一、最短路径问题
【google笔试题】一个环形公路,给出相邻两点的距离(一个数组),求任意两点的最短距离,要求空间复杂度不超过O(N)。
如果从有向图中某一顶点(称为源点)到达另一顶点(称为终点)的路径可能不止一条,如何找到一条路径使得沿此路径上各边上的权值总和达到最小。
最短路径问题是图论研究中的一个经典算法问题,旨在寻找图(由结点和路径组成的)中两结点之间的最短路径。算法具体的形式包括:
- 确定起点的最短路径问题- 即已知起始结点,求最短路径的问题。适合使用Dijkstra算法。
- 确定终点的最短路径问题- 与确定起点的问题相反,该问题是已知终结结点,求最短路径的问题。在无向图中该问题与确定起点的问题完全等同,在有向图中该问题等同于把所有路径方向反转的确定起点的问题。
- 确定起点终点的最短路径问题- 即已知起点和终点,求两结点之间的最短路径。
- 全局最短路径问题- 求图中所有的最短路径。适合使用Floyd-Warshall算法 。
解决最短路的问题有以下算法,Dijkstra算法,Bellman-Ford算法,Floyd算法和SPFA算法等。
二、邻接矩阵和邻接表的比较?
图的存储结构主要分两种,一种是邻接矩阵,一种是邻接表。
图的邻接矩阵存储方式是用两个数组来表示图。一个一维数组存储图中顶点信息,一个二维数组(邻接矩阵)存储图中的边或弧的信息。
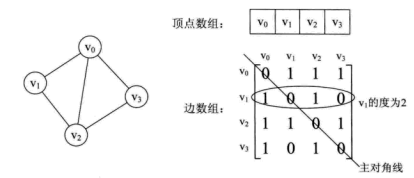
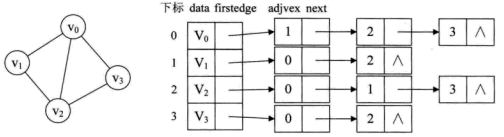
邻接表是数组与链表相结合的存储方法。
对于带权值的网图,可以在边表结点定义中再增加一个weight的数据域,存储权值信息即可。如下图所示。
邻接表的处理方法是这样的:
- 图中顶点用一个一维数组存储,当然,顶点也可以用单链表来存储,不过,数组可以较容易的读取顶点的信息,更加方便。
- 图中每个顶点vi的所有邻接点构成一个线性表,由于邻接点的个数不定,所以,用单链表存储,无向图称为顶点vi的边表,有向图则称为顶点vi作为弧尾的出边表。
三、Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法-解决单源最短路径
1.定义
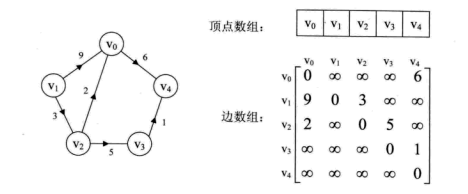
Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法是典型的单源最短路径算法,用于计算一个节点到其他所有节点的最短路径。主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。Dijkstra算法是很有代表性的最短路径算法,在很多专业课程中都作为基本内容有详细的介绍,如数据结构,图论,运筹学等等。举例来说,如果图中的顶点表示城市,而边上的权重表示著城市间开车行经的距离,该算法可以用来找到两个城市之间的最短路径。
2.基本思想
每次找到离源点(如1号结点)最近的一个顶点,然后以该顶点为中心进行扩展,最终得到源点到其余所有点的最短路径。
3.基本步骤
- 设置标记数组book[]:将所有的顶点分为两部分,已知最短路径的顶点集合P和未知最短路径的顶点集合Q,很显然最开始集合P只有源点一个顶点。book[i]为1表示在集合P中;
- 设置最短路径数组dst[]并不断更新:初始状态下,令dst[i] = edge[s][i](s为源点,edge为邻接矩阵),很显然此时dst[s]=0,book[s]=1。此时,在集合Q中可选择一个离源点s最近的顶点u加入到P中。并依据以u为新的中心点,对每一条边进行松弛操作(松弛是指由结点s-->j的途中可以经过点u,并令dst[j]=min{dst[j], dst[u]+edge[u][j]}),并令book[u]=1;
- 在集合Q中再次选择一个离源点s最近的顶点v加入到P中。并依据v为新的中心点,对每一条边进行松弛操作(即dst[j]=min{dst[j], dst[v]+edge[v][j]}),并令book[v]=1;
- 重复3,直至集合Q为空。
4.图示

5.代码
代码来自于书《Data Structure & Algorithm in JAVA》
-
// path.java -
// demonstrates shortest path with weighted, directed graphs -
// to run this program: C>java PathApp -
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// -
class DistPar // distance and parent -
{ // items stored in sPath array -
public int distance; // distance from start to this vertex -
public int parentVert; // current parent of this vertex -
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
public DistPar(int pv, int d) // constructor -
{ -
distance = d; -
parentVert = pv; -
} -
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
} // end class DistPar -
-
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// -
class Vertex { -
public char label; // label (e.g. 'A') -
public boolean isInTree; -
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
public Vertex(char lab) // constructor -
{ -
label = lab; -
isInTree = false; -
} -
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
} // end class Vertex -
-
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// -
