第三周的课程是目标检测 ,编程作业是以yolo网络为主。编程作业的主要部分是对yolo网络输出进行
anchor boxes过滤、IOU过滤、非极大抑制处理。
理论知识
交并比(Intersection-over-Union,IoU),目标检测中使用的一个概念,是产生的候选框(candidate bound)与原标记框(ground truth bound)的交叠率,即它们的交集与并集的比值。IOU值越大,说明得到的候选框越准确,最理想情况是完全重叠,即比值为1。
IOU
anchor boxes
anchor boxes(候选区域)
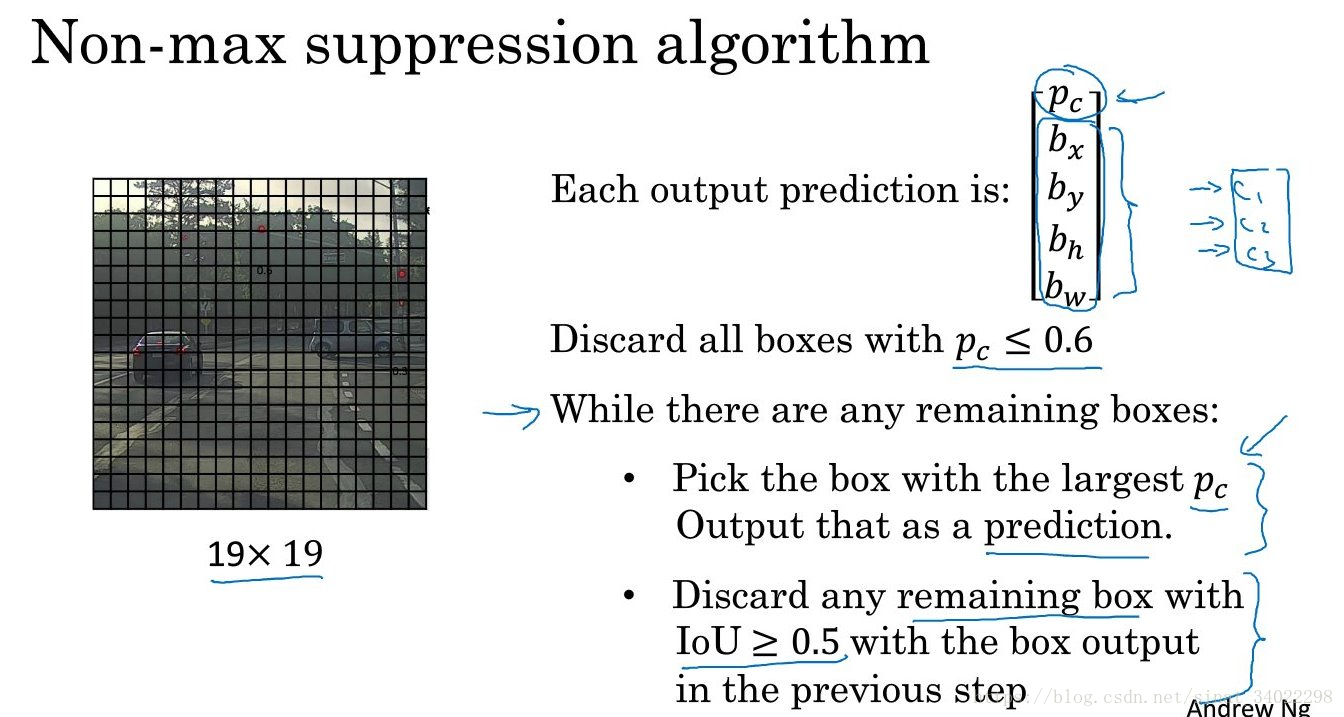
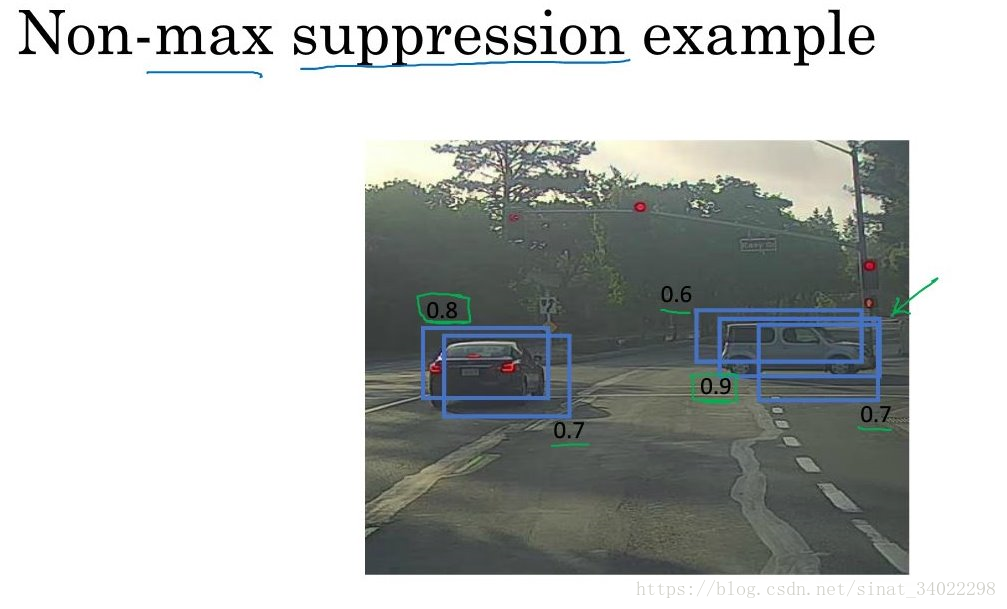
非极大抑制
非极大抑制,在检测的时候可能存在重叠的备选框,对于非极大可能性的被选框进行抛弃。
如果是多目标检测,就进行多次非极大抑制。
从算法中可以看到,做了两步discard:
第一步是对Pc <=0.6 的格子进行discard
第二步是对剩下的格子中,重叠区域 IOU>0.5 的进行非极大discard
程序
pycharm版
原本编程作业是 jupyter notebook ,但是环境没配好,所以这里使用pycharm将程序进行整合、调试。
import argparse
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow
import scipy.io
import scipy.misc
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import PIL
import tensorflow as tf
from keras import backend as K
from keras.layers import Input, Lambda, Conv2D
from keras.models import load_model, Model
from yolo_utils import read_classes, read_anchors, generate_colors, preprocess_image, draw_boxes, scale_boxes
from yad2k.models.keras_yolo import yolo_head, yolo_boxes_to_corners, preprocess_true_boxes, yolo_loss, yolo_body
from keras.utils import plot_model
def yolo_filter_boxes(box_confidence, boxes, box_class_probs, threshold=.6):
"""Filters YOLO boxes by thresholding on object and class confidence.
Arguments:
box_confidence -- tensor of shape (19, 19, 5, 1)
boxes -- tensor of shape (19, 19, 5, 4)
box_class_probs -- tensor of shape (19, 19, 5, 80)
threshold -- real value, if [ highest class probability score < threshold], then get rid of the corresponding box
Returns:
scores -- tensor of shape (None,), containing the class probability score for selected boxes
boxes -- tensor of shape (None, 4), containing (b_x, b_y, b_h, b_w) coordinates of selected boxes
classes -- tensor of shape (None,), containing the index of the class detected by the selected boxes
Note: "None" is here because you don't know the exact number of selected boxes, as it depends on the threshold.
For example, the actual output size of scores would be (10,) if there are 10 boxes.
