本文来源于liuyubobobo的“算法与数据结构--综合提升篇”视频教程
图的基本概念
先了解图的一些概念。
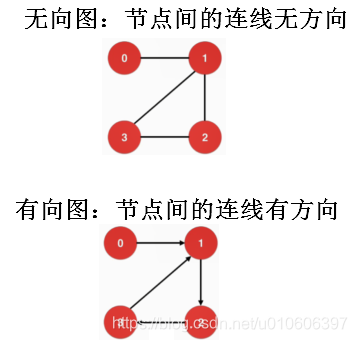

图在数学、代码中的实现方式,
一般来说使用邻接矩阵表示稠密图,使用邻接表表示稀疏图。下面会对邻接矩阵、邻接表加以说明。

实现代码:
// 稠密图 -- 邻接矩阵
public class DenseGraph {
private int nodeTotal; // 节点数
private int nodeEdgeNum; // 节点的边数
private boolean directed; // 是否为有向图
private boolean[][] data2Arr; // 图的具体数据
// 构造函数
public DenseGraph( int nodeTotal , boolean directed ){
assert nodeTotal >= 0;
this.nodeTotal = nodeTotal;
this.nodeEdgeNum = 0; // 初始化没有任何边
this.directed = directed;
// boolean型变量的默认值为false
// 图的数据data2Arr初始化为nodeTotal*nodeTotal的布尔矩阵, 每一个data2Arr[i][j]均为false, 表示没有任何边
data2Arr = new boolean[nodeTotal][nodeTotal];
}
public int getNodeTotal(){ return nodeTotal;} // 返回节点个数
public int getNodeEdgeNum(){ return nodeEdgeNum;} // 返回节点边的个数
// 向图中添加一个边
public void addEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
if( hasEdge(node1, node2) )
return;
data2Arr[node1][node2] = true;
if( !directed ){
//无向图,node2、node1也相连
data2Arr[node2][node1] = true;
}
nodeEdgeNum++;
}
// 验证图中是否有从node1到node2的边
public boolean hasEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
return data2Arr[node1][node2];
}
// 显示图的信息
public void show(){
for(int i = 0; i < nodeTotal; i ++ ){
for(int j = 0; j < nodeTotal; j ++ )
System.out.print(data2Arr[i][j]+"\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DenseGraph dg = new DenseGraph(4, false);
dg.addEdge(1,2);
dg.show();
}
}
实现代码
public class SparseGraph {
private int nodeTotal; // 节点数
private int nodeEdgeNum; // 节点的边数
private boolean directed; // 是否为有向图
private Vector<Integer>[] dataArrVector; // 图的具体数据
// 构造函数
public SparseGraph( int nodeTotal , boolean directed ){
assert nodeTotal >= 0;
this.nodeTotal = nodeTotal;
this.nodeEdgeNum = 0; // 初始化没有任何边
this.directed = directed;
// dataArrVector初始化为nodeTotal个空的vector, 表示每一个dataArrVector[i]都为空, 即没有任何边
dataArrVector = (Vector<Integer>[])new Vector[nodeTotal];
for(int i = 0 ; i < nodeTotal ; i ++)
dataArrVector[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
}
public int getNodeTotal(){ return nodeTotal;} // 返回节点个数
public int getNodeEdgeNum(){ return nodeEdgeNum;} // 返回节点边的个数
// 向图中添加一个边
public void addEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
dataArrVector[node1].add(node2);
if( node1 != node2 && !directed )
dataArrVector[node2].add(node1);
nodeEdgeNum++;
}
// 验证图中是否有从node1到node2的边
public boolean hasEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
for(int i = 0; i < dataArrVector[node1].size() ; i ++ )
if( dataArrVector[node1].elementAt(i) == node2)
return true;
return false;
}
// 显示图的信息
public void show(){
for(int i = 0; i < nodeTotal; i ++ ){
System.out.print("vertex " + i + ":\t");
for(int j = 0; j < dataArrVector[i].size() ; j ++ )
System.out.print(dataArrVector[i].elementAt(j) + "\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparseGraph dg = new SparseGraph(4, false);
dg.addEdge(1,2);
dg.show();
}
}从数据文件中读取一个图
一般来说,图中点、边的数据是记录在一个文件中的,下面创建三个TXT文件,记录图的点和边的关系。
下面给出两个数据文件

testG1.txt
13 13
0 5
4 3
0 1
9 12
6 4
5 4
0 2
11 12
9 10
0 6
7 8
9 11
5 3
testG2.txt
6 8
0 1
0 2
0 5
1 2
1 3
1 4
3 4
3 5
testG.txt
7 8
0 1
0 2
0 5
0 6
3 4
3 5
4 5
4 6
定义一个图的接口
// 图的接口
public interface Graph {
public int getNodeTotal();
public int getNodeEdgeNum();
public void addEdge(int v, int w);
boolean hasEdge(int v, int w);
void show();
public Iterable<Integer> getNodeEdges(int v);
}创建读取图的类
/**
* 从文件中读取一个图
*/
public class ReadGraph {
private Scanner scanner;
/**
