图的存储方式有很多种,这里事宜邻接表存储为例实现的。图的基本操作包括初始化一个空图、插入一节点、插入条边、深度优先遍历、广度优先遍历、销毁图等
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define OK 1
#define ERROR -1
#define MAX_VEX 10//最大顶点数
typedef int InfoType;
typedef char VexType;//顶点的类型
typedef int WeightType;//权值的类型图的种类(有向图、无向图、加权有向图、加权无向图),采用枚举法
typedef enum
{
DG = 1, AG, WDG, WAG//有向图 无向图 带权有向图 带权无向图
}GraphKind;邻接表的前半部分是顺序表,所以定义一个顺序表的结构体
typedef struct VexNode
{
VexType data;//顶点的值
int indegree;//顶点的度
LinkNode *firstarc;//指向第一个表节点,有向图是入度或出度或没有
}VexNode;//顶点节点类型定义邻接表后半部分是链表,所以定一个链表的结构体
typedef struct LinkNode
{
int adjvex;//邻接点在头结点数组中的位置(下标)
InfoType info;//节点信息 如权值
struct LinkNode *nextarc;//指向下一个表节点
}LinkNode;接下来定义图的结构体
typedef struct
{
GraphKind kind;
int vexnum;//顶点的个数
VexNode AdjList[MAX_VEX];//头结点的类型的数组
}ALGraph;在图的一系列基本操作中需要队列的帮助
//队列的结构体
typedef struct SqQueue
{
VexType array[MAX_VEX];
int front;
int rear;
}SqQueue;
//初始化一个空队列
SqQueue Creat_SqQueue()
{
SqQueue Q;
Q.front = 0;
Q.rear = 0;
return Q;
}
//入队列 若成功返回1 否则返回-1
int InsertQueue(SqQueue *Q, VexType e)
{
if ((Q->rear+1)%MAX_VEX == Q->front)
{
printf("The queue is full.\n");
return ERROR;
}
else
{
Q->array[Q->rear] = e;
Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1) % MAX_VEX;
//printf("Insert success!\n\n");
}
return OK;
}
//出队列 若成功返回弹出的元素 若不成功返回-1
VexType DeletaQueue(SqQueue *Q)
{
VexType e = 0;
if (Q->front == Q->rear)
{
printf("This queue is empty!\n");
return ERROR;
}
else
{
e = Q->array[Q->front];
Q->front = (Q->front + 1) % MAX_VEX;
//printf("Delete success!\n");
}
return e;
}建立一个空图
ALGraph CreatGraph() {
ALGraph G;
int i;//循环变量
int a = 0;
printf("1.DG\n2.AG\n3.WDG\n4.WAG\n");
printf("please enter the type of graph(according to the code):\n");
scanf("%d", &a);//确定图的类型
switch (a)
{
case 1:
G.kind = DG;
break;
case 2:
G.kind = AG;
break;
case 3:
G.kind = WDG;
break;
case 4:
G.kind = WAG;
break;
default:
printf("The type of the graph is error\n");
break;
}
G.vexnum = 0;//结点个数置为0
for (i = 0; i < MAX_VEX; i++)//把所有节点的度置为0
{
G.AdjList[i].indegree = 0;
G.AdjList[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
return G;
}插入节点时需要判断节点是否在,若不存在插入,如存在插入失败
//定位节点 若存在返回1 若不存在返回-1
int LocateVex(ALGraph *G, VexType v) {
int i = 0;
int a = 0;
printf("v = %c\n", v);
for (i = 0; i < G->vexnum; i++)
{
if (G->AdjList[i].data == v)
{
a++;
break;
}
}
if (a == 0)
{
return ERROR;
}
return OK;
}在图中插入一个节点
void InsertVex(ALGraph *G){
int res = 0;
if (G->vexnum + 1 == MAX_VEX)
{
printf("The graph is overflow!\n");
}
else
{
VexType u = '\0';
printf("please enter data:\n");
getchar();
scanf("%c", &u);
res = LocateVex(G, u);
if (res == -1)//没有节点 添加
{