"""
# Step 1: Compute box scores
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line)
box_scores = box_confidence * box_class_probs # 每个cell里面各种分类的概率
### END CODE HERE ###
# Step 2: Find the box_classes thanks to the max box_scores, keep track of the corresponding score
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines)
box_classes = K.argmax(box_scores, axis=-1) # 各种分类概率里面找到值最大的
box_class_scores = K.max(box_scores, axis=-1, keepdims=False) # 值最大的分类的概率,即score
### END CODE HERE ###
# Step 3: Create a filtering mask based on "box_class_scores" by using "threshold". The mask should have the
# same dimension as box_class_scores, and be True for the boxes you want to keep (with probability >= threshold)
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line)
filtering_mask = box_class_scores >= threshold # mask,用与屏蔽threshold值以下的cell
### END CODE HERE ###
# Step 4: Apply the mask to scores, boxes and classes
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines)
scores = tf.boolean_mask(box_class_scores, filtering_mask)
boxes = tf.boolean_mask(boxes, filtering_mask)
classes = tf.boolean_mask(box_classes, filtering_mask)
### END CODE HERE ###
return scores, boxes, classes
def iou(box1, box2):
"""Implement the intersection over union (IoU) between box1 and box2
Arguments:
box1 -- first box, list object with coordinates (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box2 -- second box, list object with coordinates (x1, y1, x2, y2)
"""
# Calculate the (y1, x1, y2, x2) coordinates of the intersection of box1 and box2. Calculate its Area.
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 5 lines)
xi1 = max(box1[0], box2[0])
yi1 = max(box1[1], box2[1])
xi2 = min(box1[2], box2[2])
yi2 = min(box1[3], box2[3])
inter_area = (yi2 - yi1) * (xi2 - xi1)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Calculate the Union area by using Formula: Union(A,B) = A + B - Inter(A,B)
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines)
box1_area = (box1[2] - box1[0]) * (box1[3] - box1[1])
box2_area = (box2[2] - box2[0]) * (box2[3] - box2[1])
union_area = box1_area + box2_area - inter_area
### END CODE HERE ###
# compute the IoU
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line)
iou = inter_area / union_area
### END CODE HERE ###
return iou
def yolo_non_max_suppression(scores, boxes, classes, max_boxes=10, iou_threshold=0.5):
"""
Applies Non-max suppression (NMS) to set of boxes
Arguments:
scores -- tensor of shape (None,), output of yolo_filter_boxes()
boxes -- tensor of shape (None, 4), output of yolo_filter_boxes() that have been scaled to the image size (see later)
classes -- tensor of shape (None,), output of yolo_filter_boxes()
max_boxes -- integer, maximum number of predicted boxes you'd like
iou_threshold -- real value, "intersection over union" threshold used for NMS filtering
Returns:
scores -- tensor of shape (, None), predicted score for each box
boxes -- tensor of shape (4, None), predicted box coordinates
classes -- tensor of shape (, None), predicted class for each box
Note: The "None" dimension of the output tensors has obviously to be less than max_boxes. Note also that this
function will transpose the shapes of scores, boxes, classes. This is made for convenience.
"""
max_boxes_tensor = K.variable(max_boxes, dtype='int32') # tensor to be used in tf.image.non_max_suppression()
K.get_session().run(tf.variables_initializer([max_boxes_tensor])) # initialize variable max_boxes_tensor
# Use tf.image.non_max_suppression() to get the list of indices corresponding to boxes you keep
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line)
nms_indices = tf.image.non_max_suppression(boxes=boxes, scores=scores, max_output_size=max_boxes, iou_threshold=iou_threshold)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Use K.gather() to select only nms_indices from scores, boxes and classes
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines)
scores = K.gather(scores, nms_indices)
boxes = K.gather(boxes, nms_indices)
classes = K.gather(classes, nms_indices)
### END CODE HERE ###
return scores, boxes, classes
def yolo_eval(yolo_outputs, image_shape=(720., 1280.), max_boxes=10, score_threshold=.6, iou_threshold=.5):
"""
Converts the output of YOLO encoding (a lot of boxes) to your predicted boxes along with their scores, box coordinates and classes.