* 读取文件,创建一个图
* @param graph
* @param filename
*/
public ReadGraph(Graph graph, String filename) {
// 读取文件
readFile(filename);
try {
// 文件第一行的两个数字是点数、边数
int V = scanner.nextInt();
if (V < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("定点数非负");
assert V == graph.getNodeTotal();
int E = scanner.nextInt();
if (E < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("边数非负");
// 从第二行开始,将数据添加到图对象中
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int v = scanner.nextInt();
int w = scanner.nextInt();
assert v >= 0 && v < V;
assert w >= 0 && w < V;
graph.addEdge(v, w);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void readFile(String filename) {
assert filename != null;
try {
File file = new File(filename);
if (file.exists()) {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
scanner = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(fis), "UTF-8");
scanner.useLocale(Locale.ENGLISH);
} else{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(filename + "doesn't exist.");
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not open " + filename, ioe);
}
}
}图的深度遍历、连通分量

深度遍历、连通分量代码、深度遍历寻址:
// 稠密图 -- 邻接矩阵
public class DenseGraph implements Graph{
private int nodeTotal; // 节点数
private int nodeEdgeNum; // 节点的边数
private boolean directed; // 是否为有向图
private boolean[][] data2Arr; // 图的具体数据
// 构造函数
public DenseGraph(int nodeTotal , boolean directed ){
assert nodeTotal >= 0;
this.nodeTotal = nodeTotal;
this.nodeEdgeNum = 0; // 初始化没有任何边
this.directed = directed;
// boolean型变量的默认值为false
// 图的数据data2Arr初始化为nodeTotal*nodeTotal的布尔矩阵, 每一个data2Arr[i][j]均为false, 表示没有任何边
data2Arr = new boolean[nodeTotal][nodeTotal];
}
public int getNodeTotal(){ return nodeTotal;} // 返回节点个数
public int getNodeEdgeNum(){ return nodeEdgeNum;} // 返回节点边的个数
// 向图中添加一个边
public void addEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
if( hasEdge(node1, node2) )
return;
data2Arr[node1][node2] = true;
if( !directed ){
//无向图,node2、node1也相连
data2Arr[node2][node1] = true;
}
nodeEdgeNum++;
}
// 验证图中是否有从node1到node2的边
public boolean hasEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
return data2Arr[node1][node2];
}
// 显示图的信息
public void show(){
for(int i = 0; i < nodeTotal; i ++ ){
for(int j = 0; j < nodeTotal; j ++ )
System.out.print(data2Arr[i][j]+"\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 获取相邻节点
* @param node
* @return
*/
public Iterable<Integer> adjacentNode(int node){
assert node >= 0 && node < nodeTotal;
Vector<Integer> nodeVector = new Vector<>();
// data2Arr[node]是一个数组,遍历此数组
for (int i=0; i<nodeTotal; i++){
// data2Arr[node][i]为true,则node和数值为i的节点相连
if (data2Arr[node][i]){
// 将节点i添加到数组中
nodeVector.add(i);
}
}
return nodeVector;
}
}
// 稀疏图 -- 邻接表
public class SparseGraph implements Graph{
private int nodeTotal; // 节点数
private int nodeEdgeNum; // 节点的边数
private boolean directed; // 是否为有向图
private Vector<Integer>[] dataArrVector; // 图的具体数据
// 构造函数
public SparseGraph(int nodeTotal , boolean directed ){
assert nodeTotal >= 0;
this.nodeTotal = nodeTotal;
this.nodeEdgeNum = 0; // 初始化没有任何边
this.directed = directed;
// dataArrVector初始化为nodeTotal个空的vector, 表示每一个dataArrVector[i]都为空, 即没有任何边
dataArrVector = (Vector<Integer>[])new Vector[nodeTotal];
for(int i = 0 ; i < nodeTotal ; i ++)
dataArrVector[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
}
public int getNodeTotal(){ return nodeTotal;} // 返回节点个数
public int getNodeEdgeNum(){ return nodeEdgeNum;} // 返回节点边的个数
// 向图中添加一个边
