目录
为增加用户认证和鉴权的功能。用户 应当存储在数据库中,并且每一个 便笺 应当关联到创建它的 用户。只有 便笺 的创建者才有删除和编辑它的权利。
从向数据库添加用户信息开始。User 和 Note 是典型的一对多关系

关系型数据库来实现会显得比较直白。每个资源都会有独立的数据库表,而创建 便笺 的 用户 ID 作为 便笺 的外键进行存储。
但如果我们使用文档数据库,就会有一些不同,体现在实现这种模型会有多种不同的方式。
目前我们是将所有的 便笺 存储在了数据库的 notes collection 中。如果我们不想改变现有的 collection, 可以将 用户 存储在另一个 collection 中, 比如users 这个 collection。
与所有的文档数据库一样,我们可以使用 Mongo 的对象 id 来引用存储其他 collection 中的文档。这有点像关系型数据库的外键。
传统的文档数据库,例如 Mongo 是不支持join queries的,但这在关系型数据库却很常见,用来聚合不同表中的数据。
如果需要一个类似 join queries 的功能,可以在应用中利用 multiple queries 来实现这个需求。在特定的场景下,Mongoose 可以处理 join 和聚合数据,使它看起来像 join 查询 一样。但是 Mongoose 其实也是在后台数据库使用了 multiple query。
References across collections
【跨 collection 引用】
如果使用关系型数据库,Note 会包含一个 外键 来指向创建它的 User。文档数据库中也可以这么做。
我们假定users collection 包含两个 User
[
{
username: 'mluukkai',
_id: 123456,
},
{
username: 'hellas',
_id: 141414,
},
];notes collection 包含三个 Note, 每个 Note 都有一个user 字段 来指向users collection 中的一个 user。
[
{
content: 'HTML is easy',
important: false,
_id: 221212,
user: 123456,
},
{
content: 'The most important operations of HTTP protocol are GET and POST',
important: true,
_id: 221255,
user: 123456,
},
{
content: 'A proper dinosaur codes with Java',
important: false,
_id: 221244,
user: 141414,
},
]文档型数据库并不要求外键存储在 Note 资源中,它可以存储在 User Collection 中,甚至可以在 Note 和 User 中都存一份。
[
{
username: 'mluukkai',
_id: 123456,
notes: [221212, 221255],
},
{
username: 'hellas',
_id: 141414,
notes: [221244],
},
]既然 User 可以包含许多个 Note, 那么存储 Note id 的 字段 就应该是一个数组。
文档型数据库还提供了一个完全不同的方式组织数据:将所有的 note 以数组的形式作为每个文档的一部分嵌套在 user collection 中。
[
{
username: 'mluukkai',
_id: 123456,
notes: [
{
content: 'HTML is easy',
important: false,
},
{
content: 'The most important operations of HTTP protocol are GET and POST',
important: true,
},
],
},
{
username: 'hellas',
_id: 141414,
notes: [
{
content:
'A proper dinosaur codes with Java',
important: false,
},
],
},
]这种 Shema 下 Note 会紧密地嵌套于 User 之中,数据库也不会为它们(指 Note)生成 ID
这种数据库结构和 schema 不像关系型数据库那样自我解释。所选择的 schema 必须最大化地支撑应用的用例。这并不是简单的设计决策,因为在设计决策时并不能对每一种用户用例都考虑周全。
与关系型数据库相比,像 Mongo 这种弱 Schema 类型的数据库要求开发者在项目的开始阶段做更多的这种关于数据组织的设计决定。
关系型数据库为应用提供的是一种或多或少合适可用的组织数据的方式。
Mongoose schema for users
我们将 note 的 id 以数组的形式存储到 user 当中。让我们定义一个 model 来表示 User , models/user.js 代码如下:
const mongoose = require('mongoose')
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
username: String,
name: String,
passwordHash: String,
notes: [
{
type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,
ref: 'Note'
}
],
})
userSchema.set('toJSON', {
transform: (document, returnedObject) => {
returnedObject.id = returnedObject._id.toString()
delete returnedObject._id
delete returnedObject.__v
// the passwordHash should not be revealed
delete returnedObject.passwordHash
}
})
const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema)
module.exports = UserNote 的 ID 以数组的形式存储在了 User 当中,定义如下:
{
type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,
ref: 'Note'
}type 字段 是ObjectId,引用了 note 的文档类型。Mongo 本质上并不知道这是一个引用 Note 的字段,这种语法完全是与 Mongoose 的定义有关。
让我们展开 model/note.js 文件中 note 的 schema,让 note 包含其创建者的信息。
const noteSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
content: {
type: String,
required: true,
minlength: 5
},
date: Date,
important: Boolean,
user: { type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: 'User' }})与关系型数据库形成鲜明对比,引用被同时存储在了两个 document 中。 Note 引用了创建它的 User, User 引用了它所创建的 Note 的数组。
Creating users
【创建 User】
实现一个创建 User 的路由。User 拥有一个唯一的username, 一个name 以及一个passwordHash。 password 的 hash 是一个 单向 Hash 函数的输出,用来存储 User 的密码。不要以明文的方式将密码存储在数据库中。
安装bcrypt 用来生成密码的哈希值。
npm install bcrypt通过 HTTP 向users发送 POST 请求,按照 RESTful 约定创建用户。
定义一个独立的router 来处理controllers/users.js 中的 User。并在 app.js 中使用这个路由,处理对 /api/users 发出的请求。
const usersRouter = require('./controllers/users')
// ...
app.use('/api/users', usersRouter)定义路由的代码:
const bcrypt = require('bcrypt')
const usersRouter = require('express').Router()
const User = require('../models/user')
usersRouter.post('/', async (request, response) => {
const body = request.body
const saltRounds = 10
const passwordHash = await bcrypt.hash(body.password, saltRounds)
const user = new User({
username: body.username,
name: body.name,
passwordHash,
})
const savedUser = await user.save()
response.json(savedUser)
})
module.exports = usersRouterrequest 当中的密码并没有直接存储在数据库中。我们存储的是 bcrypt.hash 函数生成的 hash 值
当前代码不包含任何用于验证用户名和密码的功能,如用户名和密码是否为所需格式等错误处理或输入校验。
编写自动化测试将使应用的开发更加容易。
最初的测试:
const bcrypt = require('bcrypt')
const User = require('../models/user')
//...
describe('when there is initially one user in db', () => {
beforeEach(async () => {
await User.deleteMany({})
const passwordHash = await bcrypt.hash('sekret', 10)
const user = new User({ username: 'root', passwordHash })
await user.save()
})
test('creation succeeds with a fresh username', async () => {
const usersAtStart = await helper.usersInDb()
const newUser = {
username: 'mluukkai',
name: 'Matti Luukkainen',
password: 'salainen',
}
await api
.post('/api/users')
.send(newUser)
.expect(200)
.expect('Content-Type', /application\/json/)
const usersAtEnd = await helper.usersInDb()
expect(usersAtEnd).toHaveLength(usersAtStart.length + 1)
const usernames = usersAtEnd.map(u => u.username)
expect(usernames).toContain(newUser.username)
})
})测试使用了tests/test_helper.js 文件中的 usersInDb() 这个辅助函数。这个函数用来帮助我们验证创建完一个用户后的数据库的状态。
const User = require('../models/user')
// ...
const usersInDb = async () => {
const users = await User.find({})
return users.map(u => u.toJSON())
}
module.exports = {
initialNotes,
nonExistingId,
notesInDb,
usersInDb,
}beforeEach 代码块向数据库增加了一个用户名为root 的 User。写一个新的测试用来验证拥有相同用户名的用户不能被创建出来。
describe('when there is initially one user in db', () => {
// ...
