
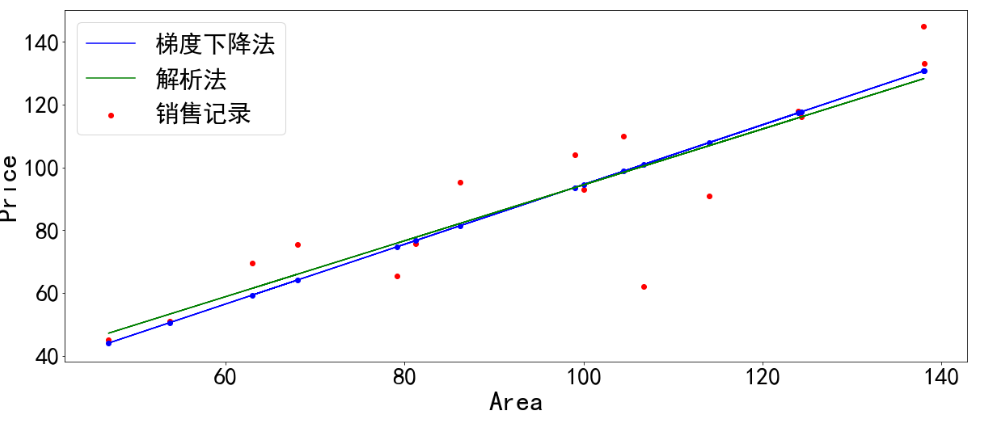


下面是一个梯度下降法对多元问题的求解:
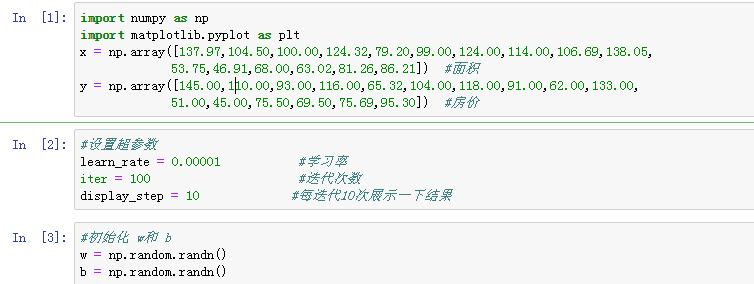
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Simhei'] 4 5 area = np.array([137.97,104.50,100.00,124.32,79.20,99.00,124.00,114.00,106.69,138.05, 6 53.75,46.91,68.00,63.02,81.26,86.21]) #面积 7 room = np.array([3,2,2,3,1,2,3,2,2,3,1,1,1,1,2,2]) #房间数 8 price = np.array([145.00,110.00,93.00,116.00,65.32,104.00,118.00,91.00,62.00,133.00, 9 51.00,45.00,75.50,69.50,75.69,95.30]) #房价 10 num = len(area) 11 x0 = np.ones(num) 12 x1 = (area - area.min())/(area.max() - area.min()) #对房间面积进行标准化 13 x2 = (room - room.min())/(room.max() - room.min()) #对房间数进行标准化 14 15 X = np.stack((x0,x1,x2), axis = 1) 16 Y = price.reshape(-1,1) 17 18 #设置超参数 19 learn_rate = 0.001 20 iter = 500 21 display_step = 50 22 23 #初始化w 24 np.random.seed(612) 25 W = np.random.randn(3,1)
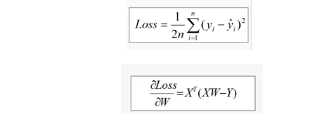