public void addEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
dataArrVector[node1].add(node2);
if( node1 != node2 && !directed )
dataArrVector[node2].add(node1);
nodeEdgeNum++;
}
// 验证图中是否有从node1到node2的边
public boolean hasEdge(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < nodeTotal;
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < nodeTotal;
for(int i = 0; i < dataArrVector[node1].size() ; i ++ )
if( dataArrVector[node1].elementAt(i) == node2)
return true;
return false;
}
// 显示图的信息
public void show(){
for(int i = 0; i < nodeTotal; i ++ ){
System.out.print("vertex " + i + ":\t");
for(int j = 0; j < dataArrVector[i].size() ; j ++ )
System.out.print(dataArrVector[i].elementAt(j) + "\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
* 获取相邻节点
* @param node
* @return
*/
public Iterable<Integer> adjacentNode(int node){
assert node >= 0 && node < nodeTotal;
// 邻接表,dataArrVector[node]中的节点都和node相连接
return dataArrVector[node];
}
}
// 连通分量
public class Components {
Graph G; // 图的引用
private boolean[] visited; // 记录深度遍历的过程中节点是否被访问
private int count; // 记录连通分量个数
private int[] id; // 每个节点所对应的连通分量标记
// 构造函数,求出无权图的连通分量
public Components(Graph graph){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
// visited数组长度是图节点的个数
visited = new boolean[G.getNodeTotal()];
id = new int[G.getNodeTotal()];
count = 0;
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.getNodeTotal() ; i ++ ){
// 刚才开始,所有节点都没遍历
visited[i] = false;
// 刚才开始,每个节点不属于任何连通分量
id[i] = -1;
}
// 求图的连通分量
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.getNodeTotal() ; i ++ )
if( !visited[i] ){
// i未遍历,深度遍历i
deepFirstSearch(i);
// i深度遍历完了,连通分量++
count++;
}
}
// 图的深度优先遍历
void deepFirstSearch(int node){
// 当前节点设置为已经遍历
visited[node] = true;
// 当前节点属于连通分量count
id[node] = count;
// 深度遍历当前节点的相邻节点
for( int i: G.adjacentNode(node) ){
if( !visited[i] )
deepFirstSearch(i);
}
}
// 返回图的连通分量个数
int count(){
return count;
}
// 查询点node1和点node2是否连通
boolean isConnected(int node1, int node2){
assert node1 >= 0 && node1 < G.getNodeTotal();
assert node2 >= 0 && node2 < G.getNodeTotal();
return id[node1] == id[node2];
}
}// 深度遍历寻址
public class Path {
private Graph G; // 图的引用
private int startNode; // 起始点
private boolean[] visited; // 记录深度遍历的过程中节点是否被访问
private int[] from; // 记录路径, from[i]表示查找的路径上i的上一个节点
// 构造函数, 寻路算法, 寻找图graph从startNode点到其他点的路径
public Path(Graph graph, int startNode){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
assert startNode >= 0 && startNode < G.getNodeTotal();
visited = new boolean[G.getNodeTotal()];
from = new int[G.getNodeTotal()];
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.getNodeTotal() ; i ++ ){
visited[i] = false;
from[i] = -1;
}
this.startNode = startNode;
// 寻路算法
deepFirstSearch(startNode);
}
// 图的深度优先遍历
private void deepFirstSearch(int node ){
visited[node] = true;
// node的相邻节点
for( int i : G.adjacentNode(node) )
// 相邻节点未被遍历过
if( !visited[i] ){
// from[i]位置存储上一个节点node
from[i] = node;
deepFirstSearch(i);
}
}
// 查询从startNode点到targetNode点是否有路径
boolean hasPath(int targetNode){
assert targetNode >= 0 && targetNode < G.getNodeTotal();
return visited[targetNode];
}
// 查询从s点到w点的路径, 存放在vec中
Vector<Integer> path(int targetNode){
assert hasPath(targetNode) ;
// 栈,先进后出
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
// 通过from数组逆向查找到从startNode到targetNode的路径, 存放到栈中
int p = targetNode;
// p不为-1,即节点p有上一个节点,上一个节点存放在from[p]中
while( p != -1 ){
s.push(p);
p = from[p];
}
// 从栈中依次取出元素,获得顺序的从startNode到targetNode的路径
