基本合流操作
在实际应用中,我们经常会遇到来源不同的多条流,需要将它们的数据进行联合处理。所以Flink中合流的操作会更加普遍,对应的API也更加丰富。
联合(Union)
最简单的合流操作,就是直接将多条流合在一起,叫作流的“联合”(union)。联合操作要求必须流中的数据类型必须相同,合并之后的新流会包括所有流中的元素,数据类型不变。
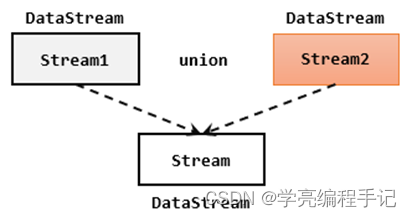
在代码中,我们只要基于DataStream直接调用.union()方法,传入其他DataStream作为参数,就可以实现流的联合了;得到的依然是一个DataStream:stream1.union(stream2, stream3, ...)
注意:union()的参数可以是多个DataStream,所以联合操作可以实现多条流的合并。
代码实现:我们可以用下面的代码做一个简单测试:
public class UnionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
DataStreamSource<Integer> ds1 = env.fromElements(1, 2, 3);
DataStreamSource<Integer> ds2 = env.fromElements(2, 2, 3);
DataStreamSource<String> ds3 = env.fromElements("2", "2", "3");
ds1.union(ds2,ds3.map(Integer::valueOf))
.print();
env.execute();
}
}
连接(Connect)
流的联合虽然简单,不过受限于数据类型不能改变,灵活性大打折扣,所以实际应用较少出现。除了联合(union),Flink还提供了另外一种方便的合流操作——连接(connect)。
1)连接流(ConnectedStreams)
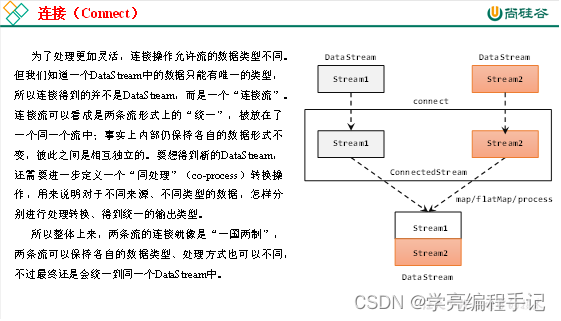
代码实现:需要分为两步:首先基于一条DataStream调用.connect()方法,传入另外一条DataStream作为参数,将两条流连接起来,得到一个ConnectedStreams;然后再调用同处理方法得到DataStream。这里可以的调用的同处理方法有.map()/.flatMap(),以及.process()方法。
public class ConnectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
// DataStreamSource<Integer> source1 = env.fromElements(1, 2, 3);
// DataStreamSource<String> source2 = env.fromElements("a", "b", "c");
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Integer> source1 = env
.socketTextStream("hadoop102", 7777)
.map(i -> Integer.parseInt(i));
DataStreamSource<String> source2 = env.socketTextStream("hadoop102", 8888);
/**
* TODO 使用 connect 合流
* 1、一次只能连接 2条流
* 2、流的数据类型可以不一样
* 3、 连接后可以调用 map、flatmap、process来处理,但是各处理各的
*/
ConnectedStreams<Integer, String> connect = source1.connect(source2);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> result = connect.map(new CoMapFunction<Integer, String, String>() {
@Override
public String map1(Integer value) throws Exception {
return "来源于数字流:" + value.toString();
}
@Override
public String map2(String value) throws Exception {
return "来源于字母流:" + value;
}
});
result.print();
env.execute(); }
}
上面的代码中,ConnectedStreams有两个类型参数,分别表示内部包含的两条流各自的数据类型;由于需要“一国两制”,因此调用.map()方法时传入的不再是一个简单的MapFunction,而是一个CoMapFunction,表示分别对两条流中的数据执行map操作。这个接口有三个类型参数,依次表示第一条流、第二条流,以及合并后的流中的数据类型。需要实现的方法也非常直白:.map1()就是对第一条流中数据的map操作,.map2()则是针对第二条流。
2)CoProcessFunction
与CoMapFunction类似,如果是调用.map()就需要传入一个CoMapFunction,需要实现map1()、map2()两个方法;而调用.process()时,传入的则是一个CoProcessFunction。它也是“处理函数”家族中的一员,用法非常相似。它需要实现的就是processElement1()、processElement2()两个方法,在每个数据到来时,会根据来源的流调用其中的一个方法进行处理。
值得一提的是,ConnectedStreams也可以直接调用.keyBy()进行按键分区的操作,得到的还是一个ConnectedStreams:
connectedStreams.keyBy(keySelector1, keySelector2);
这里传入两个参数keySelector1和keySelector2,是两条流中各自的键选择器;当然也可以直接传入键的位置值(keyPosition),或者键的字段名(field),这与普通的keyBy用法完全一致。ConnectedStreams进行keyBy操作,其实就是把两条流中key相同的数据放到了一起,然后针对来源的流再做各自处理,这在一些场景下非常有用。
