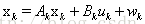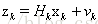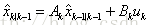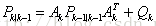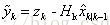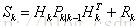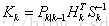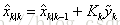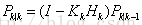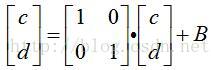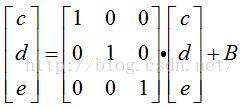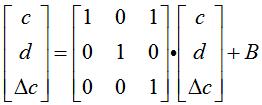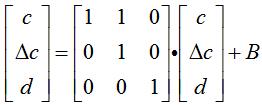转自:https://blog.csdn.net/gdfsg/article/details/50904811
本文将简要回顾一下卡尔曼滤波理论,然后详细介绍如何在OpenCV中使用卡尔曼滤波进行跟踪,最后给两个程序实例。
1. 卡尔曼滤波理论回顾
对于一个动态系统,我们首先定义一组状态空间方程
状态方程:
测量方程:
xk是状态向量,zk是测量向量,Ak是状态转移矩阵,uk是控制向量,Bk是控制矩阵,wk是系统误差(噪声),Hk是测量矩阵,vk是测量误差(噪声)。wk和vk都是高斯噪声,即
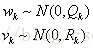
整个卡尔曼滤波的过程就是个递推计算的过程,不断的“预测——更新——预测——更新……”
预测
预测状态值:
预测最小均方误差:
更新
测量误差:
测量协方差:
最优卡尔曼增益:
修正状态值:
修正最小均方误差:
2.OpenCV中的KalmanFilter详解
OpenCV中有两个版本的卡尔曼滤波方法KalmanFilter(C++)和CvKalman(C),用法差不太多,这里只介绍KalmanFilter。
C++版本中将KalmanFilter封装到一个类中,其结构如下所示:
- class CV_EXPORTS_W KalmanFilter
- {
- public:
- CV_WRAP KalmanFilter(); //构造默认KalmanFilter对象
- CV_WRAP KalmanFilter(int dynamParams, int measureParams, int controlParams=0, int type=CV_32F); //完整构造KalmanFilter对象方法
- void init(int dynamParams, int measureParams, int controlParams=0, int type=CV_32F); //初始化KalmanFilter对象,会替换原来的KF对象
- CV_WRAP const Mat& predict(const Mat& control=Mat()); //计算预测的状态值
- CV_WRAP const Mat& correct(const Mat& measurement); //根据测量值更新状态值
- Mat statePre; //预测值 (x'(k)): x(k)=A*x(k-1)+B*u(k)
- Mat statePost; //状态值 (x(k)): x(k)=x'(k)+K(k)*(z(k)-H*x'(k))
- Mat transitionMatrix; //状态转移矩阵 (A)
- Mat controlMatrix; //控制矩阵 B
- Mat measurementMatrix; //测量矩阵 H
- Mat processNoiseCov; //系统误差 Q
- Mat measurementNoiseCov; //测量误差 R
- Mat errorCovPre; //最小均方误差 (P'(k)): P'(k)=A*P(k-1)*At + Q)
- Mat gain; //卡尔曼增益 (K(k)): K(k)=P'(k)*Ht*inv(H*P'(k)*Ht+R)
- Mat errorCovPost; //修正的最小均方误差 (P(k)): P(k)=(I-K(k)*H)*P'(k)
- // 临时矩阵
- Mat temp1;
- Mat temp2;
- Mat temp3;
- Mat temp4;
- Mat temp5;
- };
- enum
- {
- OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW = CV_LKFLOW_INITIAL_GUESSES,
- OPTFLOW_LK_GET_MIN_EIGENVALS = CV_LKFLOW_GET_MIN_EIGENVALS,
- OPTFLOW_FARNEBACK_GAUSSIAN = 256
- };
函数原型见:…..\OpenCV2\sources\modules\ocl\src\kalman.cpp
只有四个方法: 构造KF对象KalmanFilter(DP,MP,CP)、初始化KF对象init(DP,MP,CP)、预测predict( )、更新correct( )。除非你要重新构造KF对象,否则用不到init( )。
KalmanFilter(DP,MP,CP)和init( )就是赋值,没什么好说的。
注意:KalmanFilter结构体中并没有测量值,测量值需要自己定义,而且一定要定义,因为后面要用。
step1:定义KalmanFilter类并初始化
//构造KF对象
KalmanFilter KF(DP, MP, 0);
//初始化相关参数
KF.transitionMatrix 转移矩阵 A
KF.measurementMatrix 测量矩阵 H
KF.processNoiseCov 过程噪声 Q
KF.measurementNoiseCov 测量噪声 R
KF.errorCovPost 最小均方误差 P
KF.statePost 系统初始状态 x(0)
Mat measurement 定义初始测量值 z(0)
step2:预测
KF.predict( ) //返回的是下一时刻的状态值KF.statePost (k+1)
step3:更新
更新measurement; //注意measurement不能通过观测方程进行计算得到,要自己定义!