test('creation fails with proper statuscode and message if username already taken', async () => {
const usersAtStart = await helper.usersInDb()
const newUser = {
username: 'root',
name: 'Superuser',
password: 'salainen',
}
const result = await api
.post('/api/users')
.send(newUser)
.expect(400)
.expect('Content-Type', /application\/json/)
expect(result.body.error).toContain('`username` to be unique')
const usersAtEnd = await helper.usersInDb()
expect(usersAtEnd).toHaveLength(usersAtStart.length)
})
})实际上是在实践测试驱动开发 TDD,也就是在函数实现之前先写测试用例。
在 Mongoose validator 的帮助下验证用户名的唯一性。Mongoose 并没有内置的 validator 来检查某个字段的唯一性。我们可以使用一个现成的解决方案mongoose-unique-validator 这个 npm 包,先安装一下:
npm install mongoose-unique-validator对models/user.js 定义的 schema 做如下修改:
const mongoose = require('mongoose')
const uniqueValidator = require('mongoose-unique-validator')
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
username: {
type: String,
unique: true },
name: String,
passwordHash: String,
notes: [
{
type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,
ref: 'Note'
}
],
})
userSchema.plugin(uniqueValidator)
// ...同样可以在创建 User 的时候实现其他验证。比如我们可以检查用户名的长度,检查仅可以使用合法字符,或者密码的强度是否足够。
增加一个路由的初始实现,即返回数据库中的所有用户:
usersRouter.get('/', async (request, response) => {
const users = await User.find({})
response.json(users)
