试函数
int main()
{
ALGraph G;
CreatGraph(&G);
printf("\n");
printf("深度优先遍历\n");
DFSTraverse(G);
printf("\n");
printf("广度优先遍历\n");
BFSTraverse(G);
CSTree T;
int count;
DFSForest(G,&T,&count);
printf("\n");
printf("连通分支个数为%d\n",count);
printf("深度优先遍历孩子兄弟链表层次遍历:\n");
LevelTraverse(T);
printf("\n");
printf("拓扑排序结果为:\n");
TopologicalSort(G);
printf("\n");
TopologicalSortve(G);
CriticalPath(G);
print(G);
}
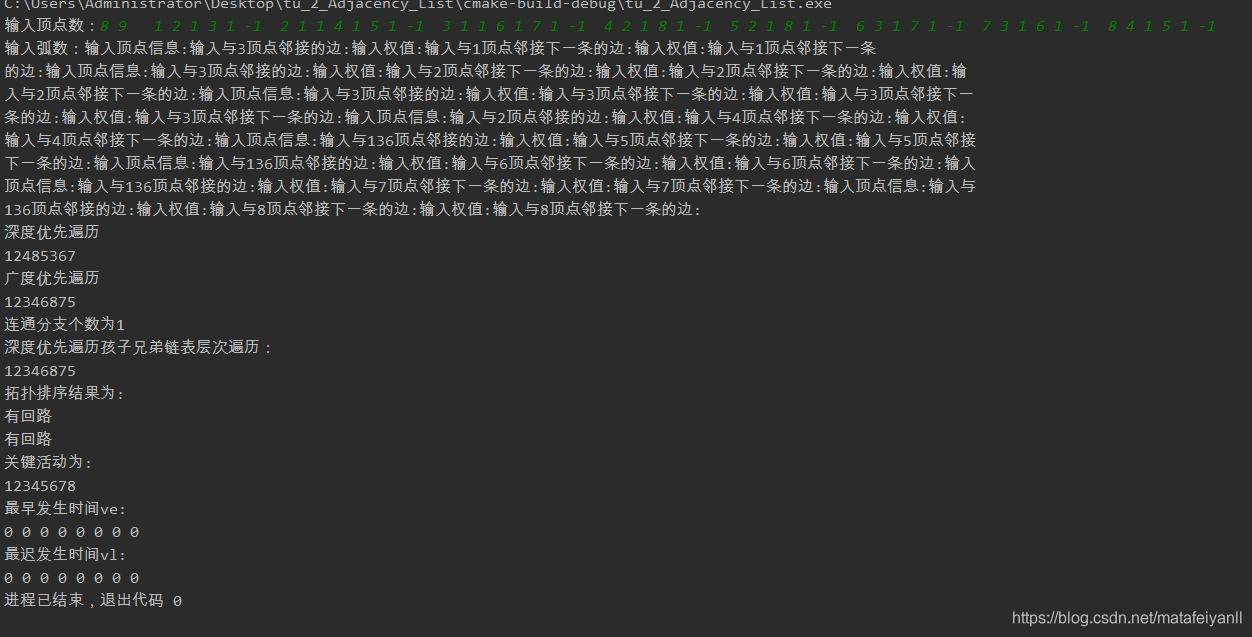
//测试数据 8 9 1 2 1 3 1 -1 2 1 1 4 1 5 1 -1 3 1 1 6 1 7 1 -1 4 2 1 8 1 -1 5 2 1 8 1 -1 6 3 1 7 1 -1 7 3 1 6 1 -1 8 4 1 5 1 -1
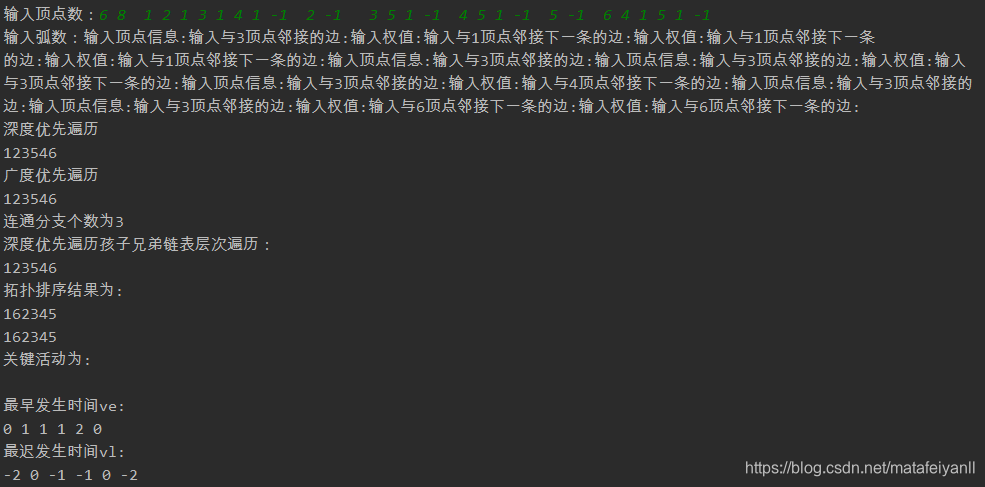
//测试数据 6 8 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 -1 2 -1 3 5 1 -1 4 5 1 -1 5 -1 6 4 1 5 1 -1
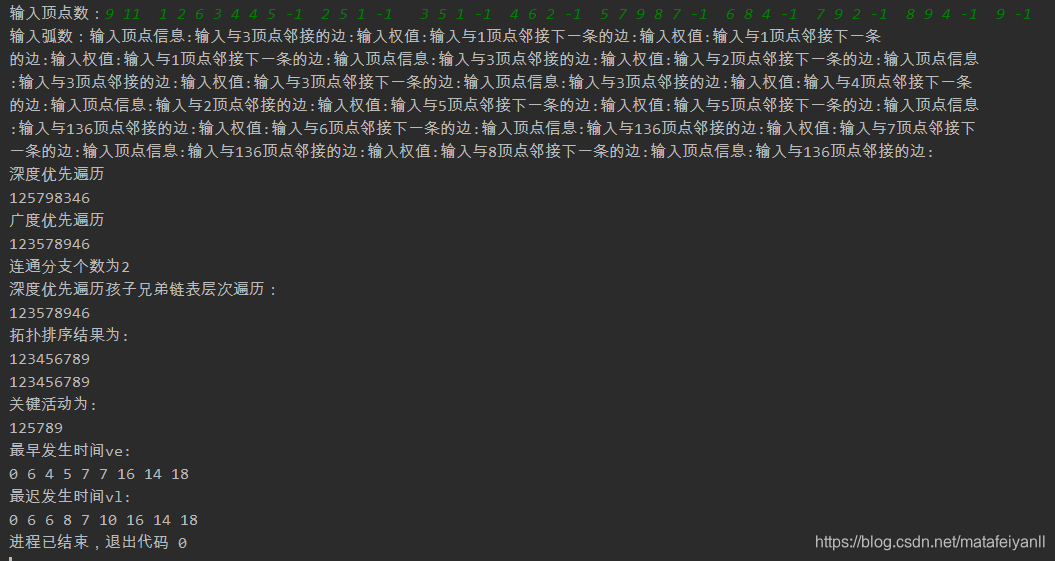
//测试数据 9 11 1 2 6 3 4 4 5 -1 2 5 1 -1 3 5 1 -1 4 6 2 -1 5 7 9 8 7 -1 6 8 4 -1 7 9 2 -1 8 9 4 -1 9 -1
2、测试结果