边学习边笔记
https://www.cnblogs.com/felixwang2/p/9190602.html

1 # https://www.cnblogs.com/felixwang2/p/9190602.html 2 # TensorFlow(十):卷积神经网络实现手写数字识别以及可视化 3 4 import tensorflow as tf 5 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data 6 7 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True) 8 9 # 每个批次的大小 10 batch_size = 100 11 # 计算一共有多少个批次 12 n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size 13 14 15 # 参数概要 16 def variable_summaries(var): 17 with tf.name_scope('summaries'): 18 mean = tf.reduce_mean(var) 19 tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean) # 平均值 20 with tf.name_scope('stddev'): 21 stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean))) 22 tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev) # 标准差 23 tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var)) # 最大值 24 tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var)) # 最小值 25 tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var) # 直方图 26 27 28 # 初始化权值 29 def weight_variable(shape, name): 30 initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) # 生成一个截断的正态分布 31 return tf.Variable(initial, name=name) 32 33 34 # 初始化偏置 35 def bias_variable(shape, name): 36 initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape) 37 return tf.Variable(initial, name=name) 38 39 40 # 卷积层 41 def conv2d(x, W): 42 # x input tensor of shape `[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]` 43 # W filter / kernel tensor of shape [filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels] 44 # `strides[0] = strides[3] = 1`. strides[1]代表x方向的步长,strides[2]代表y方向的步长 45 # padding: A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"` 46 return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') 47 48 49 # 池化层 50 def max_pool_2x2(x): 51 # ksize [1,x,y,1] 52 return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') 53 54 55 # 命名空间 56 with tf.name_scope('input'): 57 # 定义两个placeholder 58 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784], name='x-input') 59 y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10], name='y-input') 60 with tf.name_scope('x_image'): 61 # 改变x的格式转为4D的向量[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]` 62 x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1], name='x_image') 63 64 with tf.name_scope('Conv1'): 65 # 初始化第一个卷积层的权值和偏置 66 with tf.name_scope('W_conv1'): 67 W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32], name='W_conv1') # 5*5的采样窗口,32个卷积核从1个平面抽取特征 68 with tf.name_scope('b_conv1'): 69 b_conv1 = bias_variable([32], name='b_conv1') # 每一个卷积核一个偏置值 70 71 # 把x_image和权值向量进行卷积,再加上偏置值,然后应用于relu激活函数 72 with tf.name_scope('conv2d_1'): 73 conv2d_1 = conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1 74 with tf.name_scope('relu'): 75 h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d_1) 76 with tf.name_scope('h_pool1'): 77 h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) # 进行max-pooling 78 79 with tf.name_scope('Conv2'): 80 # 初始化第二个卷积层的权值和偏置 81 with tf.name_scope('W_conv2'): 82 W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64], name='W_conv2') # 5*5的采样窗口,64个卷积核从32个平面抽取特征 83 with tf.name_scope('b_conv2'): 84 b_conv2 = bias_variable([64], name='b_conv2') # 每一个卷积核一个偏置值 85 86 # 把h_pool1和权值向量进行卷积,再加上偏置值,然后应用于relu激活函数 87 with tf.name_scope('conv2d_2'): 88 conv2d_2 = conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2 89 with tf.name_scope('relu'): 90 h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d_2) 91 with tf.name_scope('h_pool2'): 92 h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) # 进行max-pooling 93 94 # 28*28的图片第一次卷积后还是28*28,第一次池化后变为14*14 95 # 第二次卷积后为14*14,第二次池化后变为了7*7 96 # 经过上面操作后得到64张7*7的平面 97 98 with tf.name_scope('fc1'): 99 # 初始化第一个全连接层的权值 100 with tf.name_scope('W_fc1'): 101 W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024], name='W_fc1') # 