})这个列表看起来像这样: 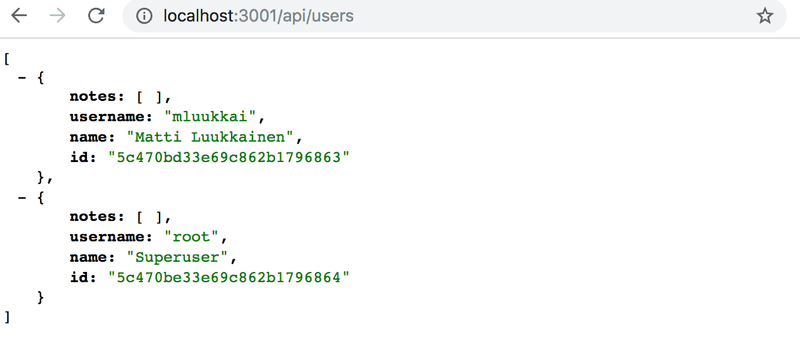
Creating a new note
【创建一个新 Note】
创建新 Note 的代码同样也需要更新,以便指向创建它的 User。
展开当前实现,在 request body 的userId 发送关于创建 Note 的信息。
const User = require('../models/user')
//...
notesRouter.post('/', async (request, response, next) => {
const body = request.body
const user = await User.findById(body.userId)
const note = new Note({
content: body.content,
important: body.important === undefined ? false : body.important,
date: new Date(),
user: user._id })
const savedNote = await note.save()
user.notes = user.notes.concat(savedNote._id) await user.save()
response.json(savedNote.)
})user同样变化了。Note 的 id 存储在了 notes field 中。
const user = await User.findById(body.userId)
// ...
user.notes = user.notes.concat(savedNote._id)
await user.save()尝试创建一个新的 Note
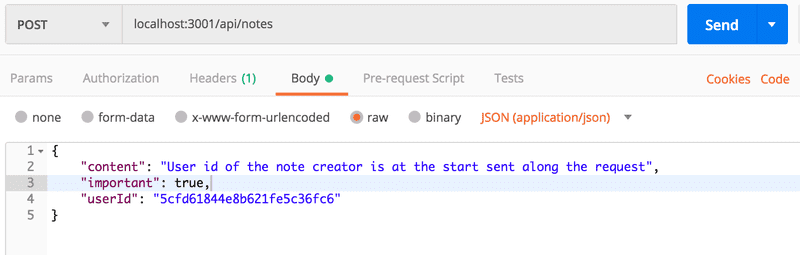
操作看起来起作用了。让我们增加另一个 Note ,并访问获取所有 User 的路由。
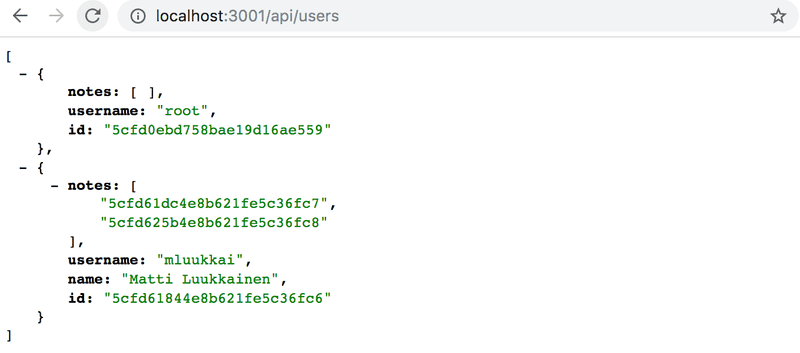
可以看到 User 拥有两个 Note 了。
同样,User 的 id 同样创建在了 Note 中。
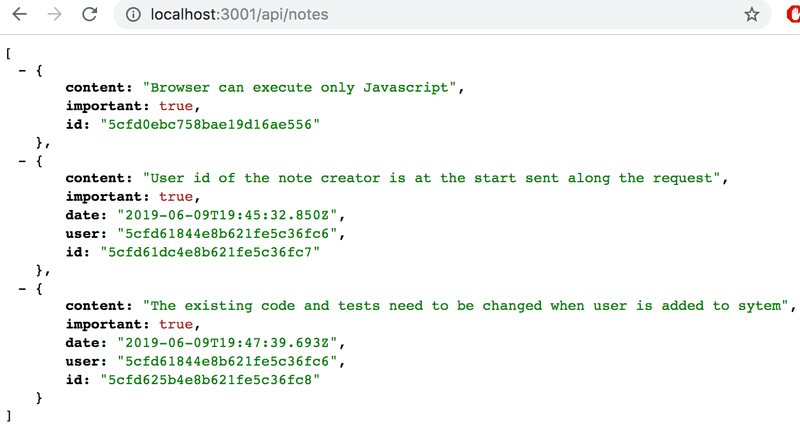
Populate
如果希望当一个 HTTP GET 请求到/api/users 路由时,User 对象同样包含其创建 Note 的内容,而不仅仅是 Note 的 id。 在关系型数据库中,这个功能需求可以通过 join query 实现。
文档型数据库不能很好地支持 collection 之间的 join queries,但是 Mongoose 库可以做一些类似 join 的工作。Mongoose 是通过 multiple queries 来实现这种类 join 查询的,这与关系型数据库中的事务性 join 查询不同,也就是数据库的状态在查询执行期间并不改变。而使用 Mongoose 的 join 查询,并不能保证 collection 在 join 时的状态是一致的,也就是如果我们在进行 Note 和 User 的 join 查询后,在查询期间 collection 的状态可能发生变化。
