转自:https://blog.csdn.net/u010812084/article/details/46636537
在程序的错误处理中时常会用到
要想判断int类型的取值范围,首先要知道:
1.int类型所占字节数;
2.整型变量数据在内存中以什么方式存储;
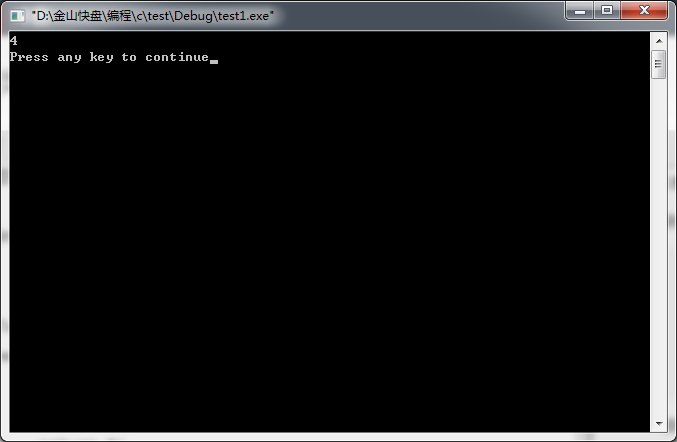
获得int型所占字节数
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d\n",sizeof(int));
return 0;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
结果:
得到int所占字节数为4;
又得知
整型数据在内存中是以补码的方式存储;
所以当数据>=0时,原码 = 反码 = 补码;
数值范围为 0 ~ 2^31 - 1;
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
int a = (pow(2, 31) - 1);
printf("%d\n", a);
return 0;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
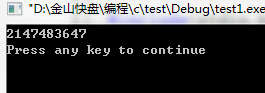
结果 == 2^31 - 1;
当让 a 为 2^31时; 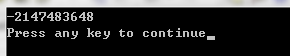
可以看到结果为 -2^31;
这是因为
当a为2^31 - 1时,在计算机中的存储为01111(31个1);(补码形式)
a为2^31时,在计算机中的存储为01111(31个1) + 1 =10000(31个0);(补码形式)即为 -2^31在计算机中的存储形式;
当数据小于0时,
范围为 -2^31 ~ 0;
当a为- 2^31 - 1时; 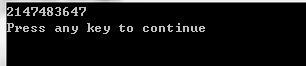
为 2^31 -1;
所以int类型的取值范围为(- 2^31 ~ 2^31 -1);