Arguments:
yolo_outputs -- output of the encoding model (for image_shape of (608, 608, 3)), contains 4 tensors:
box_confidence: tensor of shape (None, 19, 19, 5, 1)
box_xy: tensor of shape (None, 19, 19, 5, 2)
box_wh: tensor of shape (None, 19, 19, 5, 2)
box_class_probs: tensor of shape (None, 19, 19, 5, 80)
image_shape -- tensor of shape (2,) containing the input shape, in this notebook we use (608., 608.) (has to be float32 dtype)
max_boxes -- integer, maximum number of predicted boxes you'd like
score_threshold -- real value, if [ highest class probability score < threshold], then get rid of the corresponding box
iou_threshold -- real value, "intersection over union" threshold used for NMS filtering
Returns:
scores -- tensor of shape (None, ), predicted score for each box
boxes -- tensor of shape (None, 4), predicted box coordinates
classes -- tensor of shape (None,), predicted class for each box
"""
### START CODE HERE ###
# Retrieve outputs of the YOLO model (≈1 line)
box_confidence, box_xy, box_wh, box_class_probs = yolo_outputs
# Convert boxes to be ready for filtering functions
boxes = yolo_boxes_to_corners(box_xy, box_wh)
# Use one of the functions you've implemented to perform Score-filtering with a threshold of score_threshold (≈1 line)
scores, boxes, classes = yolo_filter_boxes(box_confidence=box_confidence, boxes=boxes, box_class_probs=box_class_probs, threshold=score_threshold)
# Scale boxes back to original image shape.
boxes = scale_boxes(boxes, image_shape)
# Use one of the functions you've implemented to perform Non-max suppression with a threshold of iou_threshold (≈1 line)
scores, boxes, classes = yolo_non_max_suppression(scores=scores, boxes=boxes, classes=classes, iou_threshold=iou_threshold)
### END CODE HERE ###
return scores, boxes, classes
def predict(sess, image_file):
"""
Runs the graph stored in "sess" to predict boxes for "image_file". Prints and plots the preditions.
Arguments:
sess -- your tensorflow/Keras session containing the YOLO graph
image_file -- name of an image stored in the "images" folder.
Returns:
out_scores -- tensor of shape (None, ), scores of the predicted boxes
out_boxes -- tensor of shape (None, 4), coordinates of the predicted boxes
out_classes -- tensor of shape (None, ), class index of the predicted boxes
Note: "None" actually represents the number of predicted boxes, it varies between 0 and max_boxes.
"""
# Preprocess your image
image, image_data = preprocess_image("images/" + image_file, model_image_size=(608, 608))
# Run the session with the correct tensors and choose the correct placeholders in the feed_dict.
# You'll need to use feed_dict={yolo_model.input: ... , K.learning_phase(): 0})
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 1 line)
out_scores, out_boxes, out_classes = sess.run([scores, boxes, classes],
feed_dict={
yolo_model.input: image_data,
K.learning_phase(): 0
})
### END CODE HERE ###
# Print predictions info
print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), image_file))