Mongoose 的 join 是通过populate 方法完成的。更新返回所有 User 的路由:
usersRouter.get('/', async (request, response) => {
const users = await User
.find({}).populate('notes')
response.json(users)
})populate 方法是 find 方法这一初始查询方法后的一个链式调用。populate 方法的入参,定义了存储在 User 中的 Note id, 这些 id 指向了 Note Collection 的 Note,而这些 id 也会被真实的 Note 所替代。
结果正如预期的那样:
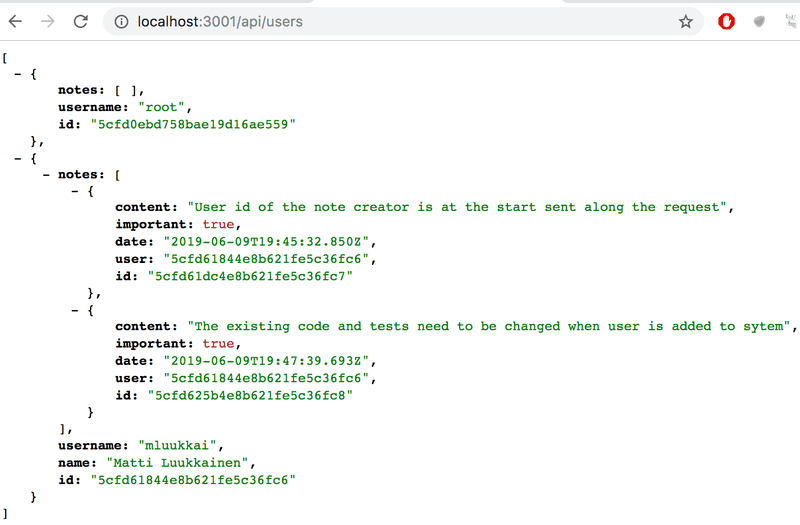
可以使用 populate 的参数来选择我们想要包含的文档 field。field 的选择遵循 Mongo 的语法:
usersRouter.get('/', async (request, response) => {
const users = await User
.find({}).populate('notes', { content: 1, date: 1 })
response.json(users)
});结果也如预期:
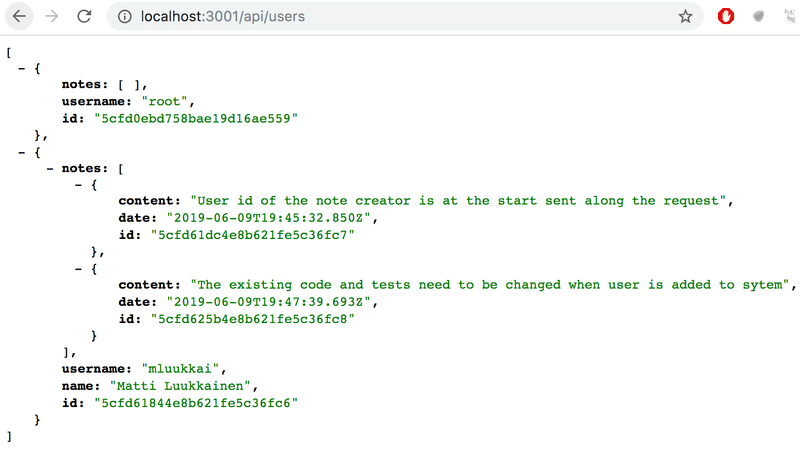
增加一组的 User 信息到 Note 中:
notesRouter.get('/', async (request, response) => {
const notes = await Note
.find({}).populate('user', { username: 1, name: 1 })
response.json(notes)
});现在用户的信息已经被添加到 Note 对象的user field 中。
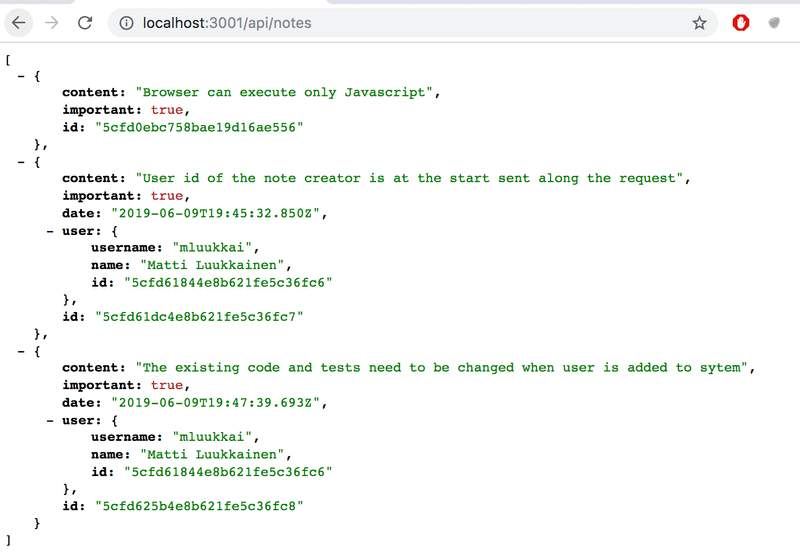
数据库实际上并不知道 Note 中user field 中的 id 实际指向了 User collection 中的 User。
Mongoose 中populate 方法的功能是基于, 们已经用 ref 选项为 Mongoose Schema 中的引用定义了类型:
const noteSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
content: {
type: String,
required: true,
minlength: 5
},
date: Date,
important: Boolean,
user: {
type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,
ref: 'User'
}
})