Problem Description
Benny has a spacious farm land to irrigate. The farm land is a rectangle, and is divided into a lot of samll squares. Water pipes are placed in these squares. Different square has a different type of pipe. There are 11 types of pipes, which is marked from A to K, as Figure 1 shows.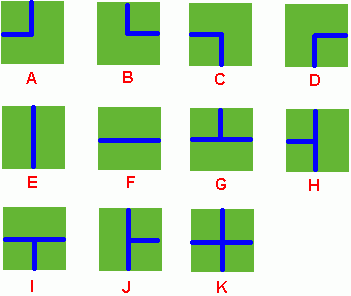
Benny has a map of his farm, which is an array of marks denoting the distribution of water pipes over the whole farm. For example, if he has a map
ADC
FJK
IHE
then the water pipes are distributed like
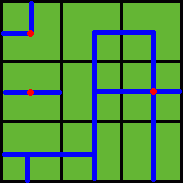
Several wellsprings are found in the center of some squares, so water can flow along the pipes from one square to another. If water flow crosses one square, the whole farm land in this square is irrigated and will have a good harvest in autumn.
Now Benny wants to know at least how many wellsprings should be found to have the whole farm land irrigated. Can you help him?
Note: In the above example, at least 3 wellsprings are needed, as those red points in Figure 2 show.
Input
There are several test cases! In each test case, the first line contains 2 integers M and N, then M lines follow. In each of these lines, there are N characters, in the range of 'A' to 'K', denoting the type of water pipe over the corresponding square. A negative M or N denotes the end of input, else you can assume 1 <= M, N <= 50.
Output
For each test case, output in one line the least number of wellsprings needed.
Sample Input
2 2 DK HF 3 3 ADC FJK IHE -1 -1
Sample Output
2 3
代码如下:
大佬的博客:https://blog.csdn.net/u013480600/article/details/20799843
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=50+5;
int n,m;
int mp[maxn][maxn];
//并查集部分
int fa[maxn*maxn];
int findset(int x){ return fa[x]==-1?x:fa[x]=findset(fa[x]); }
int bind(int u,int v)
{
int fu=findset(u);
int fv=findset(v);
if(fu!=fv)
{
fa[fu]=fv;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
//原始矩形的连通情况
int con[11][4]={
{1,0,1,0},//A块的上下左右
{1,0,0,1},//B
{0,1,1,0},//C
{0,1,0,1},//D
{1,1,0,0},//E
{0,0,1,1},//F
{1,0,1,1},//G
{1,1,1,0},//H
{0,1,1,1},//I
{1,1,0,1},//J
{1,1,1,1}//K
};
//往上下左右四个方向移动时,X(行),Y(列)的增量(注意这是对x行,和y行的变化)
int dir_x[]={-1,1,0,0};//上下左右
int dir_y[]={0,0,-1,1};
//通过下面可以发现dir_x和dir_y用了两次,前提是要保证移动的每次方向和原始矩阵的联通情况的方向一一对应。
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)==2 && n>=0 && m>=0)
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
char ch;
scanf(" %c",&ch);
mp[i][j]=ch-'A';
}
memset(fa,-1,sizeof(fa));
int ans=n*m;//原始连通分量数目
//遍历矩阵,合并连通分量
for(int x=0;x<n;x++)//行
for(int y=0;y<m;y++)//列
{
int id=x*m+y;//当前格子的编号
for(int dir=0;dir<4;dir++)//判断dir方向的格子是否连通
{
int nx=x+dir_x[dir];
int ny=y+dir_y[dir];
int ndir=dir%2==0?dir+1:dir-1;//dir的反向
if(nx>=0&&nx<n&&ny>=0&&ny<m)
{
int nid=nx*m+ny;//相邻格子的编号
if(con[mp[x][y]][dir]==1&&con[mp[nx][ny]][ndir]==1)//如果连通
{
ans-=bind(id,nid);
}
}
}
}
//输出结果
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