Vector<Integer> res = new Vector<Integer>();
while( !s.empty() )
res.add( s.pop() );
return res;
}
// 打印出从startNode到targetNode的路径
void showPath(int targetNode){
assert hasPath(targetNode) ;
Vector<Integer> vec = path(targetNode);
for( int i = 0 ; i < vec.size() ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(vec.elementAt(i));
if( i == vec.size() - 1 )
System.out.println();
else
System.out.print(" -> ");
}
}
}
// 测试图的联通分量、深度遍历寻址
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//// TestG1.txt
//String filename1 = "note\\src\\main\\java\\com\\datastructure_arithmetic\\testG1.txt";
//SparseGraph g1 = new SparseGraph(13, false);
//ReadGraph readGraph1 = new ReadGraph(g1, filename1);
//Components component1 = new Components(g1);
//System.out.println("TestG1.txt, 连通分量: " + component1.count());
//System.out.println();
//
//// TestG2.txt
//String filename2 = "note\\src\\main\\java\\com\\datastructure_arithmetic\\testG2.txt";
//SparseGraph g2 = new SparseGraph(6, false);
//ReadGraph readGraph2 = new ReadGraph(g2, filename2);
//Components component2 = new Components(g2);
//System.out.println("TestG2.txt, 连通分量: " + component2.count());
String filename1 = "note\\src\\main\\java\\com\\datastructure_arithmetic\\testG1.txt";
SparseGraph g = new SparseGraph(13, false);
ReadGraph readGraph = new ReadGraph(g, filename1);
g.show();
System.out.println();
Path path = new Path(g,0);
System.out.println("Path from 0 to 6 : ");
path.showPath(6);
}
}无权图:两个节点之间连线没有长短之分,两点之间连接则为1,不连接则为0。

使用队列可以实现图的广度遍历,广度遍历可以求出无权图的最短路径
// 广度优先遍历
public class ShortestPath {
private Graph G; // 图的引用
private int startNode; // 起始点
private boolean[] visited; // 记录dfs的过程中节点是否被访问
private int[] from; // 记录路径, from[i]表示查找的路径上i的上一个节点
private int[] ord; // 记录路径中节点的次序。ord[i]表示i节点在路径中的次序。
// 构造函数, 寻路算法, 寻找图graph从startNode点到其他点的路径
public ShortestPath(Graph graph, int startNode){
// 算法初始化
G = graph;
assert startNode >= 0 && startNode < G.getNodeTotal();
visited = new boolean[G.getNodeTotal()];
from = new int[G.getNodeTotal()];
ord = new int[G.getNodeTotal()];
for( int i = 0 ; i < G.getNodeTotal() ; i ++ ){
visited[i] = false;
from[i] = -1;
ord[i] = -1;
}
this.startNode = startNode;
// 无向图最短路径算法, 从startNode开始广度优先遍历整张图
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(startNode);
visited[startNode] = true;
ord[startNode] = 0;
while( !q.isEmpty() ){
int v = q.remove();
for( int i : G.adjacentNode(v) )
if( !visited[i] ){
q.add(i);
visited[i] = true;
from[i] = v;
ord[i] = ord[v] + 1;
}
}
}
// 查询从startNode点到target点是否有路径
public boolean hasPath(int target){
assert target >= 0 && target < G.getNodeTotal();
return visited[target];
}
// 查询从startNode点到target点的路径, 存放在vec中
public Vector<Integer> path(int target){
assert hasPath(target) ;
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
// 通过from数组逆向查找到从startNode到target的路径, 存放到栈中
int p = target;
while( p != -1 ){
s.push(p);
p = from[p];
}
// 从栈中依次取出元素, 获得顺序的从startNode到target的路径
Vector<Integer> res = new Vector<Integer>();
while( !s.empty() )
res.add( s.pop() );
return res;
}
// 打印出从startNode点到target点的路径
public void showPath(int target){
assert hasPath(target) ;
Vector<Integer> vec = path(target);
for( int i = 0 ; i < vec.size() ; i ++ ){
System.out.print(vec.elementAt(i));
if( i == vec.size() - 1 )
System.out.println();
else
System.out.print(" -> ");
}
}
// 查看从startNode点到target点的最短路径长度
// 若从startNode到target不可达,返回-1
public int length(int w){
assert w >= 0 && w < G.getNodeTotal();
return ord[w];
}
}