G->AdjList[G->vexnum].data = u;
G->AdjList[G->vexnum].firstarc = NULL;
G->vexnum++;
//printf("insert vertex success\n");
}
else
{
printf("insert vertex fail\n");
}
}
}在图中插入一条边时,要判断图的类型,不同的类型,插入操作是不一样的
void InsertArc(ALGraph *G) {
if (G->kind == DG)//有向图
{
LinkNode *p;
LinkNode *r;
int tail = 0;//弧尾(起点)
int head = 0;//弧头(终点)
p = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
printf("please enter the tail:");
scanf("%d", &tail);
printf("please enter the head:");
scanf("%d", &head);
if (tail < G->vexnum && head < G->vexnum)
{
p->adjvex = head;
p->nextarc = NULL;
p->info = 0;
r = G->AdjList[tail].firstarc;
p->nextarc = r;
G->AdjList[tail].firstarc = p;
G->AdjList[tail].indegree++;
printf("insert arc success\n");
}
else
{
printf("vertex is not exit.");
}
}
else if(G->kind == AG)//无向图
{
LinkNode *p;
LinkNode *q;
LinkNode *r;
LinkNode *s;
int tail = 0;
int head = 0;
p = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
q = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
s = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
printf("please enter the tail:");
scanf("%d", &tail);
printf("please enter the head:");
scanf("%d", &head);
if (tail < G->vexnum && head < G->vexnum)
{
p->adjvex = head;
p->info = 0;
p->nextarc = NULL;
r = G->AdjList[tail].firstarc;
p->nextarc = r;
G->AdjList[tail].firstarc = p;
s->adjvex = tail;
s->info = 0;
q = G->AdjList[head].firstarc;
s->nextarc = q;
G->AdjList[head].firstarc = s;
G->AdjList[tail].indegree++;
G->AdjList[head].indegree++;
printf("insert arc success\n");
}
else
{
printf("vertex is not exit.\n");
}
}
else if (G->kind == WDG)//加权有向图
{
LinkNode *p;
LinkNode *r;
int info = 0;
int tail = 0;//弧尾(起点)
int head = 0;//弧头(终点)
p = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
printf("please enter the tail:");
scanf("%d", &tail);
printf("please enter the head:");
scanf("%d", &head);
printf("please enter the information:");
scanf("%d", &info);
if (tail < G->vexnum && head < G->vexnum)
{
p->adjvex = head;
p->nextarc = NULL;
p->info = info;
r = G->AdjList[tail].firstarc;
p->nextarc = r;
G->AdjList[tail].firstarc = p;
G->AdjList[tail].indegree++;
printf("insert arc success\n");
}
else
{
printf("vertex is not exit.\n");
}
}
else if(G->kind == WAG)//加权无向图
{
LinkNode *p;
LinkNode *q;
LinkNode *r;
LinkNode *s;
int info = 0;
int tail = 0;
int head = 0;
p = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
q = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
s = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
printf("please enter the tail:");
scanf("%d", &tail);
printf("please enter the head:");
scanf("%d", &head);