更新KF KF.correct(measurement)
最终的结果应该是更新后的statePost.
相关参数的确定
对于系统状态方程,简记为Y=AX+B,X和Y是表示系统状态的列向量,A是转移矩阵,B是其他项。
状态值(向量)只要能表示系统的状态即可,状态值的维数决定了转移矩阵A的维数,比如X和Y是N×1的,则A是N×N的。
A的确定跟X有关,只要保证方程中不相干项的系数为0即可,看下面例子
X和Y是二维的,
X和Y是三维的,
X和Y是三维的,但c和△ c是相关项
上面的1也可以是其他值。
下面对predict( ) 和correct( )函数介绍下,可以不用看,不影响编程。
- CV_EXPORTS const oclMat& KalmanFilter::predict(const oclMat& control)
- {
- gemm(transitionMatrix, statePost, 1, oclMat(), 0, statePre);
- oclMat temp;
- if(control.data)
- gemm(controlMatrix, control, 1, statePre, 1, statePre);
- gemm(transitionMatrix, errorCovPost, 1, oclMat(), 0, temp1);
- gemm(temp1, transitionMatrix, 1, processNoiseCov, 1, errorCovPre, GEMM_2_T);
- statePre.copyTo(statePost);
- return statePre;
- }
gemm( )是矩阵的广义乘法
void gemm(const GpuMat& src1, constGpuMat& src2, double alpha, const GpuMat& src3, double beta,GpuMat& dst, int flags=0, Stream& stream=Stream::Null())
dst = alpha · src1 · src2 +beta· src3
上面,oclMat()其实是uk,只不过默认为0,所以没赋值。整个过程就计算了x'和P’。(用x'代表x的预测值,用P'代表P的预测值)。GEMM_2_T表示对第2个参数转置。
可见,和第一部分的理论介绍完全一致。x’(k)=1·A·x(k-1)
如果B非空, x'(k) = 1·B·u + 1·x'(k-1)
temp1 = 1·A·P(k-1) + 0·u(k)
P’(k) = 1· temp1·AT + 1· Qk= A·P(k-1)·AT + 1· Qk
- CV_EXPORTS const oclMat& KalmanFilter::correct(const oclMat& measurement)
- {
- CV_Assert(measurement.empty() == false);
- gemm(measurementMatrix, errorCovPre, 1, oclMat(), 0, temp2);
- gemm(temp2, measurementMatrix, 1, measurementNoiseCov, 1, temp3, GEMM_2_T);
- Mat temp;
- solve(Mat(temp3), Mat(temp2), temp, DECOMP_SVD);
- temp4.upload(temp);
- gain = temp4.t();
- gemm(measurementMatrix, statePre, -1, measurement, 1, temp5);
- gemm(gain, temp5, 1, statePre, 1, statePost);
- gemm(gain, temp2, -1, errorCovPre, 1, errorCovPost);
- return statePost;
- }
求解线型最小二乘估计
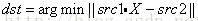
temp2 = 1· H·P’ + 0·u(k)
temp3 = 1· temp2·HT + 1·R = H·P’·HT+ 1· R 也就是上面的Sk
temp = argmin||tem2- temp3||
K=temp
temp5 = -1· H·x’ + 1·zk 就是上面的y’。
x = 1·K·temp5 + 1·x’ = KT·y’ +x’
P =-1·K·temp2 + 1·P’ = -K·H·P’+P’ = (I- K·H) P’也和第一部分的理论完全一致。
通过深入函数内部,学到了两个实用的函数哦。矩阵广义乘法gemm( )、最小二乘估计solve( )
补充:
1)以例2为例,为什么状态值一般都设置成(x,y,△x,△y)?我们不妨设置成(x,y,△x),对应的转移矩阵也改成3×3的。可以看到仍能跟上,不过在x方向跟踪速度快,在y方向跟踪速度慢。进一步设置成(x,y)和2×2的转移矩阵,程序的跟踪速度简直是龟速。所以,简单理解,△x和△y严重影响对应方向上的跟踪速度。
3.实例
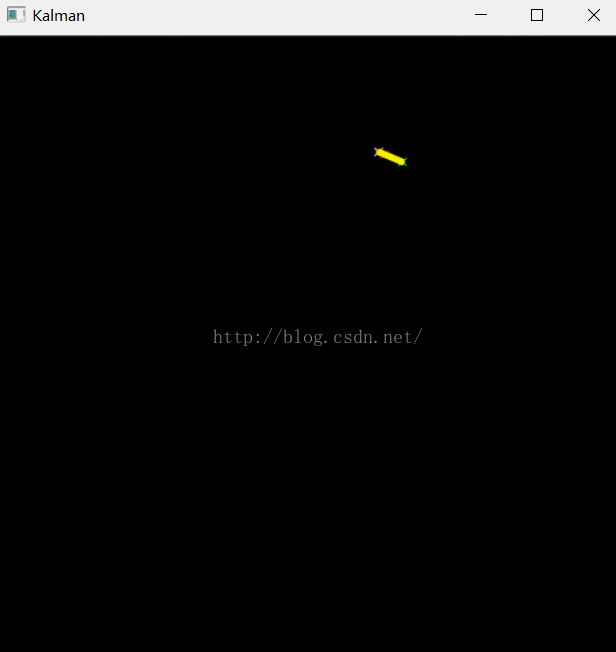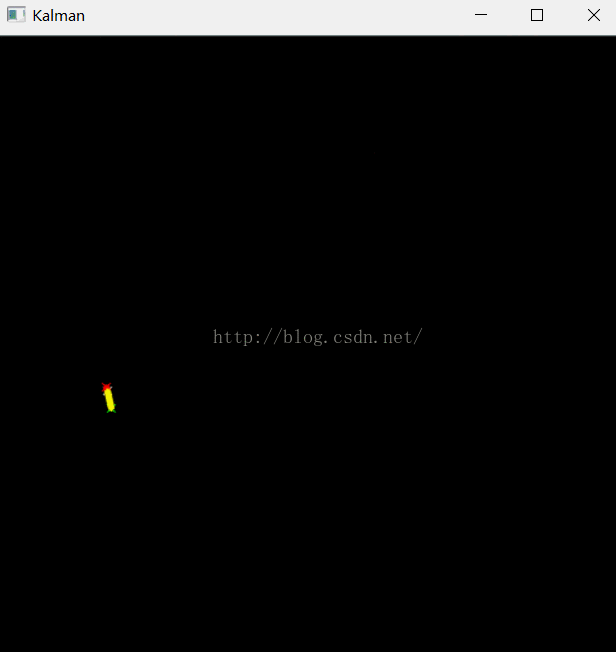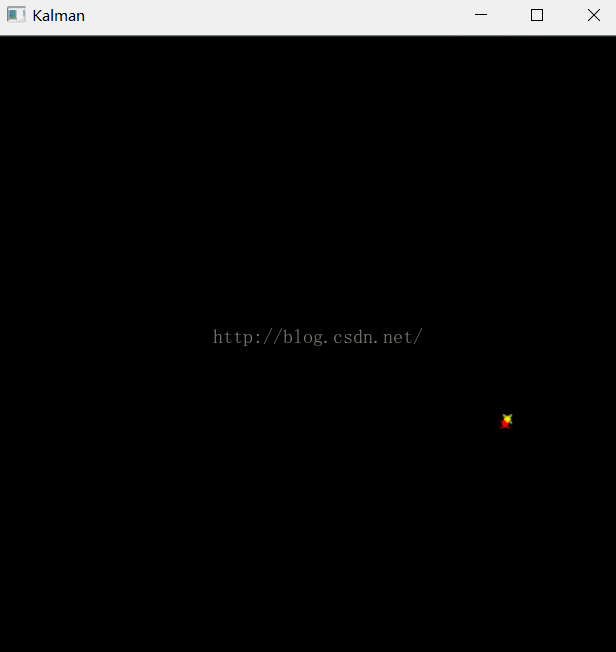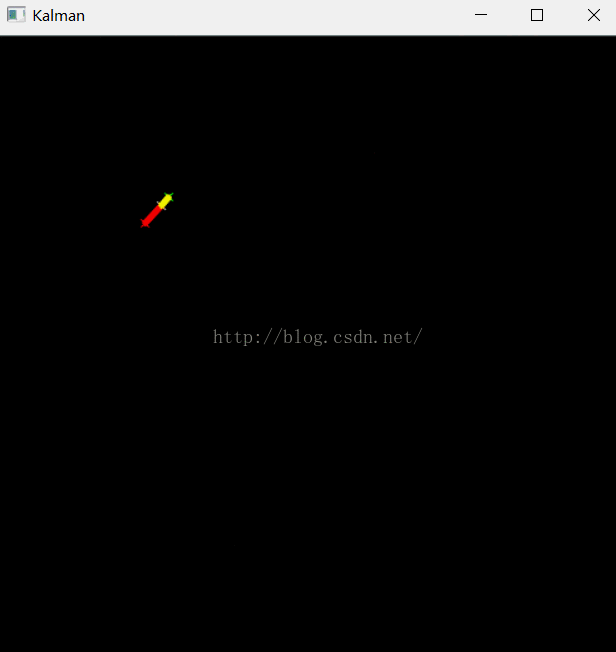
例1 OpenCV自带的示例程序
- #include "opencv2/video/tracking.hpp"
- #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
- #include <iostream>
- #include <stdio.h>
- using namespace std;
- using namespace cv;
- //计算相对窗口的坐标值,因为坐标原点在左上角,所以sin前有个负号
- static inline Point calcPoint(Point2f center, double R, double angle)
- {
- return center + Point2f((float)cos(angle), (float)-sin(angle))*(float)R;
- }
- static void help()
- {
- printf( "\nExamle of c calls to OpenCV's Kalman filter.\n"
- " Tracking of rotating point.\n"
- " Rotation speed is constant.\n"
- " Both state and measurements vectors are 1D (a point angle),\n"
- " Measurement is the real point angle + gaussian noise.\n"
- " The real and the estimated points are connected with yellow line segment,\n"
- " the real and the measured points are connected with red line segment.\n"
- " (if Kalman filter works correctly,\n"
- " the yellow segment should be shorter than the red one).\n"
- "\n"
- " Pressing any key (except ESC) will reset the tracking with a different speed.\n"
- " Pressing ESC will stop the program.\n"
- );
- }
- int main(int, char**)
- {
- help();
- Mat img(500, 500, CV_8UC3);
- KalmanFilter KF(2, 1, 0); //创建卡尔曼滤波器对象KF
- Mat state(2, 1, CV_32F); //state(角度,△角度)
- Mat processNoise(2, 1, CV_32F);
- Mat measurement = Mat::zeros(1, 1, CV_32F); //定义测量值
- char code = (char)-1;
- for(;;)
- {
- //1.初始化
- randn( state, Scalar::all(0), Scalar::all(0.1) ); //
- KF.transitionMatrix = *(Mat_<float>(2, 2) << 1, 1, 0, 1); //转移矩阵A[1,1;0,1]
- //将下面几个矩阵设置为对角阵
- setIdentity(KF.measurementMatrix); //测量矩阵H
- setIdentity(KF.processNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-5)); //系统噪声方差矩阵Q
- setIdentity(KF.measurementNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-1)); //测量噪声方差矩阵R
- setIdentity(KF.errorCovPost, Scalar::all(1)); //后验错误估计协方差矩阵P
- randn(KF.statePost, Scalar::all(0), Scalar::all(0.1)); //x(0)初始化
- for(;;)
- {
- Point2f center(img.cols*0.5f, img.rows*0.5f); //center图像中心点
- float R = img.cols/3.f; //半径
- double stateAngle = state.at<float>(0); //跟踪点角度
- Point statePt = calcPoint(center, R, stateAngle); //跟踪点坐标statePt
- //2. 预测
- Mat prediction = KF.predict(); //计算预测值,返回x'
- double predictAngle = prediction.at<float>(0); //预测点的角度
- Point predictPt = calcPoint(center, R, predictAngle); //预测点坐标predictPt
- //3.更新
- //measurement是测量值
- randn( measurement, Scalar::all(0), Scalar::all(KF.measurementNoiseCov.at<float>(0))); //给measurement赋值N(0,R)的随机值
- // generate measurement
- measurement += KF.measurementMatrix*state; //z = z + H*x;
- double measAngle = measurement.at<float>(0);
- Point measPt = calcPoint(center, R, measAngle);
- // plot points
- //定义了画十字的方法,值得学习下
- #define drawCross( center, color, d ) \
- line( img, Point( center.x - d, center.y - d ), \
- Point( center.x + d, center.y + d ), color, 1, CV_AA, 0); \
- line( img, Point( center.x + d, center.y - d ), \
- Point( center.x - d, center.y + d ), color, 1, CV_AA, 0 )
- img = Scalar::all(0);
- drawCross( statePt, Scalar(255,255,255), 3 );
- drawCross( measPt, Scalar(0,0,255), 3 );
- drawCross( predictPt, Scalar(0,255,0), 3 );
- line( img, statePt, measPt, Scalar(0,0,255), 3, CV_AA, 0 );
- line( img, statePt, predictPt, Scalar(0,255,255), 3, CV_AA, 0 );
- //调用kalman这个类的correct方法得到加入观察值校正后的状态变量值矩阵
- if(theRNG().uniform(0,4) != 0)
- KF.correct(measurement);
- //不加噪声的话就是匀速圆周运动,加了点噪声类似匀速圆周运动,因为噪声的原因,运动方向可能会改变
- randn( processNoise, Scalar(0), Scalar::all(sqrt(KF.processNoiseCov.at<float>(0, 0)))); //vk
- state = KF.transitionMatrix*state + processNoise;
- imshow( "Kalman", img );
- code = (char)waitKey(100);
- if( code > 0 )
- break;
- }
- if( code == 27 || code == 'q' || code == 'Q' )
- break;
- }
- return 0;
- }
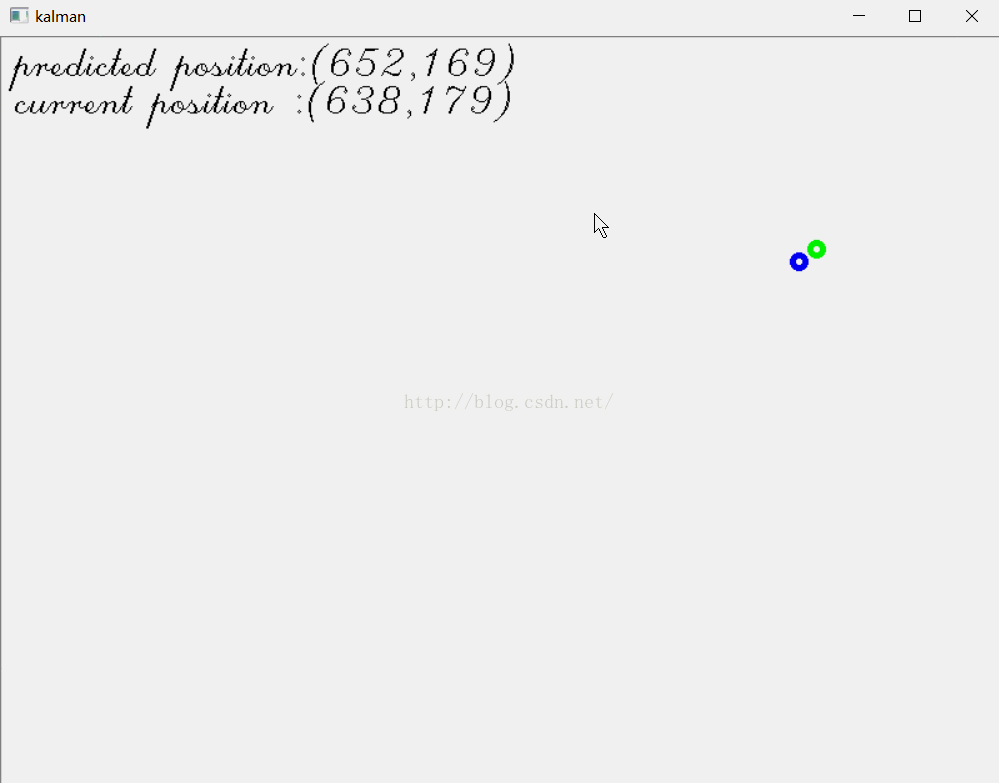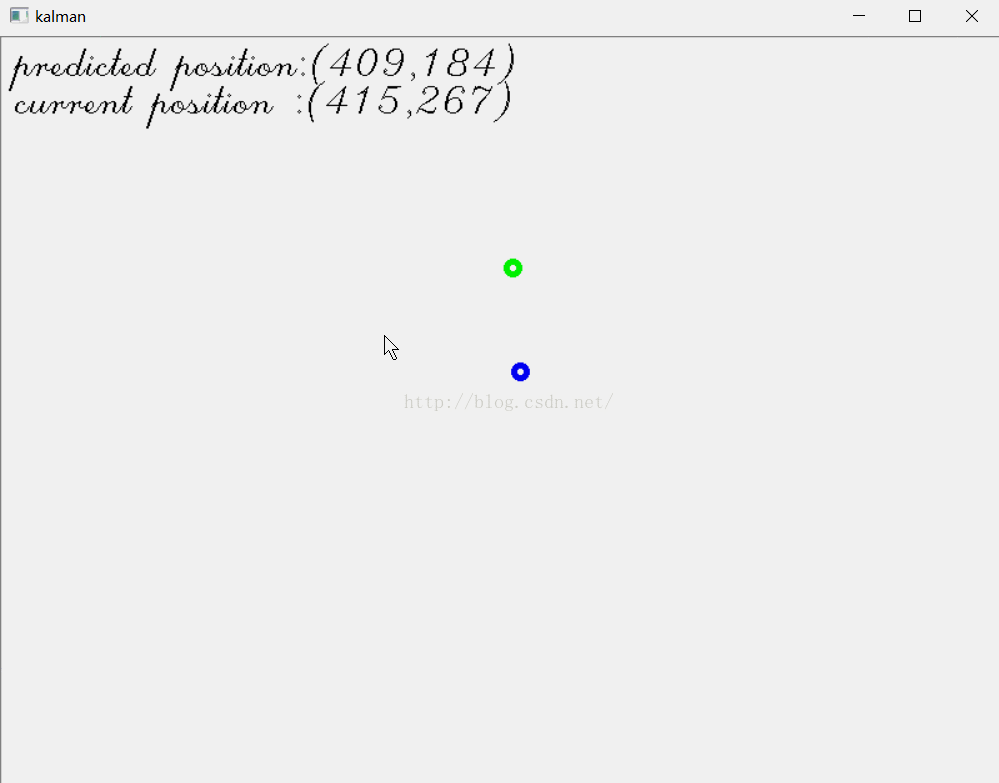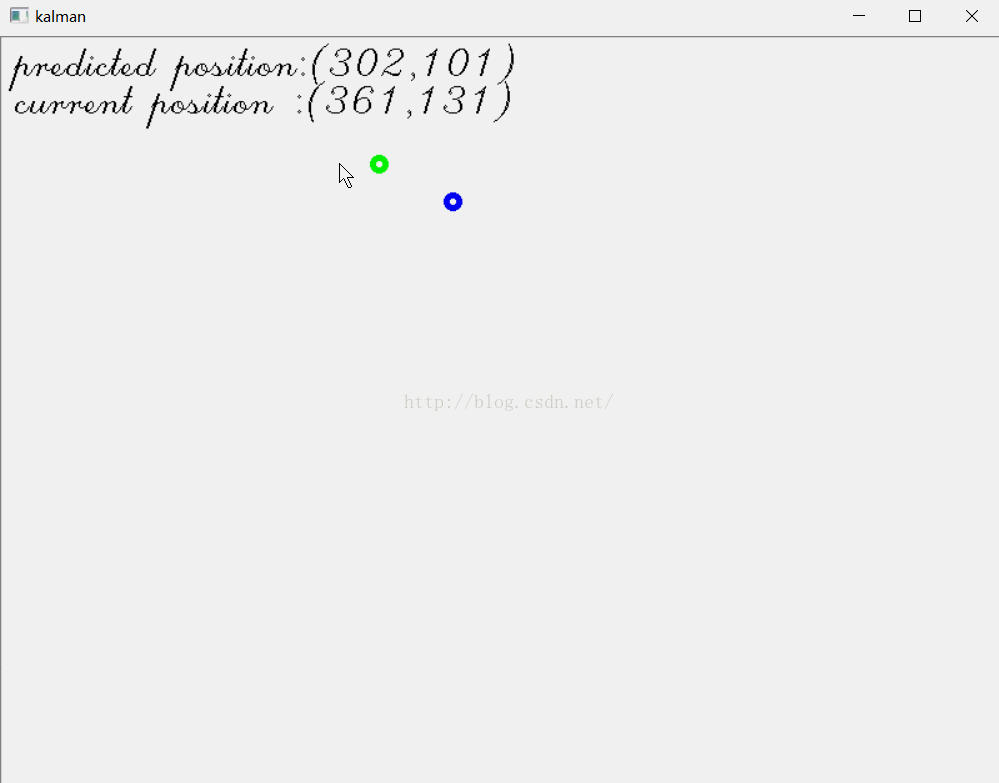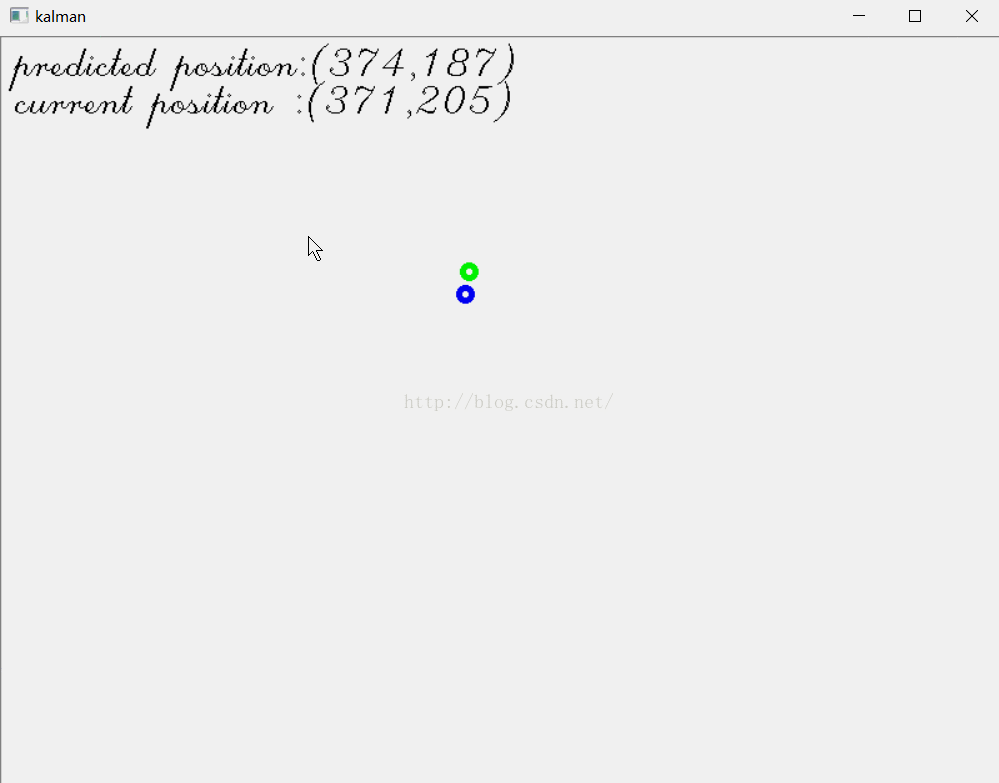
例2 跟踪鼠标位置
在我介绍粒子滤波的博文“学习Opencv2——粒子滤波Condensation算法”里,有个例3,是跟踪鼠标位置。现在我们用卡尔曼滤波来实现。
- #include "opencv2/video/tracking.hpp"
- #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
- #include <stdio.h>
- using namespace cv;
- using namespace std;
- const int winHeight=600;
- const int winWidth=800;
- Point mousePosition= Point(winWidth>>1,winHeight>>1);
- //mouse event callback
- void mouseEvent(int event, int x, int y, int flags, void *param )
- {
- if (event==CV_EVENT_MOUSEMOVE) {
- mousePosition = Point(x,y);
- }
- }
- int main (void)
- {
- RNG rng;
- //1.kalman filter setup
- const int stateNum=4; //状态值4×1向量(x,y,△x,△y)
- const int measureNum=2; //测量值2×1向量(x,y)
- KalmanFilter KF(stateNum, measureNum, 0);
- KF.transitionMatrix = *(Mat_<float>(4, 4) <<1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1); //转移矩阵A
- setIdentity(KF.measurementMatrix); //测量矩阵H
- setIdentity(KF.processNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-5)); //系统噪声方差矩阵Q
- setIdentity(KF.measurementNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-1)); //测量噪声方差矩阵R
- setIdentity(KF.errorCovPost, Scalar::all(1)); //后验错误估计协方差矩阵P
- rng.fill(KF.statePost,RNG::UNIFORM,0,winHeight>winWidth?winWidth:winHeight); //初始状态值x(0)
- Mat measurement = Mat::zeros(measureNum, 1, CV_32F); //初始测量值x'(0),因为后面要更新这个值,所以必须先定义
- namedWindow("kalman");
- setMouseCallback("kalman",mouseEvent);
- Mat image(winHeight,winWidth,CV_8UC3,Scalar(0));
- while (1)
- {
- //2.kalman prediction
- Mat prediction = KF.predict();
- Point predict_pt = Point(prediction.at<float>(0),prediction.at<float>(1) ); //预测值(x',y')
- //3.update measurement
- measurement.at<float>(0) = (float)mousePosition.x;
- measurement.at<float>(1) = (float)mousePosition.y;
- //4.update
- KF.correct(measurement);
- //draw
- image.setTo(Scalar(255,255,255,0));
- circle(image,predict_pt,5,Scalar(0,255,0),3); //predicted point with green
- circle(image,mousePosition,5,Scalar(255,0,0),3); //current position with red
- char buf[256];
- sprintf_s(buf,256,"predicted position:(%3d,%3d)",predict_pt.x,predict_pt.y);
- putText(image,buf,Point(10,30),CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_COMPLEX,1,Scalar(0,0,0),1,8);
- sprintf_s(buf,256,"current position :(%3d,%3d)",mousePosition.x,mousePosition.y);
- putText(image,buf,cvPoint(10,60),CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_COMPLEX,1,Scalar(0,0,0),1,8);
- imshow("kalman", image);
- int key=waitKey(3);
- if (key==27){//esc
- break;
- }
- }
- }
结果
例3
- #include "opencv2/video/tracking.hpp"
- #include <opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp> //#include "cvAux.h"
- #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
- #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
- #include <stdio.h>
- using namespace cv;
- using namespace std;
- int main( )
- {
- float A[10][3] =
- {
- 10, 50, 15.6,
- 12, 49, 16,
- 11, 52, 15.8,
- 13, 52.2, 15.8,
- 12.9, 50, 17,
- 14, 48, 16.6,
- 13.7, 49, 16.5,
- 13.6, 47.8, 16.4,
- 12.3, 46, 15.9,
- 13.1, 45, 16.2
- };
- const int stateNum=3;
- const int measureNum=3;
- KalmanFilter KF(stateNum, measureNum, 0);
- KF.transitionMatrix = *(Mat_<float>(3, 3) <<1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1); //转移矩阵A
- setIdentity(KF.measurementMatrix); //测量矩阵H
- setIdentity(KF.processNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-5)); //系统噪声方差矩阵Q
- setIdentity(KF.measurementNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-1)); //测量噪声方差矩阵R
- setIdentity(KF.errorCovPost, Scalar::all(1));
- Mat measurement = Mat::zeros(measureNum, 1, CV_32F);
- //初始状态值
- KF.statePost = *(Mat_<float>(3, 1) <<A[0][0],A[0][1],A[0][2]);
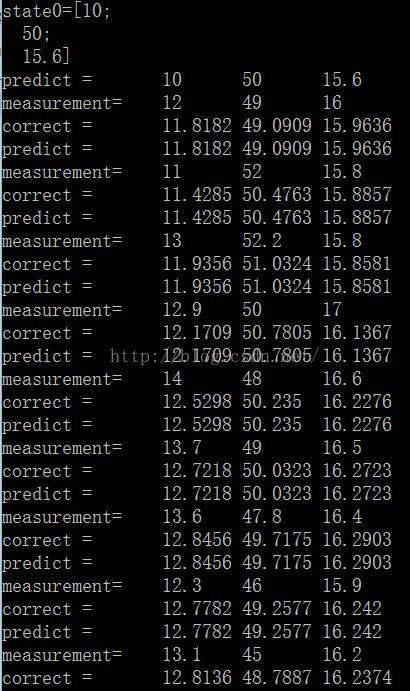
- cout<<"state0="<<KF.statePost<<endl;
- for(int i=1;i<=9;i++)
- {
- //预测
- Mat prediction = KF.predict();
- //计算测量值
- measurement.at<float>(0) = (float)A[i][0];
- measurement.at<float>(1) = (float)A[i][1];
- measurement.at<float>(2) = (float)A[i][2];
- //更新
- KF.correct(measurement);
- //输出结果
- cout<<"predict ="<<"\t"<<prediction.at<float>(0)<<"\t"<<prediction.at<float>(1)<<"\t"<<prediction.at<float>(2)<<endl;
- cout<<"measurement="<<"\t"<<measurement.at<float>(0)<<"\t"<<measurement.at<float>(1)<<"\t"<<measurement.at<float>(2)<<endl;
- cout<<"correct ="<<"\t"<<KF.statePost.at<float>(0)<<"\t"<<KF.statePost.at<float>(1)<<"\t"<<KF.statePost.at<float>(2)<<endl;
- }
- system("pause");
- }