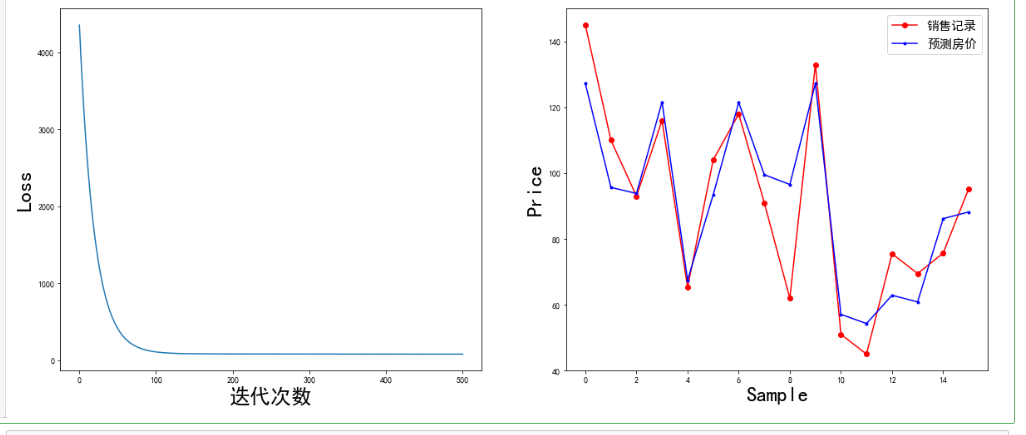
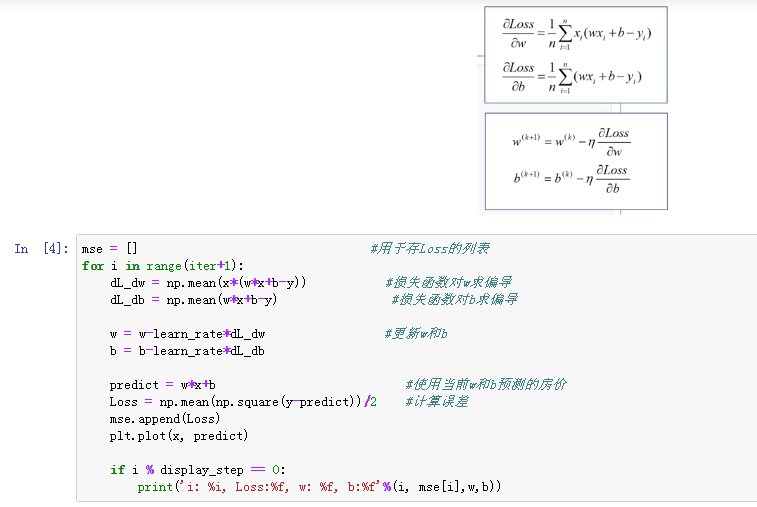
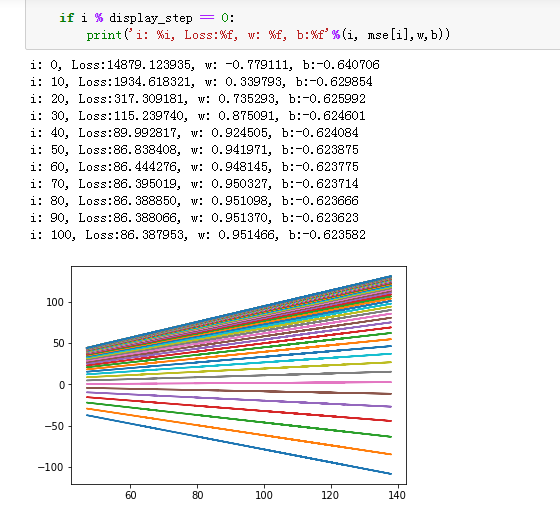
1 #训练模型 2 mse = [] 3 for i in range(iter+1): 4 dL_dw = np.matmul(np.transpose(X),np.matmul(X,W)-Y) #对W的偏导 5 W = W-learn_rate*dL_dw #更新权值 6 7 PREDIC = np.matmul(X,W) #房价估计值 8 Loss = np.mean(np.square(Y-PREDIC))/2 9 mse.append(Loss) 10 11 if i % display_step ==0: 12 print('i: %i, Loss:%f'%(i,mse[i])) 13 14 #可视化结果 15 plt.figure(figsize=(20,8)) 16 17 plt.subplot(1,2,1) 18 plt.plot(mse) 19 plt.xlabel('迭代次数', fontsize = 25) 20 plt.ylabel('Loss', fontsize = 25) 21 22 plt.subplot(1,2,2) 23 PREDIC = PREDIC.reshape(-1) 24 plt.plot(price,color = 'red', marker = 'o', label = '销售记录') 25 plt.plot(PREDIC, color = 'blue', marker = '.', label='预测房价') 26 plt.xlabel('Sample', fontsize = 25) 27 plt.ylabel('Price', fontsize=25) 28 29 plt.legend(fontsize=15) 30 plt.show()