printf("please enter the information:");
scanf("%d", &info);
if (tail < G->vexnum && head < G->vexnum)
{
p->adjvex = head;
p->nextarc = NULL;
p->info = info;
r = G->AdjList[tail].firstarc;
p->nextarc = r;
G->AdjList[tail].firstarc = p;
s->adjvex = tail;
s->info = info;
q = G->AdjList[head].firstarc;
s->nextarc = q;
G->AdjList[head].firstarc = s;
G->AdjList[tail].indegree++;
G->AdjList[head].indegree++;
printf("insert arc success\n");
}
else
{
printf("vertex is not exit.\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("The type of the graph is error\n");
}
}图的深度优先遍历
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
1730403 查看本文章


void DFSTraverse(ALGraph *G, int v, int visit[]) {
LinkNode *p;
if (visit[v] == 0)
{
printf("%c\n", G->AdjList[v].data);
visit[v] = 1;
p = G->AdjList[v].firstarc;
while (p != NULL)
{
if (visit[p->adjvex] == 0)
{
DFSTraverse(G, p->adjvex, visit);
}
p = p->nextarc;
}
}
}图的广度优先遍历
void BFSTraverse(ALGraph *G){
int i = 0;//循环变量
int k = 0;//循环变量
SqQueue Q = Creat_SqQueue();
//visited为访问标志数组,为0则该节点没被访问过,为1则被访问过
int visited[MAX_VEX];
LinkNode *p;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_VEX; i++)//访问标志初始化
{
visited[i] = 0;
}
//广度优先遍历图
for (k = 0; k < G->vexnum; k++)
{
if (visited[k] == 0)//若该节点没有被访问过
{
InsertQueue(&Q, k);
visited[k] = 1;
if (G->AdjList[k].firstarc != NULL)
{
p = G->AdjList[k].firstarc;
while (p != NULL)
{
if(visited[p->adjvex] == 0)
{
InsertQueue(&Q, p->adjvex);
visited[p->adjvex] = 1;
}
p = p->nextarc;
}
}
}
else//若该节点被访问过
{
if (G->AdjList[k].firstarc != NULL)
{
p = G->AdjList[k].firstarc;
while (p != NULL)
{
if(visited[p->adjvex] == 0)
{
InsertQueue(&Q, p->adjvex);
visited[p->adjvex] = 1;
}
p = p->nextarc;
}
}
}
}
while (Q.front != Q.rear)//循环弹出队列中的元素
{
printf("%c\n", G->AdjList[DeletaQueue(&Q)].data);
}
}销毁一个图
int DestroyGeaph(ALGraph *G) {
int i = 0;//循环变量
for (i = 0; i < G->vexnum; i++)
{
G->AdjList[i].data = 0;
G->AdjList[i].indegree = 0;
G->AdjList[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
G->vexnum = 0;
return OK;
}以邻接表的形式输出图
void OutPutGraph(ALGraph G)
{
int i = 0;//循环变量
printf("value\tindegree\tfirstarc\n");
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
printf("%c\t", G.AdjList[i].data);
printf("%d\t\t", G.AdjList[i].indegree);
LinkNode *p;
p = G.AdjList[i].firstarc;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("->");
printf("%c \t", G.AdjList[p->adjvex].data);
p = p->nextarc;
}
printf("\n");
printf("----------------------\n");
}
}示例:
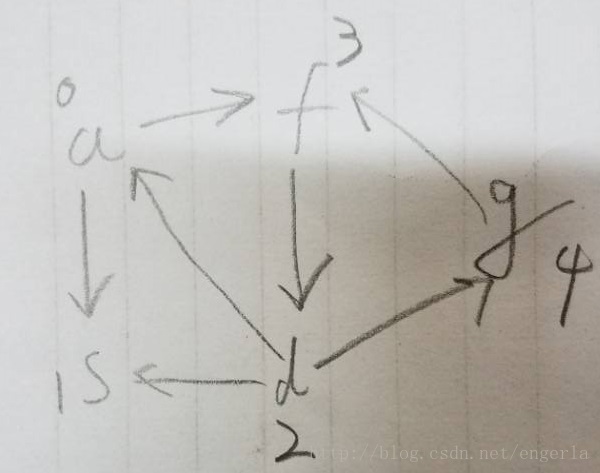
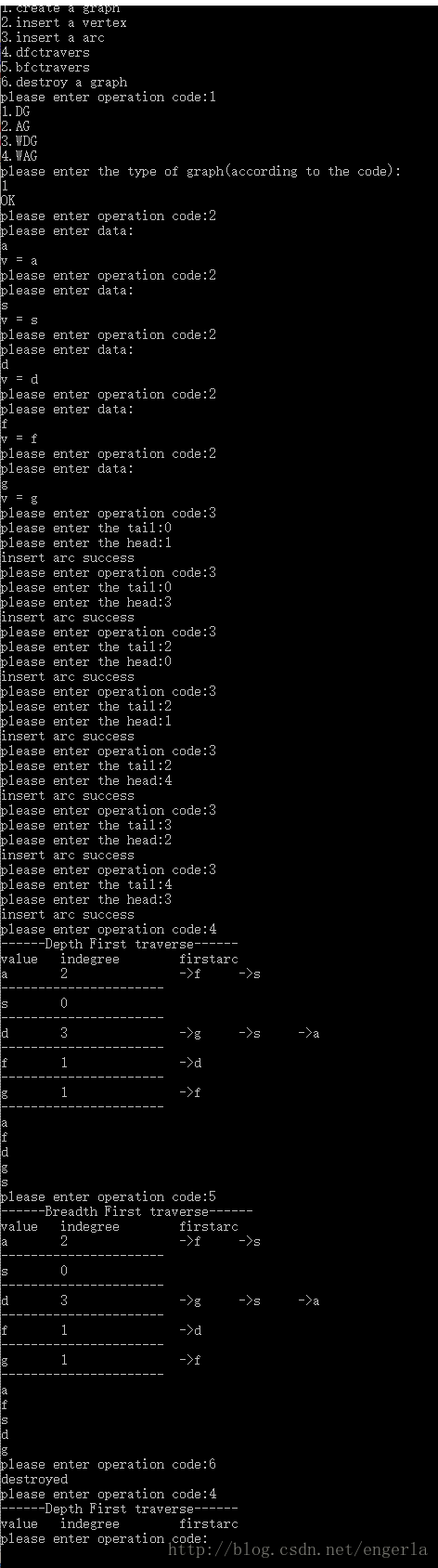
运行结果:
以上就是图的基本操作了,主方法就不写了,大家根据可以自己的需要写,希望大家看了以后能帮得上忙。