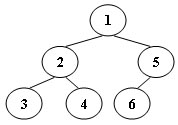
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: “Push X” where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or “Pop” meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
分析
题目大意就是中序非递归遍历需要用到一个栈,给定针对这个栈的操作,就可以唯一确定一个树,我们的任务就是后序遍历这棵树
回忆一下如何利用栈进行中序遍历,首先根入栈,其左结点循环入栈,如果此时栈不空,出栈栈顶结点并输出,再让栈顶结点等于其右子结点,直到整个栈为空且结点为空
所以对于 push 操作要做的事有两种可能:
- 入栈当前结点的左儿子结点
- 入栈当前结点的右儿子结点
好像说了废话,想想非递归遍历的操作,如果左儿子结点一直都有,那么入栈的一直是左儿子结点,只有当左儿子结点已经没有了,才"勉为其难"入栈右儿子结点。
而对于 pop 操作要做的事也有两种可能:
- 当前结点的左儿子结点为空时出栈
- 当前结点的右儿子结点为空时出栈
抱歉又说了废话…其实也不是,每次 push 后第一个 pop 时肯定代表着当前结点的左儿子为空,其后的 pop 代表着当前右儿子为空(想一想为什么?)
大概轮廓有了,剩下的就是细节了,最麻烦的一个就是,如何找到"当前结点"
当 pop 时,出栈的栈顶结点肯定是"当前结点"了,
而当 push 时,入栈的结点肯定是"当前结点"啦
还原出了树用递归实现后序遍历,(毕竟非递归有点麻烦)
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct TreeNode *Tree;
struct TreeNode{
string data;
Tree left; // 左子树
Tree right; // 右子树
};
// 初始化一个树结点
Tree create(){
Tree T;
T = (Tree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
T->left = NULL;
T->right = NULL;
return T;
}
// 根据中序遍历整理出这棵树
Tree restore(Tree T){
int n;
string str;
stack<Tree> s;
Tree node = T;
bool flag = false;
string value;
scanf("%d\n",&n);
// 根节点赋值
getline(cin,str);
value = str.substr(5); // 从第五个开始截取
node->data = value;
// 根结点入栈
s.push(node);
for(int i=1;i<2*n;i++){
getline(cin,str);
if(str=="Pop"){// 如果是 pop 操作
node = s.top();
s.pop();
}else{ // push
value = str.substr(5); // 从第五个开始截取
Tree tmp = create();
tmp->data = value;
if(!node->left){// 如果左儿子空,新结点就是左儿子
node->left = tmp;
node = node->left;
}else if(!node->right){ // 如果右儿子空,新结点就是右儿子
node->right = tmp;
node = node->right;
}
s.push(tmp);
}
}
return T;
}
// 后序递归遍历
void bl(Tree T,bool &flag){
if(T){
bl(T->left,flag);
bl(T->right,flag);
if(!flag)
flag = true;
else
cout<<" ";
cout<<T->data;
}
}
int main(){
Tree T;
bool flag = false;
string str;
T = create();
T = restore(T);
bl(T,flag);
return 0;
}