案例需求:连接两条流,输出能根据id匹配上的数据(类似inner join效果)
public class ConnectKeybyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(2);
DataStreamSource<Tuple2<Integer, String>> source1 = env.fromElements(
Tuple2.of(1, "a1"),
Tuple2.of(1, "a2"),
Tuple2.of(2, "b"),
Tuple2.of(3, "c")
);
DataStreamSource<Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer>> source2 = env.fromElements(
Tuple3.of(1, "aa1", 1),
Tuple3.of(1, "aa2", 2),
Tuple3.of(2, "bb", 1),
Tuple3.of(3, "cc", 1)
);
ConnectedStreams<Tuple2<Integer, String>, Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer>> connect = source1.connect(source2);
// 多并行度下,需要根据 关联条件 进行keyby,才能保证key相同的数据到一起去,才能匹配上
ConnectedStreams<Tuple2<Integer, String>, Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer>> connectKey = connect.keyBy(s1 -> s1.f0, s2 -> s2.f0);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> result = connectKey.process(
new CoProcessFunction<Tuple2<Integer, String>, Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer>, String>() {
// 定义 HashMap,缓存来过的数据,key=id,value=list<数据>
Map<Integer, List<Tuple2<Integer, String>>> s1Cache = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, List<Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer>>> s2Cache = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void processElement1(Tuple2<Integer, String> value, Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
Integer id = value.f0;
// TODO 1.来过的s1数据,都存起来
if (!s1Cache.containsKey(id)) {
// 1.1 第一条数据,初始化 value的list,放入 hashmap
List<Tuple2<Integer, String>> s1Values = new ArrayList<>();
s1Values.add(value);
s1Cache.put(id, s1Values);
} else {
// 1.2 不是第一条,直接添加到 list中
s1Cache.get(id).add(value);
}
//TODO 2.根据id,查找s2的数据,只输出 匹配上 的数据
if (s2Cache.containsKey(id)) {
for (Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer> s2Element : s2Cache.get(id)) {
out.collect("s1:" + value + "<--------->s2:" + s2Element);
}
}
}
@Override
public void processElement2(Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer> value, Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
Integer id = value.f0;
// TODO 1.来过的s2数据,都存起来
if (!s2Cache.containsKey(id)) {
// 1.1 第一条数据,初始化 value的list,放入 hashmap
List<Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer>> s2Values = new ArrayList<>();
s2Values.add(value);
s2Cache.put(id, s2Values);
} else {
// 1.2 不是第一条,直接添加到 list中
s2Cache.get(id).add(value);
}
//TODO 2.根据id,查找s1的数据,只输出 匹配上 的数据
if (s1Cache.containsKey(id)) {
for (Tuple2<Integer, String> s1Element : s1Cache.get(id)) {
out.collect("s1:" + s1Element + "<--------->s2:" + value);
}
}
}
});
result.print();
env.execute();
}
}