Github:https://github.com/yjfiejd/Tensorflow_leaning/blob/master/tensorflow_20.3_RNN_lstm_regression.py
# -*- coding:utf8 -*- # @TIME : 2018/4/30 下午2:35 # @Author : Allen # @File : tensorflow_20.3_RNN_lstm_regression.py #使用RNN进行回归训练,会用到自己创建对sin曲线,预测一条cos曲线, #【1】设置RNN各种参数 #import state as state import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt BATCH_START = 0 #建立batch data时候对index TIME_STEPS = 20 #backpropagation through time 的 time_steps BATCH_SIZE = 50 INPUT_SIZE = 1 #sim 数据输入size OUTPUT_SIZE = 1 #cos数据输出size CELL_SIZE = 10 #RNN的hidden unit size LR = 0.006 #【2】 生成数据的get_batch function: def get_batch(): global BATCH_START, TIME_STEPS # xs shape (50batch, 20steps) xs = np.arange(BATCH_START, BATCH_START + TIME_STEPS*BATCH_SIZE).reshape((BATCH_SIZE, TIME_STEPS)) / (10*np.pi) seq = np.sin(xs) res = np.cos(xs) BATCH_START += TIME_STEPS # returned seq, res and xs; shape(batch, step, input) return [seq[:, :, np.newaxis], res[:, :, np.newaxis], xs] #【3】定义LSTMRNN的主体结构 #使用一个 class 来定义这次的 LSTMRNN 会更加方便. 第一步定义 class 中的 __init__ 传入各种参数: class LSTMRNN(object): def __init__(self, n_steps, input_size, output_size, cell_size, batch_size): self.n_steps = n_steps self.input_size = input_size self.output_size = output_size self.cell_size = cell_size self.batch_size = batch_size with tf.name_scope('inputs'): self.xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps, input_size], name='xs') self.ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps, output_size], name='ys') with tf.variable_scope('in_hidden'): self.add_input_layer() with tf.variable_scope('LSTM_cell'): self.add_cell() with tf.variable_scope('out_hidden'): self.add_output_layer() with tf.name_scope('cost'): self.compute_cost() with tf.name_scope('train'): self.train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(LR).minimize(self.cost) #设置add_input_layer()函数,添加input_layer() def add_input_layer(self,): l_in_x = tf.reshape(self.xs, [-1, self.input_size], name = '2_2D') #(batch*n_step, in_size) #Ws (in_size, cell_size) Ws_in = self._weight_variable([self.input_size, self.cell_size]) #bs (cell_size) bs_in = self._bias_variable([self.cell_size,]) #l_in_y = (batch * n_steps, cell_size) with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): l_in_y = tf.matmul(l_in_x, Ws_in) +bs_in #reshape l_in_y ==> (batch, n_steps, cell_size) self.l_in_y = tf.reshape(l_in_y, [-1, self.n_steps, self.cell_size], name='2_3D') #设置add_cell功能,添加cell, 注意此处的self.cell_init_state, 因为我们在 training 的时候, 这个地方要特别说明. def add_cell(self): lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(self.cell_size, forget_bias = 1.0, state_is_tuple = True) with tf.name_scope('initial_state'): self.cell_init_state = lstm_cell.zero_state(self.batch_size, dtype= tf.float32) self.cell_outputs, self.cell_final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(lstm_cell, self.l_in_y, initial_state=self.cell_init_state, time_major=False) #设置add_output_layer功能, 添加output_layer: def add_output_layer(self): # shape= (batch * steps, cell_size) l_out_x = tf.reshape(self.cell_outputs, [-1, self.cell_size], name= '2_2D') Ws_out = self._weight_variable([self.cell_size, self.output_size]) bs_out = self._bias_variable([self.output_size, ]) # shape = (batch * steps, output_size) with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): self.pred = tf.matmul(l_out_x, Ws_out) + bs_out #添加RNN 剩余部分 def compute_cost(self): losses = tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq.sequence_loss_by_example( [tf.reshape(self.pred, [-1], name='reshape_pred')], [tf.reshape(self.ys, [-1], name= 'reshape_target')], [tf.ones([self.batch_size * self.n_steps], dtype = tf.float32)], average_across_timesteps = True, softmax_loss_function = self.ms_error, name= 'losses' ) with tf.name_scope('average_cost'): self.cost = tf.div( tf.reduce_sum(losses, name='losses_sum'), tf.cast(self.batch_size, tf.float32), name = 'average_cost') tf.summary.scalar('cost', self.cost) @staticmethod def ms_error(labels, logits): return tf.square(tf.subtract(labels, logits)) #没有加@staticmethod时候报错, TypeError: ms_error() got multiple values for argument 'labels' #解决办法:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18950054/class-method-generates-typeerror-got-multiple-values-for-keyword-argument def _weight_variable(self, shape, name='weights'): initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(mean=0., stddev=1., ) return tf.get_variable(shape=shape, initializer=initializer, name=name) def _bias_variable(self, shape, name='biases'): initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.1) return tf.get_variable(name=name, shape = shape, initializer=initializer) #【4】 训练LSTMRNN if __name__ == '__main__': model = LSTMRNN(TIME_STEPS, INPUT_SIZE, OUTPUT_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, BATCH_SIZE) sess = tf.Session() merged = tf.summary.merge_all() writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("logs", sess.graph) if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1: init = tf.initialize_all_variables() else: init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) # relocate to the local dir and run this line to view it on Chrome (http://0.0.0.0:6006/): # $ tensorboard --logdir='logs' plt.ion() plt.show() for i in range(200): seq, res, xs = get_batch() if i == 0: feed_dict = { model.xs: seq, model.ys: res, # create initial state } else: feed_dict = { model.xs: seq, model.ys: res, model.cell_init_state: state # use last state as the initial state for this run } _, cost, state, pred = sess.run( [model.train_op, model.cost, model.cell_final_state, model.pred], feed_dict=feed_dict) # plotting plt.plot(xs[0, :], res[0].flatten(), 'r', xs[0, :], pred.flatten()[:TIME_STEPS], 'b--') plt.ylim((-1.2, 1.2)) plt.draw() plt.pause(0.3) if i % 20 == 0: print('cost: ', round(cost, 4)) result = sess.run(merged, feed_dict) writer.add_summary(result, i)
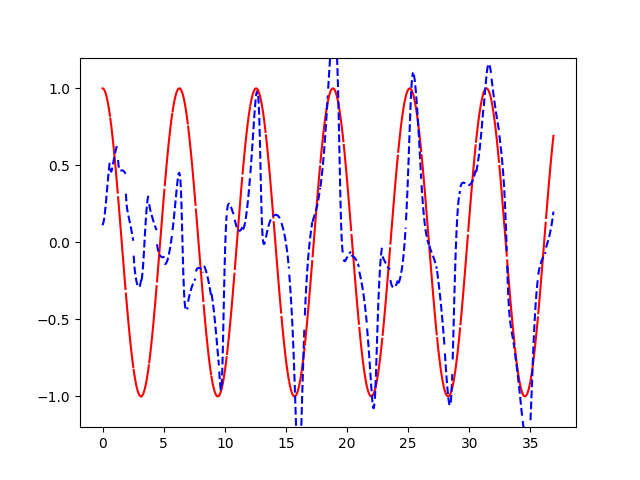
到后面,蓝色是我们的学习曲线,它越来越接近红色sin函数曲线了