class Graph { -
private final int MAX_VERTS = 20; -
private final int INFINITY = 1000000; -
private Vertex vertexList[]; // list of vertices -
private int adjMat[][]; // adjacency matrix -
private int nVerts; // current number of vertices -
private int nTree; // number of verts in tree -
private DistPar sPath[]; // array for shortest-path data -
private int currentVert; // current vertex -
private int startToCurrent; // distance to currentVert -
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
public Graph() // constructor -
{ -
vertexList = new Vertex[MAX_VERTS]; -
// adjacency matrix -
adjMat = new int[MAX_VERTS][MAX_VERTS]; -
nVerts = 0; -
nTree = 0; -
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_VERTS; j++) // set adjacency -
for (int k = 0; k < MAX_VERTS; k++) // matrix -
adjMat[j][k] = INFINITY; // to infinity -
sPath = new DistPar[MAX_VERTS]; // shortest paths -
} // end constructor -
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
public void addVertex(char lab) { -
vertexList[nVerts++] = new Vertex(lab); -
} -
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
public void addEdge(int start, int end, int weight) { -
adjMat[start][end] = weight; // (directed) -
} -
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
// find all shortest paths -
public void path() { -
//step1 initial -
int startTree = 0; // start at vertex 0 -
vertexList[startTree].isInTree = true; //isInTree records whether the vertex's visited -
nTree = 1; //record how many vertices has been visited -
-
// transfer row of distances from adjMat to sPath -
for (int j = 0; j < nVerts; j++) { -
int tempDist = adjMat[startTree][j]; -
sPath[j] = new DistPar(startTree, tempDist); //sPath is the note, here represent as an array -
} -
-
while (nTree < nVerts) { //base case: until all vertices are in the tree -
//step2 get minimum from sPath -
int indexMin = getMin(); -
int minDist = sPath[indexMin].distance; -
-
//special case: if all infinite or in tree,sPath is complete -
if (minDist == INFINITY) { -
System.out.println("There are unreachable vertices"); -
break; -
} else { // reset currentVert -
currentVert = indexMin; // to closest vert -
// minimum distance from startTree is to currentVert, and is startToCurrent -
startToCurrent = sPath[indexMin].distance; -
} -
// put current vertex in tree -
vertexList[currentVert].isInTree = true; -
nTree++; -
-
//step3 update path -
updatePath(); // update sPath[] array -
} // end while(nTree<nVerts) -
-
//step4 printout all shortest path -
displayPaths(); // display sPath[] contents -
-
nTree = 0; // clear tree -
for (int j = 0; j < nVerts; j++) -
vertexList[j].isInTree = false; -
} // end path() -
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
public int getMin() // get entry from sPath -
{ // with minimum distance -
int minDist = INFINITY; // assume minimum -
int indexMin = 0; -
for (int j = 1; j < nVerts; j++) // for each vertex, -
{ // if it's in tree and -
if (!vertexList[j].isInTree && // smaller than old one -
sPath[j].distance < minDist) { -
minDist = sPath[j].distance; -
indexMin = j; // update minimum -
} -
} // end for -
return indexMin; // return index of minimum -
} // end getMin() -
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
public void updatePath() { -
// adjust values in shortest-path array sPath -
int column = 1; // skip starting vertex -
while (column < nVerts) // go across columns -
{ -
// if this column's vertex already in tree, skip it -
if (vertexList[column].isInTree) { -
column++; -
continue; -
} -
// calculate distance for one sPath entry -
// get edge from currentVert to column -
int currentToFringe = adjMat[currentVert][column]; -
// add distance from start -
int startToFringe = startToCurrent + currentToFringe; -
// get distance of current sPath entry -
int sPathDist = sPath[column].distance; -
-
// compare distance from start with sPath entry -
if (startToFringe < sPathDist) // if shorter, -
{ // update sPath -
sPath[column].parentVert = currentVert; -
sPath[column].distance = startToFringe; -
} -
column++; -
} // end while(column < nVerts) -
} // end adjust_sPath() -
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
public void displayPaths() { -
for (int j = 0; j < nVerts; j++) // display contents of sPath[] -
{ -
System.out.print(vertexList[j].label + "="); // B= -
if (sPath[j].distance == INFINITY) -
System.out.print("inf"); // inf -
else -
System.out.print(sPath[j].distance); // 50 -
char parent = vertexList[sPath[j].parentVert].label; -
System.out.print("(" + parent + ") "); // (A) -
} -
System.out.println(""); -
} -
// ------------------------------------------------------------- -
} // end class Graph -
-
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// -
class PathApp { -
public static void main(String[] args) { -
Graph theGraph = new Graph(); -
theGraph.addVertex('A'); // 0 (start) -
theGraph.addVertex('B'); // 1 -
theGraph.addVertex('C'); // 2 -
theGraph.addVertex('D'); // 3 -
theGraph.addVertex('E'); // 4 -
-
theGraph.addEdge(0, 1, 50); // AB 50 -
theGraph.addEdge(0, 3, 80); // AD 80 -
theGraph.addEdge(1, 2, 60); // BC 60 -
theGraph.addEdge(1, 3, 90); // BD 90 -
theGraph.addEdge(2, 4, 40); // CE 40 -
theGraph.addEdge(3, 2, 20); // DC 20 -
theGraph.addEdge(3, 4, 70); // DE 70 -
theGraph.addEdge(4, 1, 50); // EB 50 -
-
System.out.println("Shortest paths"); -
theGraph.path(); // shortest paths -
System.out.println(); -
} // end main() -
} // end class PathApp -
//代码来自于书《Data Structure & Algorithm in JAVA》
四、Floyd(弗洛伊德算法)-解决多源最短路径
1.基本思想
Floyd算法是一个经典的动态规划算法。用通俗的语言来描述的话,首先我们的目标是寻找从点i到点j的最短路径。从动态规划的角度看问题,我们需要为这个目标重新做一个诠释(这个诠释正是动态规划最富创造力的精华所在)。
