资源
完全参照 享元模式|菜鸟教程 ,但不包括IOS代码
享元模式
享元模式(Flyweight Pattern)主要用于减少创建对象的数量,以减少内存占用和提高性能。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它提供了减少对象数量从而改善应用所需的对象结构的方式。
享元模式尝试重用现有的同类对象,如果未找到匹配的对象,则创建新对象。我们将通过创建 5 个对象来画出 20 个分布于不同位置的圆来演示这种模式。由于只有 5 种可用的颜色,所以 color 属性被用来检查现有的 Circle 对象。
介绍
意图: 运用共享技术有效地支持大量细粒度的对象。
主要解决: 在有大量对象时,有可能会造成内存溢出,我们把其中共同的部分抽象出来,如果有相同的业务请求,直接返回在内存中已有的对象,避免重新创建。
何时使用:
1、系统中有大量对象。
2、这些对象消耗大量内存。
3、这些对象的状态大部分可以外部化。
4、这些对象可以按照内蕴状态分为很多组,当把外蕴对象从对象中剔除出来时,每一组对象都可以用一个对象来代替。
5、系统不依赖于这些对象身份,这些对象是不可分辨的。
如何解决: 用唯一标识码判断,如果在内存中有,则返回这个唯一标识码所标识的对象。
关键代码: 用 HashMap 存储这些对象。
应用实例:
1、JAVA 中的 String,如果有则返回,如果没有则创建一个字符串保存在字符串缓存池里面。
2、数据库的数据池。
优点: 大大减少对象的创建,降低系统的内存,使效率提高。
缺点: 提高了系统的复杂度,需要分离出外部状态和内部状态,而且外部状态具有固有化的性质,不应该随着内部状态的变化而变化,否则会造成系统的混乱。
使用场景:
1、系统有大量相似对象。
2、需要缓冲池的场景。
注意事项:
1、注意划分外部状态和内部状态,否则可能会引起线程安全问题。
2、这些类必须有一个工厂对象加以控制。
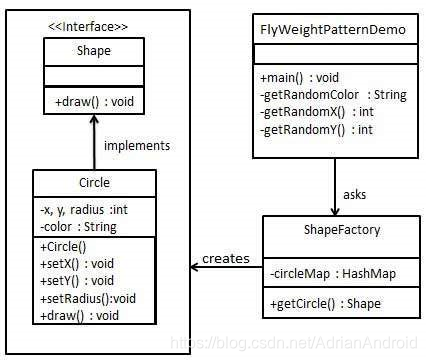
Android
Shape.java
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
Circle.java
public class Circle implements Shape {
private String color;
private int x;
private int y;
private int radius;
public Circle(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public void setRadius(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Circle: Draw() [Color : " + color
+", x : " + x +", y :" + y +", radius :" + radius);
}
}
ShapeFactory.java
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ShapeFactory {
private static final HashMap<String, Shape> circleMap = new HashMap<>();
public static Shape getCircle(String color) {
Circle circle = (Circle)circleMap.get(color);
if(circle == null) {
circle = new Circle(color);
circleMap.put(color, circle);
System.out.println("Creating circle of color : " + color);
}
return circle;
}
}
FlyweightPatternDemo.java
public class FlyweightPatternDemo {
private static final String colors[] =
{ "Red", "Green", "Blue", "White", "Black" };
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0; i < 20; ++i) {
Circle circle =
(Circle)ShapeFactory.getCircle(getRandomColor());
circle.setX(getRandomX());
circle.setY(getRandomY());
circle.setRadius(100);
circle.draw();
}
}
private static String getRandomColor() {
return colors[(int)(Math.random()*colors.length)];
}
private static int getRandomX() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100 );
}
private static int getRandomY() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100);
}
}
结果
Creating circle of color : Black
Circle: Draw() [Color : Black, x : 36, y :71, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Green
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 27, y :27, radius :100
Creating circle of color : White
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 64, y :10, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Red
Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 15, y :44, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 19, y :10, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 94, y :32, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 69, y :98, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Blue
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 13, y :4, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 21, y :21, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 55, y :86, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 90, y :70, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 78, y :3, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 64, y :89, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 3, y :91, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 62, y :82, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 97, y :61, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 86, y :12, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 38, y :93, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 76, y :82, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 95, y :82, radius :100
IOS
Shape.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@protocol Shape <NSObject>
-(void)draw;
@end
@interface Circle : NSObject <Shape>
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *color;
@property (nonatomic, assign) int x;
@property (nonatomic, assign) int y;
@property (nonatomic, assign) int radius;
-(instancetype)initWithColor:(NSString*)color;
@end
Shape.m
#import "Shape.h"
@implementation Circle
- (instancetype)initWithColor:(NSString *)color{
if(self = [super init]) {
self.color = color;
}
return self;
}
- (void)draw{
NSLog(@"Circle: Draw() [Color : %@, x : %d, y : %d, radius : %d", self.color, self.x, self.y, self.radius);
}
@end
ShapeFactory.h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Shape.h"
@interface ShapeFactory : NSObject
+(id<Shape>)getCircle:(NSString*) color;
@end
ShapeFactory.m
#import "ShapeFactory.h"
@implementation ShapeFactory
+ (id<Shape>)getCircle:(NSString *)color{
static NSMutableDictionary *dict;
if(dict == nil) {
dict = [[NSMutableDictionary alloc]init];
}
Circle *circle = [dict objectForKey:color];
if(circle == nil) {
circle = [[Circle alloc]initWithColor:color];
[dict setObject:circle forKey:color];
NSLog(@"Creating circle of color : %@" , color);
}
return circle;
}
@end
ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
NSArray *array = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:@"Red", @"Green", @"Blue", @"White", @"Black" ,nil];
for (int i=0; i < 20; ++i) {
NSString *key = [array objectAtIndex:arc4random()%5];
Circle *circle = [ShapeFactory getCircle:key];
[circle setX:arc4random() % 100];
[circle setY:arc4random() % 100];
[circle setRadius:100];
[circle draw];
}
}