# Generate colors for drawing bounding boxes.
colors = generate_colors(class_names)
# Draw bounding boxes on the image file
draw_boxes(image, out_scores, out_boxes, out_classes, class_names, colors)
# Save the predicted bounding box on the image
image.save(os.path.join("out", image_file), quality=90)
# Display the results in the notebook
output_image = scipy.misc.imread(os.path.join("out", image_file))
imshow(output_image)
return out_scores, out_boxes, out_classes
if __name__ == '__main__':
sess = K.get_session()
class_names = read_classes("model_data/coco_classes.txt")
anchors = read_anchors("model_data/yolo_anchors.txt")
image_shape = (720.0, 1280.0)
yolo_model = load_model("model_data/yolo.h5")
yolo_model.summary()
yolo_outputs = yolo_head(yolo_model.output, anchors, len(class_names))
scores, boxes, classes = yolo_eval(yolo_outputs, image_shape)
print(yolo_outputs)
print("scores:", scores)
print("boxes:", boxes)
print("classes:", classes)
plot_model(yolo_model, to_file='yolo.png', show_shapes=True)
'''
pics = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk("images/"):
for file in files:
if os.path.splitext(file)[1] == '.jpg': # 其中os.path.splitext()函数将路径拆分为文件名+扩展名
pics.append(file)
for pic in pics:
out_scores, out_boxes, out_classes = predict(sess, pic)
'''
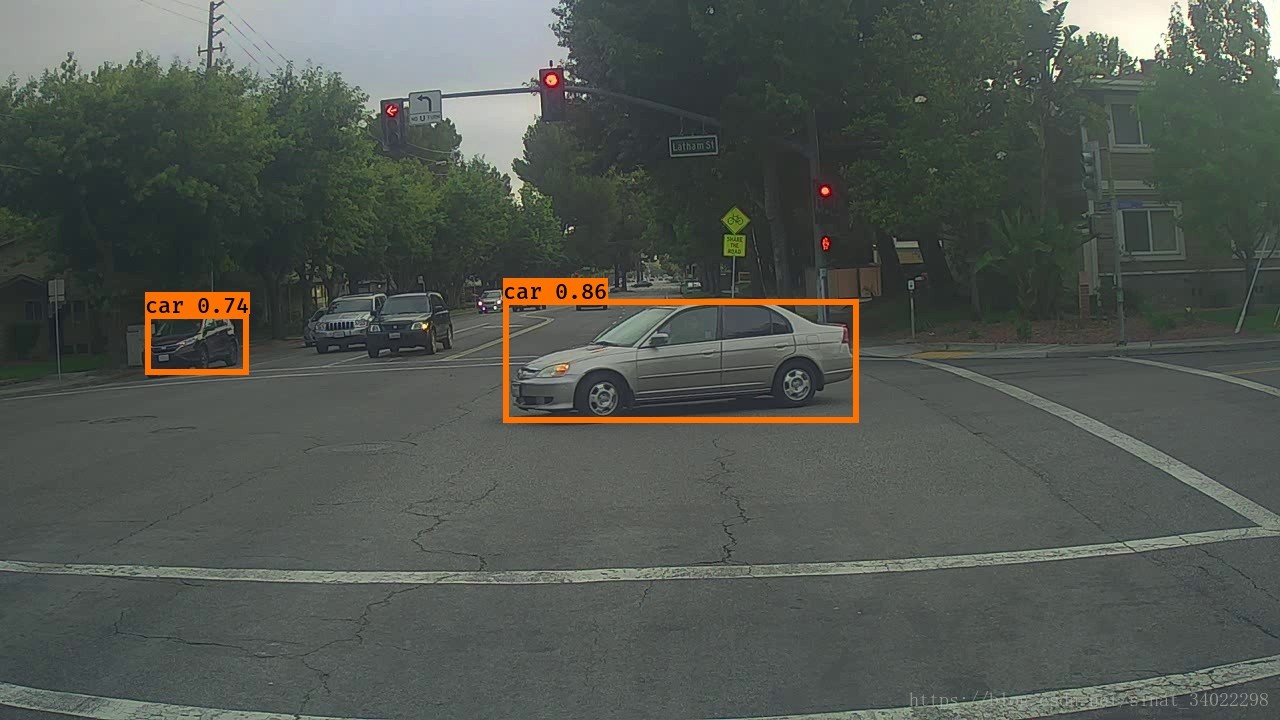
print("END!")结果
可以看到用这个模型预测图片的结果,并没有特别准确,好多漏掉的car。


注意问题
yolo.h5
主程序中有载入yolo模型的语句
yolo_model = load_model("model_data/yolo.h5")
文件中是没有这个文件的,处理方式是自己生成,或者自己下载,这里提供一个下载地址:yolo.h5
github文件过大
yolo.h5这个文件100M+,超过了GitHub允许上传的最大文件大小,所以git push前一定不要把这个文件放在里面,否则很难处理。。
如果已经把较大文件 git push 了,这里提供两种方法解决:
1、处理GitHub不允许上传大于100M文件问题, 笔者尝试了,并没解决问题。
2、删除整个本地库,从远程再次clone该库,然后添加新文件(注意删除大文件),再次添加,提交。