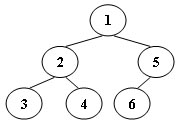
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
代码如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <malloc.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=35;
int n,ci=0;
struct tree
{
int data;
struct tree *left,*right;
};
tree* root;
tree* traverse ()
{
if(ci==n*2)
return NULL;
char s[10];
scanf("%s",s);
if(!strcmp(s,"Push"))
{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
tree* t=(tree*)malloc(sizeof(tree));
t->data=x;
ci++;
t->left=traverse();
ci++;
t->right=traverse ();
return t;
}
else
return NULL;
}
void post (tree* t)
{
if(t==NULL)
return;
post(t->left);
post(t->right);
if(t==root)
printf("%d\n",t->data);
else
printf("%d ",t->data);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
root=traverse();
post(root);
return 0;
}