【玩转YOLOv5】YOLOv5的Openvino转换和部署
本文禁止转载!
1. YOLOv5环境配置:
可以看我之前写的几篇:
【小白CV教程】Pytorch训练YOLOv5并量化压缩(VOC格式数据集)
2. 修改模型文件:
由于YOLOv5的许多算子openvino仍然不支持,因此我们需要做出几点修改。首先我们需要将 Hardswish 激活函数替换掉,换成 LeackyReLU。
具体修改的地方有:
1. models/yolo.py
models/yolo.py:
# 第32行
self.act = nn.Hardswish() if act else nn.Identity()
修改为:
# 第32行
self.act = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True) if act else nn.Identity()
2. models/export.py
# 第46行
if isinstance(m, models.common.Conv) and isinstance(m.act, nn.Hardswish):
m.act = Hardswish() # assign activation
修改为:
# 第46行
if isinstance(m, models.common.Conv) and isinstance(m.act, nn.LeakyReLU):
m.act = LeakyReLU() # assign activation
3. utils/torch_utils.py
# 第90行
elif t in [nn.Hardswish, nn.LeakyReLU, nn.ReLU, nn.ReLU6]:
修改为:
# 第90行
elif t in [nn.LeakyReLU, nn.LeakyReLU, nn.ReLU, nn.ReLU6]:
3. 训练模型:
然后训练模型:
python train.py --img 640 --batch 8 --epoch 100 --data ./data/voc.yaml --cfg ./models/yolov5m.yaml --weights weights/yolov5m.pt --workers 16 --device 0,1,2,3 --multi-scale --name 1206

其中 name 参数是模型保存的路径,我的训练好的模型权重就被保存在 runs/train/exp0_1206/weights 文件夹下,名称为 last.pt:


4. torch模型转onnx:
yolov5 官方给出了转换的代码,就是 models/export.py 代码,由于我们还需要将他转到 openvino,所以我们需要做出一点修改:
# 第53行
torch.onnx.export(model, img, f, verbose=False, opset_version=11, input_names=['data'],
output_names=['prob']if y is None else ['output'])
修改为:
# 第53行
torch.onnx.export(model, img, f, verbose=False, opset_version=10, input_names=['data'],
output_names=['prob']if y is None else ['output'])
否则 11 版本的算子库在转到openvino会报错。
将 export.py 放置在根目录:
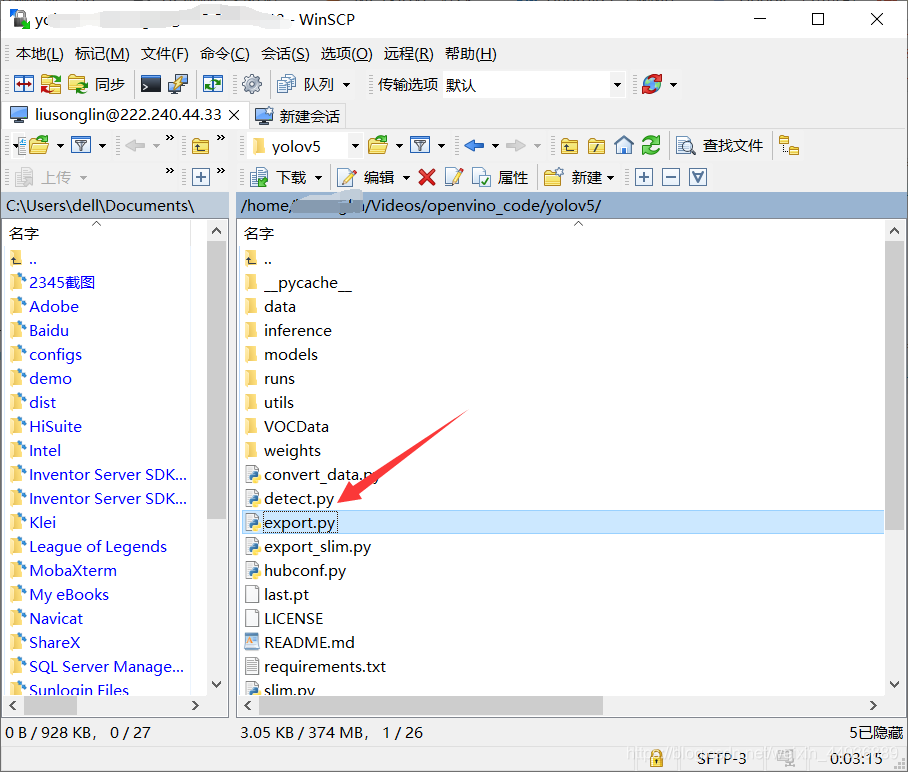
运行以下命令进行转换:
python export.py --weights runs/exp0_1206/weights/last.pt --img-size 640 --batch-size 1
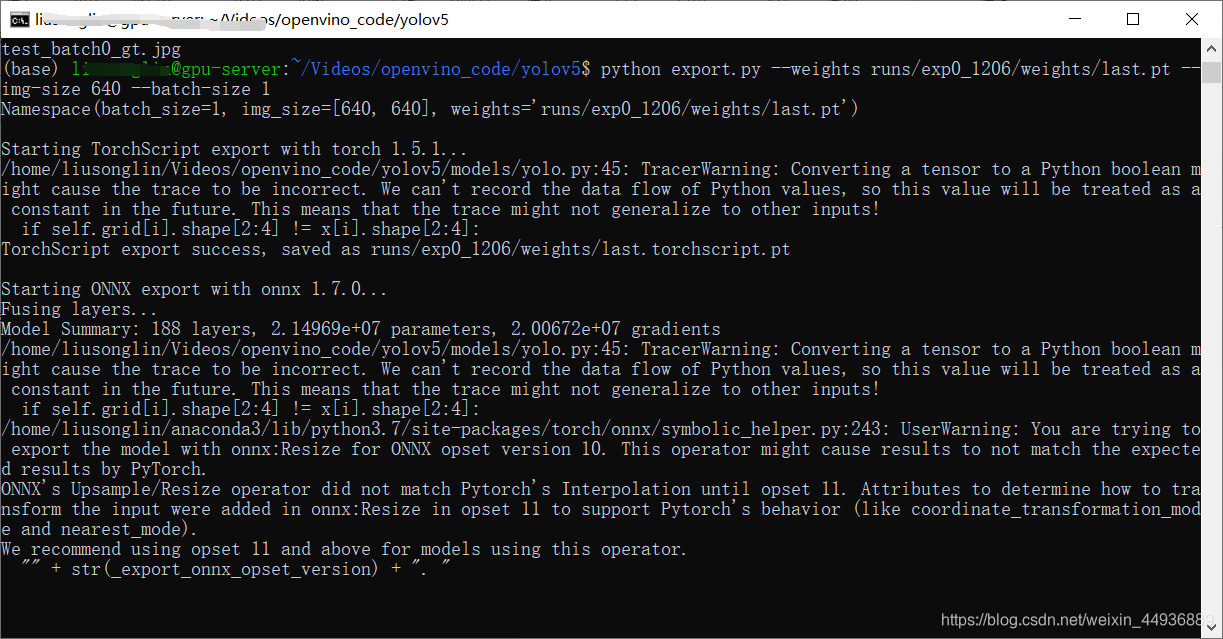
转换成功:
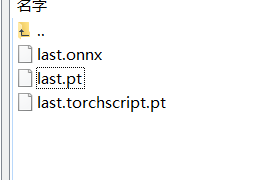
可以看到 runs/exp0_1206/weights/ 目录下生成了 last.onnx 文件:
5. onnx转openvino:
5.1 激活环境:
这里我没有在 Linux 服务器配置 openvino 环境,因此我下载到我的 Windows 进行转换。
首先我们打开 openvino 模型转换目录,将 last.onnx 拷贝进去:

我本地的目录是:
C:\Program Files (x86)\IntelSWTools\openvino\deployment_tools\model_optimizer
在该目录打开 cmd,激活 conda 和 openvino环境:
activate torch107
"C:\Program Files (x86)\IntelSWTools\openvino_2020.4.287\bin\setupvars.bat"

5.2 安装依赖:
pip install -r requirements_onnx.txt

5.3 脚本转换:
运行模型转换脚本:
python mo.py --input_model last.onnx --output_dir E:\result --input_shape [1,3,640,640] --data_type FP16
(这里导出半精度模型)

转换成功:

可以看到模型输出路径下生成了 bin 和 xml 文件:

6. 模型测试:
我们创建 run.py:
from __future__ import print_function
import logging as log
import os
import pathlib
import json
import cv2
import numpy as np
from openvino.inference_engine import IENetwork, IECore
import torch
import torchvision
import time
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = torch.zeros_like(x) if isinstance(
x, torch.Tensor) else np.zeros_like(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def non_max_suppression(prediction, conf_thres=0.1, iou_thres=0.6, merge=False, classes=None, agnostic=False):
"""Performs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results
Returns:
detections with shape: nx6 (x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, cls)
"""
prediction = torch.from_numpy(prediction)
if prediction.dtype is torch.float16:
prediction = prediction.float() # to FP32
nc = prediction[0].shape[1] - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Settings
# (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096
max_det = 300 # maximum number of detections per image
time_limit = 10.0 # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label = nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
t = time.time()
output = [None] * prediction.shape[0]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5, None], j[:, None].float()), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float()), 1)[
conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not torch.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[torch.isfinite(x).all(1)]
# If none remain process next image
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n:
continue
# Sort by confidence
# x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)]
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
# boxes (offset by class), scores
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4]
i = torchvision.ops.boxes.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres)
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
try: # update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float(
) / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
except: # possible CUDA error https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/1139
print(x, i, x.shape, i.shape)
pass
output[xi] = x[i]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
break # time limit exceeded
return output
device = 'CPU'
# device = 'CPU'
input_h, input_w, input_c, input_n = (640, 640, 3, 1)
log.basicConfig(level=log.DEBUG)
# For objection detection task, replace your target labels here.
label_id_map = ["face", "normal", "phone",
"write", "smoke", "eat", "computer", "sleep"]
exec_net = None
def init(model_xml):
if not os.path.isfile(model_xml):
log.error(f'{model_xml} does not exist')
return None
model_bin = pathlib.Path(model_xml).with_suffix('.bin').as_posix()
net = IENetwork(model=model_xml, weights=model_bin)
ie = IECore()
global exec_net
exec_net = ie.load_network(network=net, device_name=device)
input_blob = next(iter(net.inputs))
n, c, h, w = net.inputs[input_blob].shape
global input_h, input_w, input_c, input_n
input_h, input_w, input_c, input_n = h, w, c, n
return net
def process_image(net, input_image):
if not net or input_image is None:
log.error('Invalid input args')
return None
ih, iw, _ = input_image.shape
if ih != input_h or iw != input_w:
input_image = cv2.resize(input_image, (input_w, input_h))
input_image = cv2.cvtColor(input_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
input_image = input_image/255
input_image = input_image.transpose((2, 0, 1))
images = np.ndarray(shape=(input_n, input_c, input_h, input_w))
images[0] = input_image
input_blob = next(iter(net.inputs))
out_blob = next(iter(net.outputs))
start = time.time()
res = exec_net.infer(inputs={
input_blob: images})
end = time.time()
print('-[INFO] inference time: {}ms'.format(end - start))
data = res[out_blob]
data = non_max_suppression(data, 0.4, 0.5)
detect_objs = []
if data[0] == None:
return json.dumps({
"objects": detect_objs})
else:
data = data[0].numpy()
for proposal in data:
if proposal[4] > 0:
confidence = proposal[4]
xmin = np.int(iw * (proposal[0]/640))
ymin = np.int(ih * (proposal[1]/640))
xmax = np.int(iw * (proposal[2]/640))
ymax = np.int(ih * (proposal[3]/640))
detect_objs.append((
int(xmin),
int(ymin),
int(xmax),
int(ymax),
label_id_map[int(proposal[5])],
float(confidence)
))
return detect_objs
def plot_bboxes(image, bboxes, line_thickness=None):
# Plots one bounding box on image img
tl = line_thickness or round(
0.002 * (image.shape[0] + image.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness
for (x1, y1, x2, y2, cls_id, pos_id) in bboxes:
if cls_id == 'smoke' or cls_id == 'phone':
color = (0, 0, 255)
else:
color = (0, 255, 0)
c1, c2 = (x1, y1), (x2, y2)
cv2.rectangle(image, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(cls_id, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
cv2.rectangle(image, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(image, '{} ID-{}'.format(cls_id, pos_id), (c1[0], c1[1] - 2), 0, tl / 3,
[225, 255, 255], thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
return image
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Test API
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--model_xml', type=str, default='result\last.xml')
parser.add_argument('--source', type=str, default='images')
opt = parser.parse_args()
predictor = init(opt.model_xml)
for p in os.listdir(opt.source):
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(opt.source, p))
result = process_image(predictor, img)
img = plot_bboxes(img, result)
cv2.imshow('result', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
运行:
python --model_xml result\last.xml --source images
其中两个参数分别为模型路径和测试图片路径,运行结果如图:

大概 CPU 能跑到 200+ FPS。




7. 交流群:

关注我的公众号:
感兴趣的同学关注我的公众号——可达鸭的深度学习教程:

