高速公路题解
我们看一看题,就知道概率是是区间内所有线段的权值和/线段个数。
那么,我们需要动态维护区间的数据结构,
很容易想到线段树,
考虑,如何将两个区间合并:
注:以下线段树上的每个点的\(sum\)在代码中为\(sum2\),仅为方便理解。
不妨设每个区间\([l,r]\)内的所有线段权值和为\(w\),\([l,r]\)的线段权值为\(sum\),左端点为\(l\)的所有线段权值和为\(lw\),右端点为\(r\)的所有线段的权值和为\(rw\),懒标记为\(lazy\),区间长度为\(lenx=r-l+1\)
假如此区间为\(x\),左区间为\(lc\),右区间为\(rc\):
\(x\)的\(w\)除去由\(lc,rc\)各自区间内部的\(w\)外,
还由经过左右两个区间的线段构成,
画图理解一下:
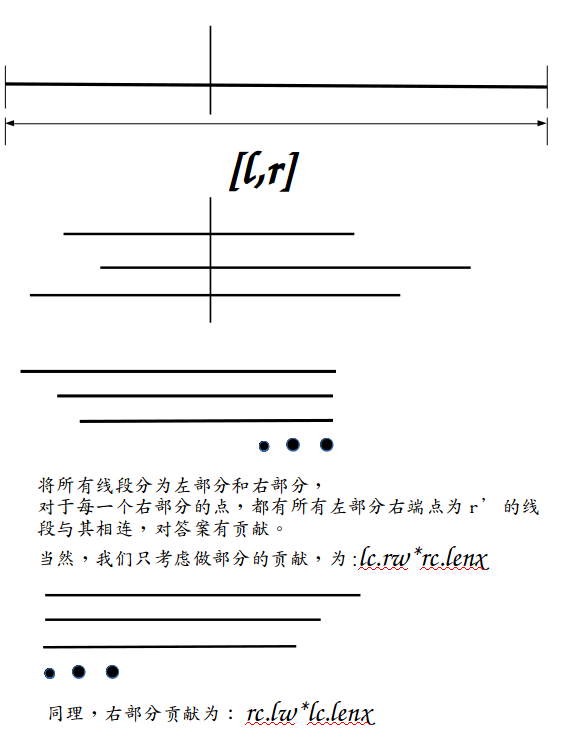
然后第二个问题来了,如何维护\(lw,rw\)?

至于\(sum,lazy\)还用说吗? 线段树模板啊!
xd pushup(xd u,xd v){
xd ans; int len=u.lenx+v.lenx;
ans.lw=u.lw+v.lw+v.lenx*u.sum2,ans.rw=u.rw+v.rw+u.lenx*v.sum2,ans.lazy=0;
ans.w=u.w+v.w+u.lenx*v.lw+v.lenx*u.rw,ans.sum2=u.sum2+v.sum2,ans.lenx=len;
return ans;
}再想想下传标记:
对于每个\(x\)的\(w\),所有线段都加了线段长度\(*lazy[x]\);
设\(sum[len]\)为长度为\(len\)的区间所有线段的长度和。
由\(l-1\)每增加一个长度,则每个长度的线段都有一个,即为:\(\sum_{i=1}^{l}=/frac{(l+1)*l}{2}\)
递推即可。
for(ll i=1;i<=n;++i) sum[i]=sum[i-1]+i*(i+1)/2;所以:
t[lc].w+=sum[t[lc].lenx]*t[x].lazy,t[rc].w+=sum[t[rc].lenx]*t[x].lazy;对于\(lw\)和\(rw\):
区间\([l,r]\)长度在[1,r-l+1]的线段都有一种:
t[lc].lw+=(t[lc].lenx+1)*t[lc].lenx/2*t[x].lazy,t[lc].rw+=(t[lc].lenx+1)*t[lc].lenx/2*t[x].lazy;
t[rc].lw+=(t[rc].lenx+1)*t[rc].lenx/2*t[x].lazy,t[rc].rw+=(t[rc].lenx+1)*t[rc].lenx/2*t[x].lazy;\(sum,lenx,lazy\)的下传也不讲了。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define lc x<<1
#define rc x<<1|1
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+6;
int n,m,t3;
ll sum[N],o,p,q,t1,t2;
char c[12];
struct xd{ll w,lazy,lw,rw,lenx,sum2;}t[N<<2];
inline int read(){
int T=0,F=1; char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-') F=-1; ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') T=(T<<3)+(T<<1)+(ch-48),ch=getchar();
return F*T;
}
ll gcd(ll u,ll v){return u%v==0?v:gcd(v,u%v);}
void pushdown(int x){
if(t[x].lazy){
t[lc].lazy+=t[x].lazy,t[rc].lazy+=t[x].lazy;
t[lc].w+=sum[t[lc].lenx]*t[x].lazy,t[rc].w+=sum[t[rc].lenx]*t[x].lazy;
t[lc].lw+=(t[lc].lenx+1)*t[lc].lenx/2*t[x].lazy,t[lc].rw+=(t[lc].lenx+1)*t[lc].lenx/2*t[x].lazy;
t[rc].lw+=(t[rc].lenx+1)*t[rc].lenx/2*t[x].lazy,t[rc].rw+=(t[rc].lenx+1)*t[rc].lenx/2*t[x].lazy;
t[lc].sum2+=t[lc].lenx*t[x].lazy,t[rc].sum2+=t[rc].lenx*t[x].lazy;
t[x].lazy=0;
}
}
xd pushup(xd u,xd v){
xd ans; int len=u.lenx+v.lenx;
ans.lw=u.lw+v.lw+v.lenx*u.sum2,ans.rw=u.rw+v.rw+u.lenx*v.sum2,ans.lazy=0;
ans.w=u.w+v.w+u.lenx*v.lw+v.lenx*u.rw,ans.sum2=u.sum2+v.sum2,ans.lenx=len;
return ans;
}
void build(int l,int r,int x){
t[x].lenx=r-l+1;
if(l==r) return;
int mid=l+r>>1;
build(l,mid,lc),build(mid+1,r,rc);
}
void update(ll l,ll r,int p,int q,int x,ll y){
if(p<=l&&r<=q){t[x].lazy+=y,t[x].w+=sum[r-l+1]*y,t[x].lw+=(r-l+1)*(r-l+2)/2*y,t[x].rw+=(r-l+1)*(r-l+2)/2*y,t[x].sum2+=(r-l+1)*y; return;}
pushdown(x); int mid=l+r>>1;
if(p<=mid) update(l,mid,p,q,lc,y);
if(q>mid) update(mid+1,r,p,q,rc,y);
t[x]=pushup(t[lc],t[rc]);
}
xd query(int l,int r,int p,int q,int x){
if(p<=l&&r<=q){return t[x];}
pushdown(x); int mid=l+r>>1; xd ans;
if(q<=mid) ans=query(l,mid,p,q,lc);
else if(p>mid) ans=query(mid+1,r,p,q,rc);
else ans=pushup(query(l,mid,p,q,lc),query(mid+1,r,p,q,rc));
return ans;
}
int main(){
n=read(),m=read(),--n;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;++i) sum[i]=sum[i-1]+i*(i+1)/2;
build(1,n,1);
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){
scanf("%s",c); t1=read(),t2=read()-1;
if(c[0]=='C') t3=read(),update(1,n,t1,t2,1,t3);
else{
o=(t2-t1+1)*(t2-t1+2)/2,p=query(1,n,t1,t2,1).w;
if(p) q=gcd(o,p),o/=q,p/=q;
else o=1;
printf("%lld/%lld\n",p,o);
}
}
return 0;
}