MATLAB实现多目标粒子群优化算法(MOPSO)
这里如何用MATLAB实现多目标粒子群优化算法。
本教程参考:MATLAB实现多目标粒子群算法
对其中的优化项、优化目标项进行了简单的修改。优化项由1个修改成了2个,优化目标由2个修改成了3个。
同时,参考MATLAB源码,将该算法在C#上也进行了实现,有需要的可以参考:C#实现多目标粒子群优化算法(MOPSO)
程序源码下载链接:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1UML4slk6PN9rMFN8rbxP9g
提取码:hzdz
程序运行效果:
在有2个优化目标函数,并且优化目标函数设置合理的情况下,理想情况下,MOPSO的优化结果在平面内成线状。
在有3个优化目标函数,并且优化目标函数设置合理的情况下,理想情况下,MOPSO的优化结果在空间内成面状,如下图所示。
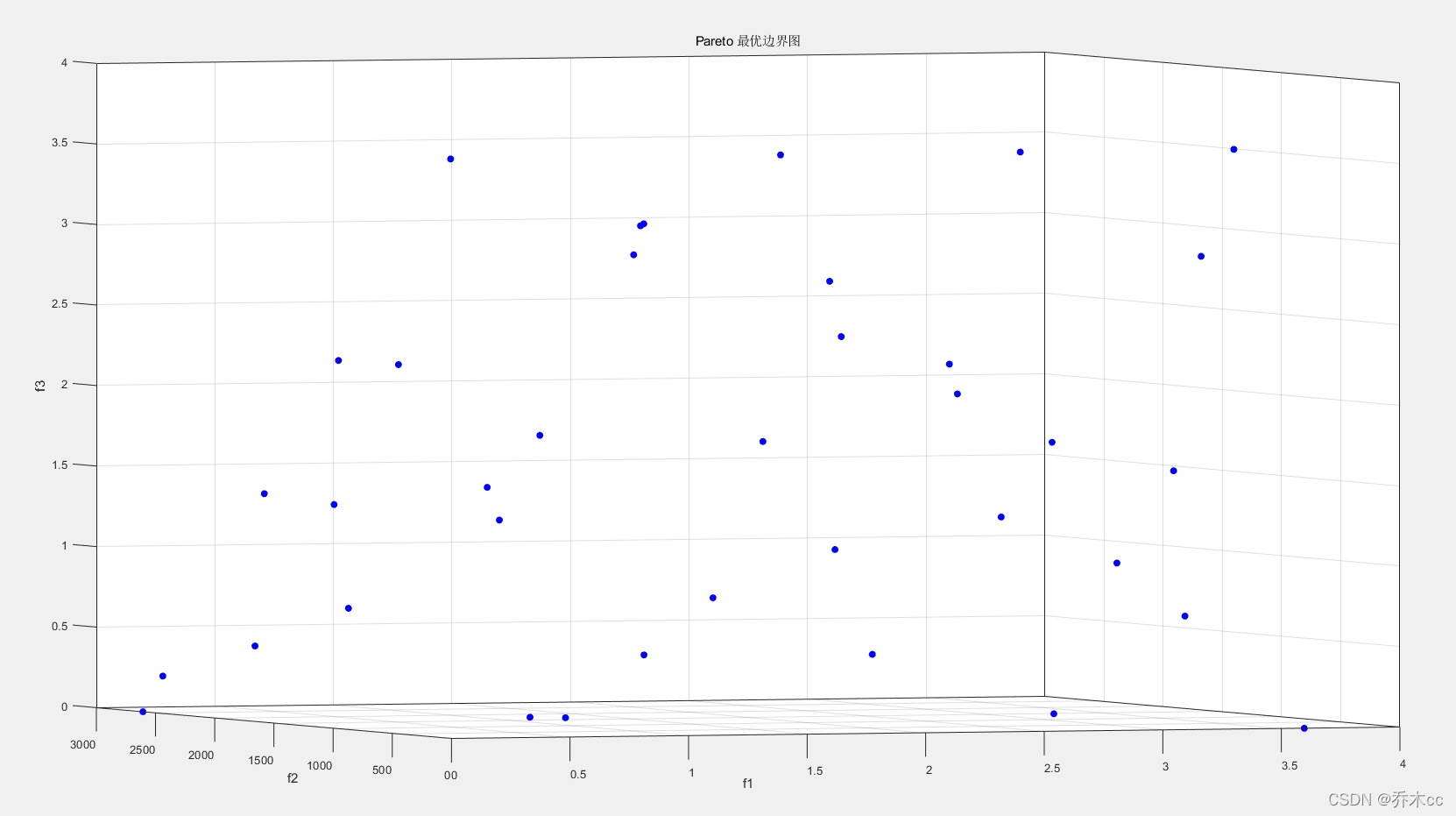
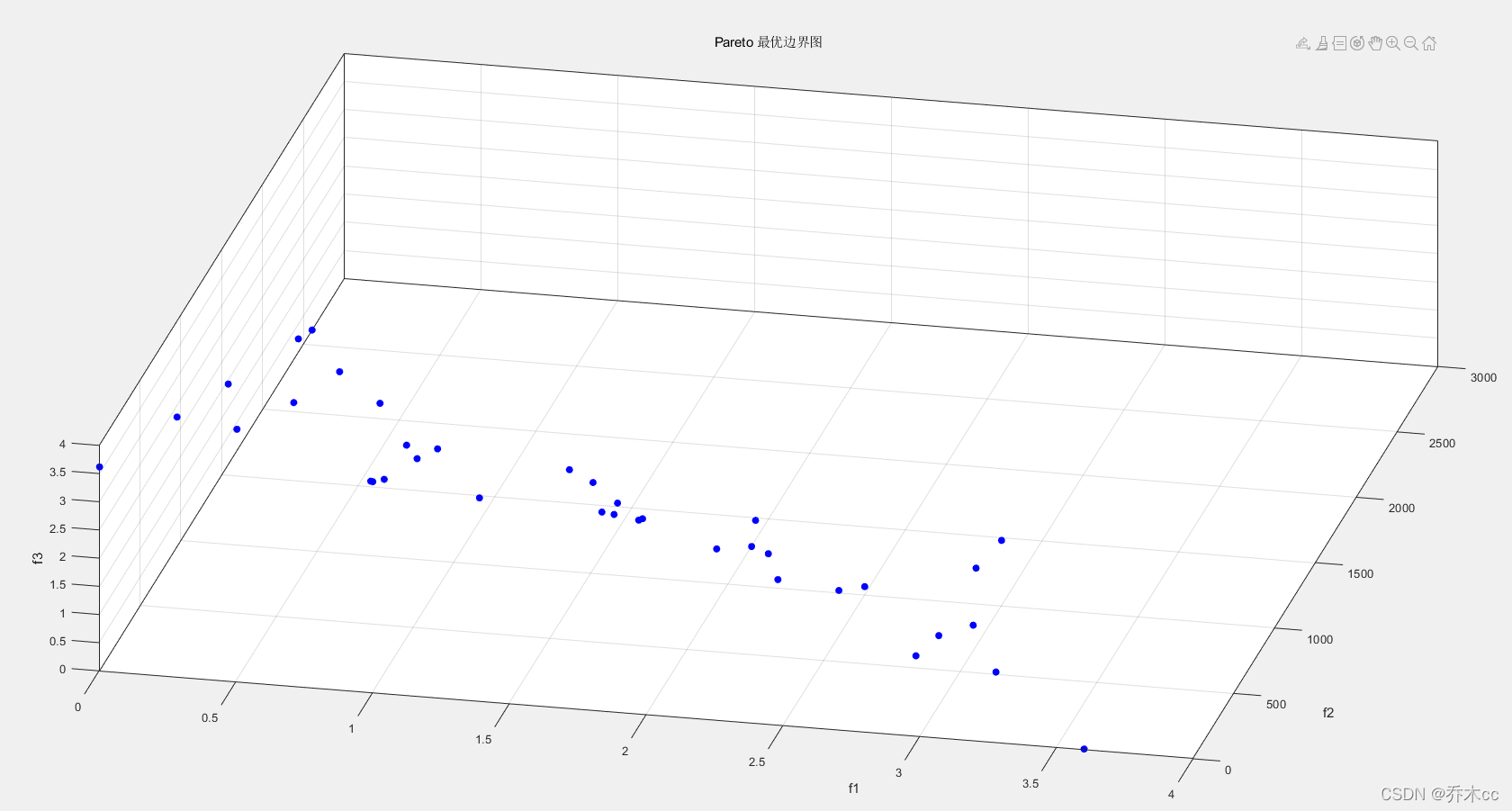
MATLAB主要程序如下:
其中,1为MOPSO的主程序,2-11均为函数。
1、MOPSO的主程序
clc;
clear;
close all;
CostFunction = @(x) evaluate_objective(x); %目标函数ZDT1
nVar = 2; %变量个数
VarSize = [1 nVar]; %变量矩阵大小
VarMin = 0; %变量值定义域
VarMax = 360; %注意: 该函数变量不能出现负值
MaxIt = 30; %最大迭代次数
N = 40; %种群规模
nRep = 50; %档案库大小
w = 0.9; %惯性权重系数
wdamp = 0.99; %惯性权重衰减率
c1 = 1.7; %个体学习因子
c2 = 1.8; %全局学习因子
nGrid = 5; %每一维的分格数
alpha = 0.1; %膨胀率
beta = 2; %最佳选择压
gamma = 2; %删除选择压
mu = 0.1; %变异概率
empty_particle.Position = []; %粒子位置向量
empty_particle.Velocity = []; %粒子速度向量
empty_particle.Cost = []; %粒子目标值向量
empty_particle.Best.Position = []; %粒子最佳位置向量
empty_particle.Best.Cost = []; %粒子最佳目标值向量
empty_particle.IsDominated = []; %粒子被支配个体向量
empty_particle.GridIndex = []; %粒子栅格索引向量
empty_particle.GridSubIndex = []; %粒子栅格子索引向量
pop = repmat(empty_particle,N,1); %repmat平铺矩阵%粒子初始空矩阵
for i = 1:N %初始化N个个体
% 产生服从均匀分布, VarSize大小的位置矩阵
pop(i).Position = unifrnd(VarMin,VarMax,VarSize);
pop(i).Velocity = zeros(VarSize);
pop(i).Cost = CostFunction(pop(i).Position);
pop(i).Best.Position = pop(i).Position;
pop(i).Best.Cost = pop(i).Cost;
end
pop = DetermineDomination(pop);
rep = pop(~[pop.IsDominated]);
Grid = CreateGrid(rep,nGrid,alpha);
for i = 1:numel(rep)
rep(i) = FindGridIndex(rep(i),Grid);
% GridIndex = 绝对位置,.GridSubIndex = 坐标位置
end
%MOPSO主循环
for it = 1:MaxIt
for i = 1:N %逐一个体更新速度和位置,0.5的概率发生变异
leader = SelectLeader(rep,beta); %从支配个体轮盘赌选出全局最佳个体
rep = [rep;pop(~[pop.IsDominated])]; %添加新的最佳栅格位置到库
pop(i).Velocity = w*pop(i).Velocity + ...
c1*rand(VarSize).*(pop(i).Best.Position-pop(i).Position)+ ...
c2*rand(VarSize).*(leader.Position-pop(i).Position); %速度更新
pop(i).Position = pop(i).Position+pop(i).Velocity; %位置更新
pop(i).Position = limitToPosition(pop(i).Position,VarMin,VarMax); %限制变量变化范围
pop(i).Cost = CostFunction(pop(i).Position); %计算目标函数值
%应用变异策略
pm = (1-(it-1)/(MaxIt-1)^(1/mu)); % 变异概率逐渐变小
NewSol.Position = Mutate(pop(i).Position,pm,VarMin,VarMax);
NewSol.Cost = CostFunction(NewSol.Position); % 计算变异后的目标值
if Dominates(NewSol,pop(i))
pop(i).Position = NewSol.Position;
pop(i).Cost = NewSol.Cost;
else %以0.5的概率决定是否接受变异
if rand < 0.5
pop(i).Position = NewSol.Position;
pop(i).Cost = NewSol.Cost;
end
end
if Dominates(pop(i),pop(i).Best) % 如果当前个体优于先前最佳个体,则替换之
pop(i).Best.Position = pop(i).Position;
pop(i).Best.Cost = pop(i).Cost;
else %以0.5的概率替换个体最佳
if rand <0.5
pop(i).Best.Position = pop(i).Position;
pop(i).Best.Cost = pop(i).Cost;
end
end
end %每个个体
rep = DetermineDomination(rep);
rep = rep(~[rep.IsDominated]);
Grid = CreateGrid(rep,nGrid,alpha);
for i =1:numel(rep)
rep(i) = FindGridIndex(rep(i),Grid);
end
if numel(rep) > nRep
Extra = numel(rep)-nRep;
for e = 1:Extra
rep = DeleteOneRepMemebr(rep,gamma);
end
end
disp(['迭代次数 =',num2str(it)]);
w = w*wdamp;
end
figure(1);
location = [rep.Cost]; %取最优结果
scatter3(location(1,:),location(2,:),location(3,:),'filled','b');
xlabel('f1');ylabel('f2'); zlabel('f3');
title('Pareto 最优边界图');
box on;
2、evaluate_objective.m(对应主程序中的CostFunction)
%=============================
%计算目标函数值
%=============================
function f =evaluate_objective(x)
f(1) = x(1)*0.01;%优化目标1
f(2) = (361-x(1))*(361-x(2))*0.02;%优化目标2
f(3) = x(2)*0.01;%优化目标3
f = [f(1);f(2);f(3)];
end
3、DetermineDomination.m
%=============================
%判断全局支配状况,返回0 = 非支配解
%=============================
function pop =DetermineDomination(pop)
nPop = numel(pop);
for i =1:nPop
pop(i).IsDominated = false; %初始化为互不支配
end
for i = 1:nPop-1
for j = i+1:nPop
if Dominates(pop(i),pop(j))
pop(j).IsDominated = true;
end
if Dominates(pop(j),pop(i))
pop(i).IsDominated = true;
end
end
end
end
4、Dominates.m
%=============================
%判断两个目标值x,y的支配状态
% x支配y,返回1;y支配x,返回0
%=============================
function b = Dominates(x,y)
if isstruct(x)
x=x.Cost;
end
if isstruct(y)
y=y.Cost;
end
b=all(x<=y) && any(x<y);
end
5、CreateGrid.m
%=============================
%创建栅格矩阵
%=============================
function Grid = CreateGrid(pop,nGrid,alpha)
c = [pop.Cost];
cmin = min(c,[],2);
cmax = max(c,[],2);
dc = cmax-cmin;
cmin = cmin-alpha*dc;
cmax = cmax+alpha*dc;
nObj = size(c,1);
empty_grid.LB = [];
empty_grid.UB = [];
Grid = repmat(empty_grid,nObj,1);
for j = 1:nObj
cj = linspace(cmin(j),cmax(j),nGrid+1);
Grid(j).LB = [-inf cj];
Grid(j).UB = [cj +inf];
end
end
6、FindGridIndex.m
%=============================
%栅格索引定位
%=============================
function particle = FindGridIndex(particle,Grid)
nObj = numel(particle.Cost);
nGrid = numel(Grid(1).LB);
particle.GridSubIndex = zeros(1,nGrid);
for j = 1:nObj
particle.GridSubIndex(j) = find(particle.Cost(j)<=Grid(j).UB,1,'first');
%从左到右找到第一个目标值小于栅格值的位置
end
particle.GridIndex = particle.GridSubIndex(1);
for j = 2:nObj % 左上角开始数到右下角,先数行再换行继续数
particle.GridIndex = particle.GridIndex-1;
particle.GridIndex = nGrid*particle.GridIndex;
particle.GridIndex = particle.GridIndex + particle.GridSubIndex(j);
end
end
7、limitToPosition.m
%=============================
%限制变量变化范围在定义域内
%=============================
function Position = limitToPosition(Position,VarMin,VarMax)
for i =1:size(Position,2)
if Position(i)<VarMin
Position(i) = VarMin;
elseif Position(i) > VarMax
Position(i) = VarMax;
end
end
end
8、SelectLeader.m
%=============================
%从全局支配个体中找出一个最佳个体
%=============================
function leader = SelectLeader(rep,beta)
GI = [rep.GridIndex];
OC = unique(GI);
%一个栅格可能被多个支配解占用
N = zeros(size(OC));
for k =1:numel(OC)
N(k) = numel(find(GI == OC(k)));
end
% 计算选择概率,为了增加多样性,尽量不选多次出现的个体
% 如果N大P就小, 即多次出现的栅格点被选中的概率小
P = exp(-beta*N);
P = P/sum(P);
sci = RouletteWheelSelection(P); %轮盘赌策略选择
sc = OC(sci); % 轮盘赌选择的栅格点
SCM = find(GI==sc);
smi = randi([1 numel(SCM)]);
sm = SCM(smi);
leader = rep(sm); %当前全局最佳位置点
end
9、RouletteWheelSelection.m
%=============================
%轮盘赌选择一个较好的支配个体
%=============================
function i = RouletteWheelSelection(P)
r = rand;
C = cumsum(P);
i = find(r<=C,1,'first');
end
10、Mutate.m
%=============================
%使用变异策略
%=============================
function xnew = Mutate(x,pm,VarMin,VarMax)
nVar = numel(x);
j = randi([1 nVar]);
dx = pm*(VarMax-VarMin);
lb = x(j)-dx;
if lb<VarMin
lb=VarMin;
end
ub = x(j)+dx;
if ub > VarMax
ub = VarMax;
end
xnew = x;
xnew(j) = unifrnd(lb,ub);
end
11、DeleteOneRepMemebr.m
%=============================
%删除档案库中的一个个体
%=============================
function rep = DeleteOneRepMemebr(rep,gamma)
GI = [rep.GridIndex];
OC = unique(GI);
N = zeros(size(OC));
for k = 1:numel(OC)
N(k) = numel(find(GI == OC(k)));
end
P = exp(gamma*N);
P = P/sum(P);
sci = RouletteWheelSelection(P);
sc = OC(sci);
SCM = find(GI == sc);
smi = randi([1 numel(SCM)]);
sm = SCM(smi);
rep(sm) = [];
end