从任意节点i到任意节点j的最短路径不外乎2种可能,一是直接从i到j,二是从i经过若干个节点k到j。所以,我们假设Dis(i,j)为节点u到节点v的最短路径的距离,对于每一个节点k,我们检查Dis(i,k) + Dis(k,j) < Dis(i,j)是否成立,如果成立,证明从i到k再到j的路径比i直接到j的路径短,我们便设置Dis(i,j) = Dis(i,k) + Dis(k,j),这样一来,当我们遍历完所有节点k,Dis(i,j)中记录的便是i到j的最短路径的距离。
2.基本步骤
- 首先把初始化距离dist数组为图的邻接矩阵,路径数组path初始化为-1。其中对于邻接矩阵中的数首先初始化为正无穷,如果两个顶点存在边则初始化为权重
- 对于每一对顶点 u 和 v,看看是否存在一个顶点 w 使得从 u 到 w 再到 v 比己知的路径更短。如果是就更新它。状态转移方程为
- 如果 dist[i][k]+dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]
- 则dist[i][j] = dist[i][k]+dist[k][j]
3.代码
-
//Floyd算法(多源最短路径算法) -
bool Floyd(){ -
for(int k = 1 ; k < this->Nv+1 ; k++){ //k代表中间顶点 -
for(int i = 1 ; i < this->Nv+1 ; i++){//i代表起始顶点 -
for(int j = 1 ; j < this->Nv+1 ; j++){//j代表终点 -
if(this->dist[i][k] + this->dist[k][j] < this->dist[i][j]){ -
this->dist[i][j] = this->dist[i][k] + this->dist[k][j]; -
if(i == j && this->dist[i][j] < 0){//发现了负值圈 -
return false; -
} -
this->path[i][j] = k; -
} -
} -
} -
} -
return true; -
}
五、Floyd-Warshall算法(动态规划)
是解决任意两点间的最短路径的一种算法,时间复杂度为O(N^3),空间复杂度为O(N^2)。可以正确处理有向图或负权的最短路径问题。
设 dist(i,j) 为从节点i到节点j的最短距离若最短路径经过点k,则dist(i,j)=dist(i,k) + dist(k,j),将该路径与先前的dist(i,j)比较获取最小值,即dist(i,j)=min( dist(i,k) + dist(k,j) ,dist(i,j) )。
Floyd-Warshall算法的描述如下:
-
//根据图的邻接矩阵,或邻接链表,初始化dist(i,j) -
//其中dist(i,j)表示由点i到点j的代价,当dist(i,j)为 inf 表示两点之间没有任何连接。 -
For i←1 to n do -
For j←1 to n do -
dist(i,j) = weight(i,j) -
//计算最短路径 -
for k ← 1 to n do -
for i ← 1 to n do -
for j ← 1 to n do -
if (dist(i,k) + dist(k,j) < dist(i,j)) then // 是否是更短的路径? -
dist(i,j) = dist(i,k) + dist(k,j)
六、Bellman-Ford(动态规划)
求单源最短路,可以判断有无负权回路(若有,则不存在最短路),时效性较好,时间复杂度O(VE)。
step1:初始化dist(i),除了初始点的值为0,其余都为infinit(表示无穷大,不可到达),pred表示经过的前一个顶点
step2:执行n-1(n等于图中点的个数)次松弛计算:dist(j)=min( dist(i)+weight(i,j),dist(j) )
step3:再重复操作一次,如国dist(j) > distdist(i)+weight(i,j)表示途中存在从源点可达的权为负的回路。
因为,如果存在从源点可达的权为负的回路,则应为无法收敛而导致不能求出最短路径。
因为负权环可以无限制的降低总花费,所以如果发现第n次操作仍可降低花销,就一定存在负权环。
-
int[] dist=new int[n]; -
int[] pre=new int[n]; -
-
public void Bellman_Ford(){ -
//初始化 -
for(int i=1;i<n-1;i++){ -
dist[i]=infinit; //TODO -
}//end for -
-
dist[s]=0 //起始点的值 -
-
for (int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){ -
for(int j=1;j<=edgenum; j++){ -
if(dist(i)+weight(i,j) <dist(j) ){ -
dist(j)=dist(i)+weight(i,j); -
pred(j)=i; -
}//end if -
}//end for -
}//end for -
-
// -
for(int j=1;j<=edgenum;j++){ -
if(dist(i)+weight(i,j)<dist()j ) -
return "有负权回路,不存在最短路径"; -
}//end for -
-
}//end Bellman_Ford()
七、总结
- Dijkstra最短路径算法是基于递推的思想设计的未达顶点的最短路径一定是由已达顶点的最短路径求出。
- Floyd最短路径算法只是Dijkstra最短路径算法的加强,其本质还是递推。
- Dijkstra求单源、无负权的最短路。时效性较好,时间复杂度为O(V*V+E)。
- Floyd求多源、无负权边的最短路。用矩阵记录图。时效性较差,时间复杂度O(V^3)。
- Bellman-Ford求单源最短路,可以判断有无负权回路(若有,则不存在最短路),时效性较好,时间复杂度O(VE)。
-
SPFA是Bellman-Ford的队列优化,时效性相对好,时间复杂度O(kE)。(k<<V)。
我的微信公众号:架构真经(id:gentoo666),分享Java干货,高并发编程,热门技术教程,微服务及分布式技术,架构设计,区块链技术,人工智能,大数据,Java面试题,以及前沿热门资讯等。每日更新哦!

参考资料: