一、概述
机器学习模型经过训练后必须使用测试集进行评估。我们这样做是为了确保模型没有过度拟合,并确保它们适用于现实生活中的数据集,与训练集相比,这些数据集的分布可能略有偏差。
模型评估通常通过保留拆分执行,其中通常进行 80/20 拆分,并且80%的数据集用于训练模型。 20% 用于评估模型。但是为了使模型真正健壮,仅使用训练/测试拆分进行评估可能还不够。K-fold 交叉验证。通过跨多个折叠生成训练/测试拆分,您可以使用不同的拆分执行多个训练和测试会话。另外我们将了解如何将 K 折交叉验证与 PyTorch、Tensorflow 结合使用。
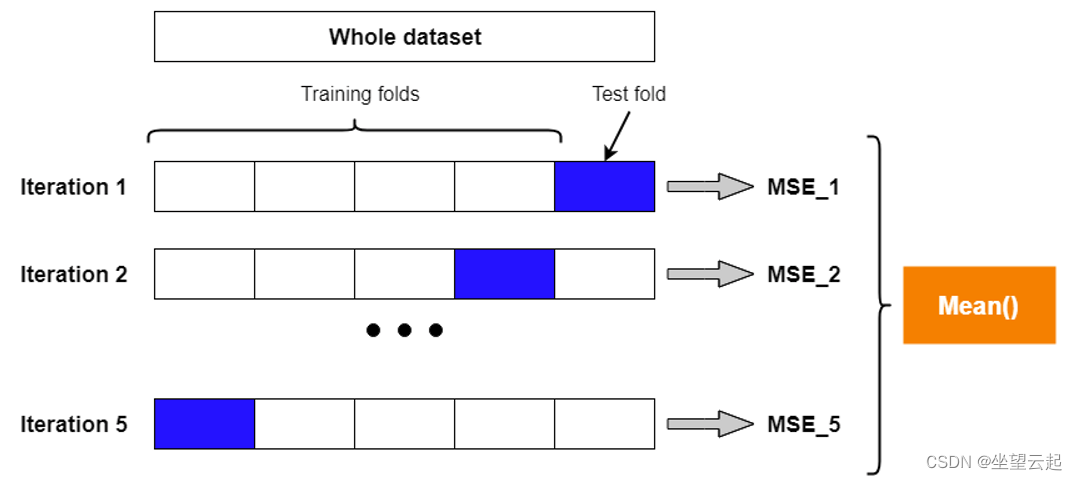
K-fold交叉验证是一种更强大的评估技术。 它将原始数据分成K组(K-Fold),将每个子集数据分别做一次验证集,其余的K-1组子集数据作为训练集,这样会得到K个模型。
假设我们将通过对 80% 的数据训练模型 5 次并在 20% 的数据上进行测试来进行 5 倍交叉验证。我们确保每个数据点在 20% 的测试集中恰好出现一次。因此,我们使用了我们必须的每个数据点,以帮助了解我们的模型在从一些数据中学习和预测一些新数据的任务方面表现如何。
但交叉验证的目的不是要得到我们的最终模型。我们不使用我们训练模型的这5个实例来进行任何真正的预测。为此,我们希望使用我们必须使用所有数据来提出可能的最佳模型。交叉验证的目的是模型检查,而不是模型构建。
现在,假设我们有两个模型,一个线性回归模型和一个神经网络。我们怎么能说哪个模型更好?我们可以进行 K 折交叉验证,看看哪一个在预测测试集点方面表现更好。但是,一旦我们使用交叉验证来选择性能更好的模型,我们就会在所有数据上训练该模型(无论是线性回归还是神经网络)。我们不会将在交叉验证期间训练的实际模型实例用于我们的最终预测模型。
二、K-fold + Pytorch
使用 Scikit-learn 的 KFold 功能在 PyTorch 中使用 K-fold 交叉验证的完整示例。
import os
import torch
from torch import nn
from torchvision.datasets import MNIST
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, ConcatDataset
from torchvision import transforms
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
def reset_weights(m):
'''
Try resetting model weights to avoid
weight leakage.
'''
for layer in m.children():
if hasattr(layer, 'reset_parameters'):
print(f'Reset trainable parameters of layer = {layer}')
layer.reset_parameters()
class SimpleConvNet(nn.Module):
'''
Simple Convolutional Neural Network
'''
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=3),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(26 * 26 * 10, 50),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(50, 20),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(20, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
'''Forward pass'''
return self.layers(x)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Configuration options
k_folds = 5
num_epochs = 1
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# For fold results
results = {}
# Set fixed random number seed
torch.manual_seed(42)
# 通过连接训练/测试部分来准备MNIST数据集
dataset_train_part = MNIST(os.getcwd(), download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor(), train=True)
dataset_test_part = MNIST(os.getcwd(), download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor(), train=False)
dataset = ConcatDataset([dataset_train_part, dataset_test_part])
# 定义 K 折交叉验证
kfold = KFold(n_splits=k_folds, shuffle=True)
# Start print
print('--------------------------------')
# K折交叉验证模型评估
for fold, (train_ids, test_ids) in enumerate(kfold.split(dataset)):
# Print
print(f'FOLD {fold}')
print('--------------------------------')
# Sample elements randomly from a given list of ids, no replacement.
train_subsampler = torch.utils.data.SubsetRandomSampler(train_ids)
test_subsampler = torch.utils.data.SubsetRandomSampler(test_ids)
# Define data loaders for training and testing data in this fold
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_size=10, sampler=train_subsampler)
testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_size=10, sampler=test_subsampler)
# Init the neural network
network = SimpleConvNet()
network.apply(reset_weights)
# Initialize optimizer
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(network.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
# Run the training loop for defined number of epochs
for epoch in range(0, num_epochs):
# Print epoch
print(f'Starting epoch {epoch+1}')
# Set current loss value
current_loss = 0.0
# Iterate over the DataLoader for training data
for i, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0):
# Get inputs
inputs, targets = data
# Zero the gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Perform forward pass
outputs = network(inputs)
# Compute loss
loss = loss_function(outputs, targets)
# Perform backward pass
loss.backward()
# Perform optimization
optimizer.step()
# Print statistics
current_loss += loss.item()
if i % 500 == 499:
print('Loss after mini-batch %5d: %.3f' %
(i + 1, current_loss / 500))
current_loss = 0.0
# Process is complete.
print('Training process has finished. Saving trained model.')
# Print about testing
print('Starting testing')
# Saving the model
save_path = f'./model-fold-{fold}.pth'
torch.save(network.state_dict(), save_path)
# Evaluationfor this fold
correct, total = 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
# Iterate over the test data and generate predictions
for i, data in enumerate(testloader, 0):
# Get inputs
inputs, targets = data
# Generate outputs
outputs = network(inputs)
# Set total and correct
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += targets.size(0)
correct += (predicted == targets).sum().item()
# Print accuracy
print('Accuracy for fold %d: %d %%' % (fold, 100.0 * correct / total))
print('--------------------------------')
results[fold] = 100.0 * (correct / total)
# Print fold results
print(f'K-FOLD CROSS VALIDATION RESULTS FOR {k_folds} FOLDS')
print('--------------------------------')
sum = 0.0
for key, value in results.items():
print(f'Fold {key}: {value} %')
sum += value
print(f'Average: {sum/len(results.items())} %')三、K-fold + Tensorflow
使用 Scikit-learn 的 KFold 功能在 Tensorflow 中使用 K-fold 交叉验证的完整示例。
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import cifar10
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, MaxPooling2D
from tensorflow.keras.losses import sparse_categorical_crossentropy
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
import numpy as np
# Merge inputs and targets
inputs = np.concatenate((input_train, input_test), axis=0)
targets = np.concatenate((target_train, target_test), axis=0)
# Define the K-fold Cross Validator
kfold = KFold(n_splits=num_folds, shuffle=True)
# K-fold Cross Validation model evaluation
fold_no = 1
for train, test in kfold.split(inputs, targets):
# Define the model architecture
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=input_shape))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(256, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(no_classes, activation='softmax'))
# Compile the model
model.compile(loss=loss_function, optimizer=optimizer, metrics=['accuracy'])
# Generate a print
print('------------------------------------------------------------------------')
print(f'Training for fold {fold_no} ...')
# Fit data to model
history = model.fit(inputs[train], targets[train],
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=no_epochs,
verbose=verbosity)
# Generate generalization metrics
scores = model.evaluate(inputs[test], targets[test], verbose=0)
print(f'Score for fold {fold_no}: {model.metrics_names[0]} of {scores[0]}; {model.metrics_names[1]} of {scores[1]*100}%')
acc_per_fold.append(scores[1] * 100)
loss_per_fold.append(scores[0])
# Increase fold number
fold_no = fold_no + 1