上一场有7*7*64个神经元,全连接层有1024个神经元 102 with tf.name_scope('b_fc1'): 103 b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024], name='b_fc1') # 1024个节点 104 105 # 把池化层2的输出扁平化为1维 106 with tf.name_scope('h_pool2_flat'): 107 h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64], name='h_pool2_flat') 108 # 求第一个全连接层的输出 109 with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b1'): 110 wx_plus_b1 = tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1 111 with tf.name_scope('relu'): 112 h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(wx_plus_b1) 113 114 # keep_prob用来表示神经元的输出概率 115 with tf.name_scope('keep_prob'): 116 keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name='keep_prob') 117 with tf.name_scope('h_fc1_drop'): 118 h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob, name='h_fc1_drop') 119 120 with tf.name_scope('fc2'): 121 # 初始化第二个全连接层 122 with tf.name_scope('W_fc2'): 123 W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10], name='W_fc2') 124 with tf.name_scope('b_fc2'): 125 b_fc2 = bias_variable([10], name='b_fc2') 126 with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b2'): 127 wx_plus_b2 = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2 128 with tf.name_scope('softmax'): 129 # 计算输出 130 prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b2) 131 132 # 交叉熵代价函数 133 with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy'): 134 cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(labels=y, logits=prediction), 135 name='cross_entropy') 136 tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy', cross_entropy) 137 138 # 使用AdamOptimizer进行优化 139 with tf.name_scope('train'): 140 train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) 141 142 # 求准确率 143 with tf.name_scope('accuracy'): 144 with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'): 145 # 结果存放在一个布尔列表中 146 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1)) # argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置 147 with tf.name_scope('accuracy'): 148 # 求准确率 149 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) 150 tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy) 151 152 # 合并所有的summary 153 merged = tf.summary.merge_all() 154 155 gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(allow_growth=True) 156 with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)) as sess: 157 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) 158 train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/train', sess.graph) 159 test_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/test', sess.graph) 160 for i in range(1001): 161 # 训练模型 162 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) 163 sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keep_prob: 0.5}) 164 # 记录训练集计算的参数 165 summary = sess.run(merged, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keep_prob: 1.0}) 166 train_writer.add_summary(summary, i) 167 # 记录测试集计算的参数 168 batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.test.next_batch(batch_size) 169 summary = sess.run(merged, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys, keep_prob: 1.0}) 170 test_writer.add_summary(summary, i) 171 172 if i % 100 == 0: 173 test_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels, keep_prob: 1.0}) 174 train_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.train.images[:10000], y: mnist.train.labels[:10000], 175 keep_prob: 1.0}) 176 print("Iter " + str(i) + ", Testing Accuracy= " + str(test_acc) + ", Training Accuracy= " + str(train_acc))
应该是随便在某个路径下,右键,打开powershell窗口,输入如下命令:
tensorboard --logdir=F:\document\PyCharm\temp\logs
之后会在窗口输出:
TensorBoard 1.10.0 at http://KOTIN:6006 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
然后在浏览器输入
http://KOTIN:6006
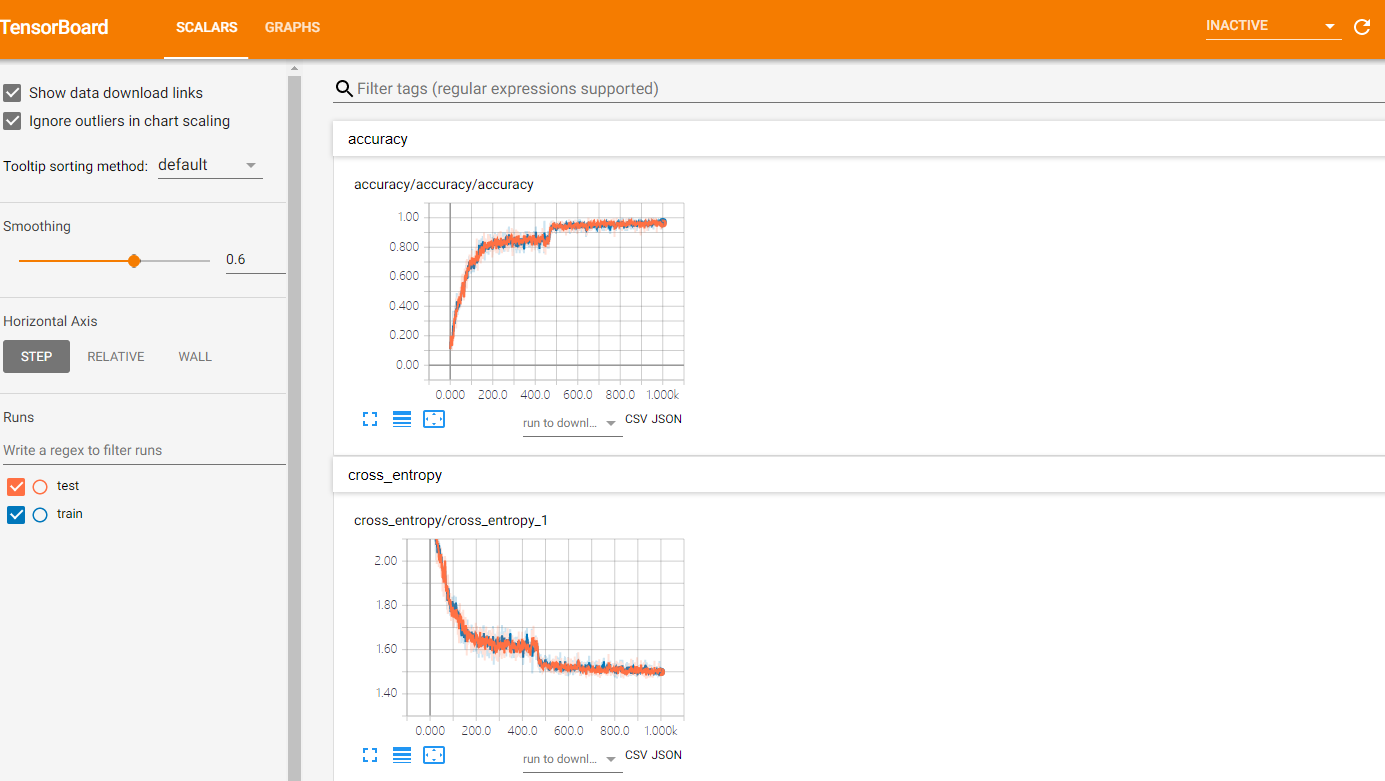
就可以进入tensorboard查看参数的可视化信息: