Tensorflow——循环神经网络RNN
观看【北京大学】TensorFlow2.0视频 笔记
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1B7411L7Qt?p=25
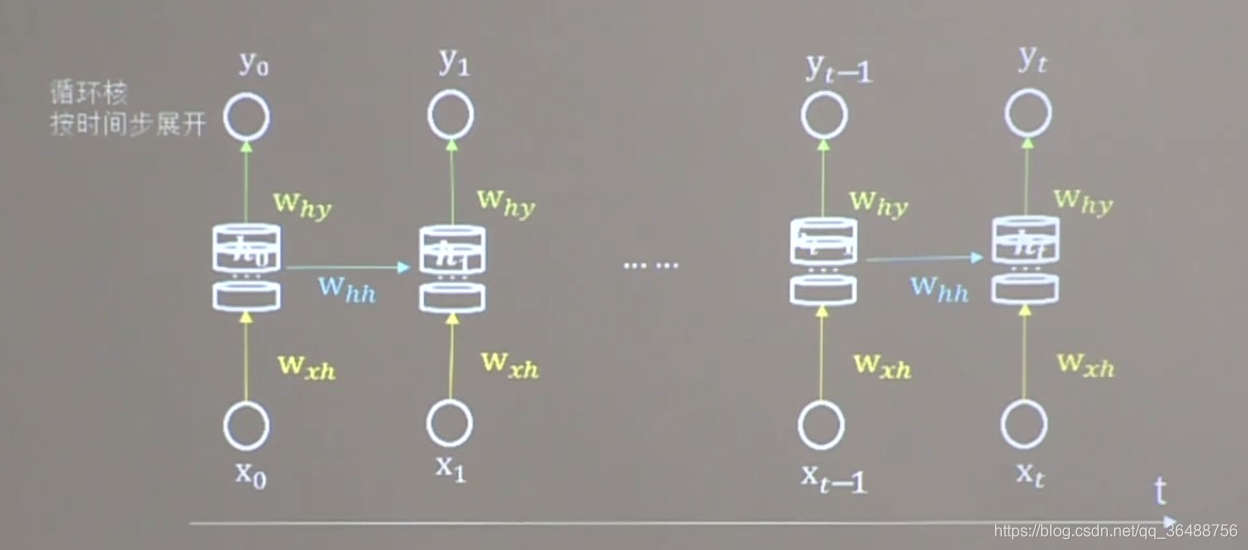
循环核
循环核具有记忆力,通过不同时刻的参数共享实现了对时间序列的信息提取

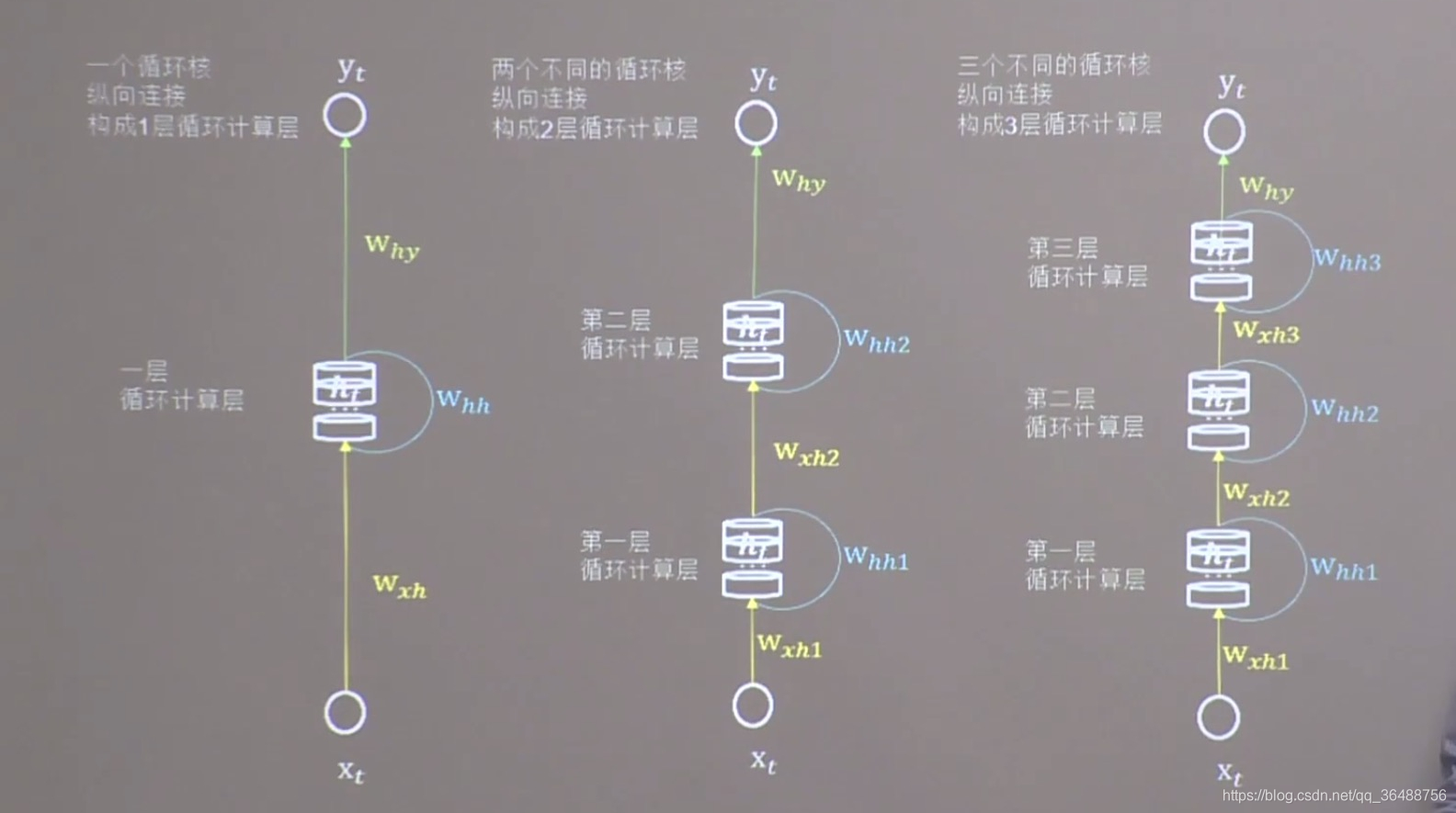
多层循环核
TensorFlow描述循环核
tf.keras.layers.SimpleRNN(
记忆体个数,
activation='', #默认tanh
return_sequences=True or False #是否每个时刻都输出ht到下一层默认true
循环神经网络
借助循环核提取时间特征后,送入全连接网络
TensorFlow描述循环神经网络
tf.keras.layers.SimpleRNN(
记忆体个数,
activation='', #默认tanh
return_sequences=True or False #是否每个时刻都输出ht到下一层默认true
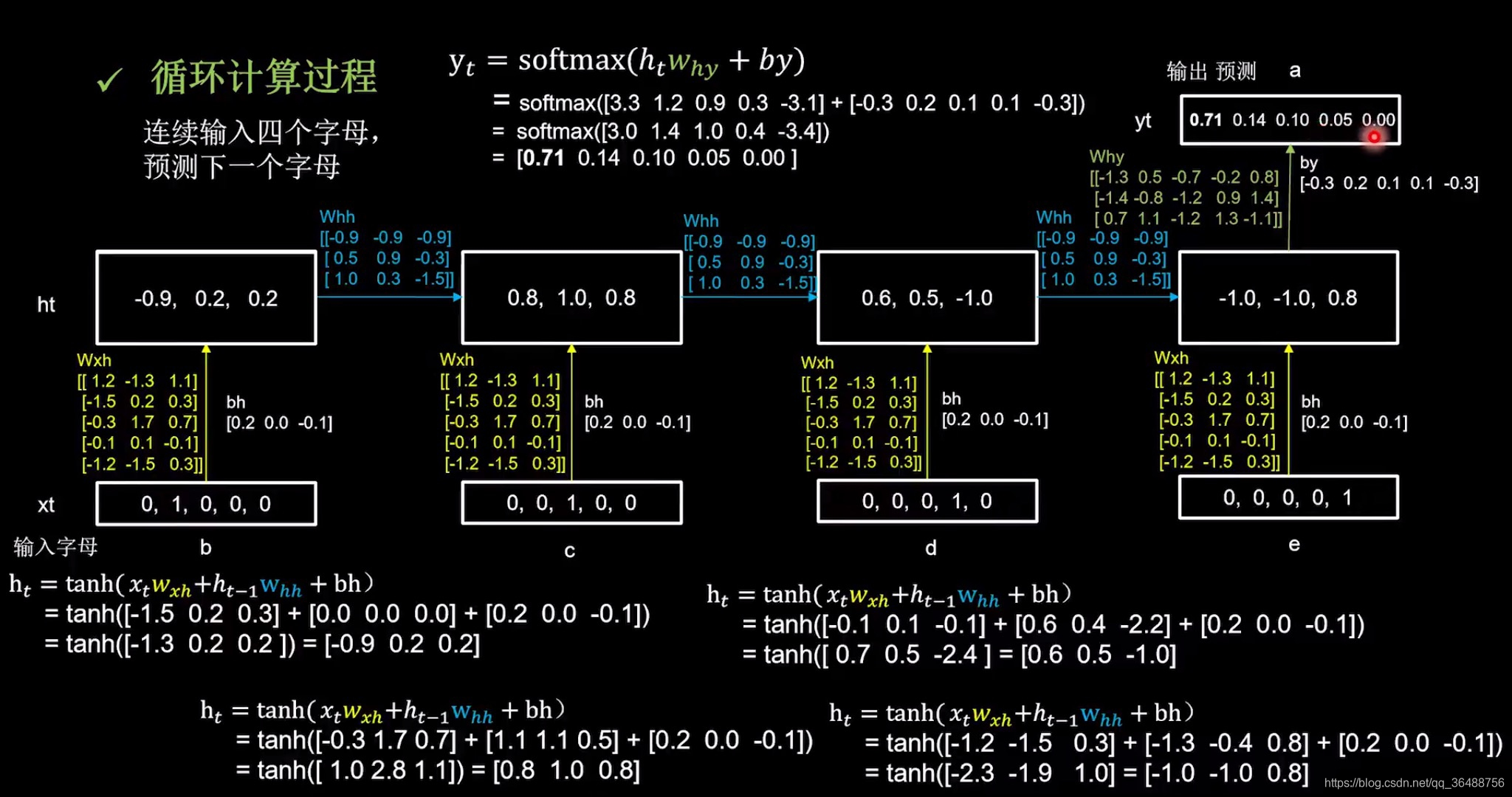
循环计算过程
输入一个字母,预测下一个字母

import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, SimpleRNN
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
input_word = "abcde"
w_to_id = {
'a': 0, 'b': 1, 'c': 2, 'd': 3, 'e': 4} # 单词映射到数值id的词典
id_to_onehot = {
0: [1., 0., 0., 0., 0.], 1: [0., 1., 0., 0., 0.], 2: [0., 0., 1., 0., 0.], 3: [0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
4: [0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]} # id编码为one-hot
x_train = [id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c']],
id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e']]]
y_train = [w_to_id['b'], w_to_id['c'], w_to_id['d'], w_to_id['e'], w_to_id['a']]
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(x_train)
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(y_train)
tf.random.set_seed(7)
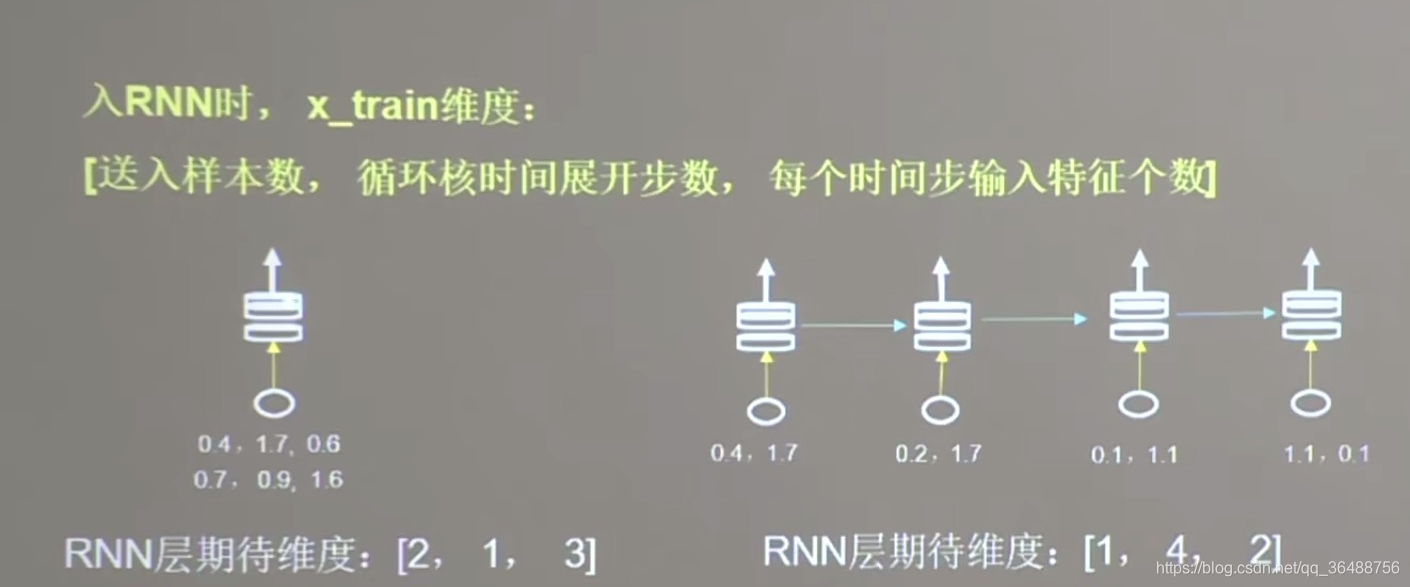
# 使x_train符合SimpleRNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]。
# 此处整个数据集送入,送入样本数为len(x_train);输入1个字母出结果,循环核时间展开步数为1; 表示为独热码有5个输入特征,每个时间步输入特征个数为5
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len(x_train), 1, 5))
y_train = np.array(y_train)
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
SimpleRNN(3),
Dense(5, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01),
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/rnn_onehot_1pre1.ckpt"
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index'):
print('-------------load the model-----------------')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
monitor='loss') # 由于fit没有给出测试集,不计算测试集准确率,根据loss,保存最优模型
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=100, callbacks=[cp_callback])
model.summary()
# print(model.trainable_variables)
file = open('./weights.txt', 'w') # 参数提取
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.shape) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy()) + '\n')
file.close()
############################################### show ###############################################
# 显示训练集和验证集的acc和loss曲线
acc = history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.title('Training Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.title('Training Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
############### predict #############
preNum = int(input("input the number of test alphabet:"))
for i in range(preNum):
alphabet1 = input("input test alphabet:")
alphabet = [id_to_onehot[w_to_id[alphabet1]]]
# 使alphabet符合SimpleRNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]。此处验证效果送入了1个样本,送入样本数为1;输入1个字母出结果,所以循环核时间展开步数为1; 表示为独热码有5个输入特征,每个时间步输入特征个数为5
alphabet = np.reshape(alphabet, (1, 1, 5))
result = model.predict([alphabet])
pred = tf.argmax(result, axis=1)
pred = int(pred)
tf.print(alphabet1 + '->' + input_word[pred])
输入四个连续字母,预测下一个字母
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, SimpleRNN
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
input_word = "abcde"
w_to_id = {
'a': 0, 'b': 1, 'c': 2, 'd': 3, 'e': 4} # 单词映射到数值id的词典
id_to_onehot = {
0: [1., 0., 0., 0., 0.], 1: [0., 1., 0., 0., 0.], 2: [0., 0., 1., 0., 0.], 3: [0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
4: [0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]} # id编码为one-hot
x_train = [
[id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d']]],
[id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e']]],
[id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a']]],
[id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b']]],
[id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b']], id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c']]],
]
y_train = [w_to_id['e'], w_to_id['a'], w_to_id['b'], w_to_id['c'], w_to_id['d']]
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(x_train)
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(y_train)
tf.random.set_seed(7)
# 使x_train符合SimpleRNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]。
# 此处整个数据集送入,送入样本数为len(x_train);输入4个字母出结果,循环核时间展开步数为4; 表示为独热码有5个输入特征,每个时间步输入特征个数为5
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len(x_train), 4, 5))
y_train = np.array(y_train)
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
SimpleRNN(3),
Dense(5, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01),
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/rnn_onehot_4pre1.ckpt"
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index'):
print('-------------load the model-----------------')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
monitor='loss') # 由于fit没有给出测试集,不计算测试集准确率,根据loss,保存最优模型
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=100, callbacks=[cp_callback])
model.summary()
# print(model.trainable_variables)
file = open('./weights.txt', 'w') # 参数提取
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.shape) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy()) + '\n')
file.close()
############################################### show ###############################################
# 显示训练集和验证集的acc和loss曲线
acc = history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.title('Training Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.title('Training Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
############### predict #############
preNum = int(input("input the number of test alphabet:"))
for i in range(preNum):
alphabet1 = input("input test alphabet:")
alphabet = [id_to_onehot[w_to_id[a]] for a in alphabet1]
# 使alphabet符合SimpleRNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]。此处验证效果送入了1个样本,送入样本数为1;输入4个字母出结果,所以循环核时间展开步数为4; 表示为独热码有5个输入特征,每个时间步输入特征个数为5
alphabet = np.reshape(alphabet, (1, 4, 5))
result = model.predict([alphabet])
pred = tf.argmax(result, axis=1)
pred = int(pred)
tf.print(alphabet1 + '->' + input_word[pred])
Embedding编码
Embedding是一种单词编码,用低维向量实现了编码,这种编码通过神经网络训练优化,能表达出单词间的相关性
TensorFlow描述Embedding编码
tf.keras.layers.Embedding(词汇表大小,编码维度) #编码维度即用几个数字表达一个单词
用Embedding编码替换独热码实现输入一个字符预测
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, SimpleRNN, Embedding
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
input_word = "abcde"
w_to_id = {
'a': 0, 'b': 1, 'c': 2, 'd': 3, 'e': 4} # 单词映射到数值id的词典
x_train = [w_to_id['a'], w_to_id['b'], w_to_id['c'], w_to_id['d'], w_to_id['e']]
y_train = [w_to_id['b'], w_to_id['c'], w_to_id['d'], w_to_id['e'], w_to_id['a']]
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(x_train)
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(y_train)
tf.random.set_seed(7)
# 使x_train符合Embedding输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数] ,
# 此处整个数据集送入所以送入,送入样本数为len(x_train);输入1个字母出结果,循环核时间展开步数为1。
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len(x_train), 1))
y_train = np.array(y_train)
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
Embedding(5, 2),
SimpleRNN(3),
Dense(5, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01),
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/run_embedding_1pre1.ckpt"
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index'):
print('-------------load the model-----------------')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
monitor='loss') # 由于fit没有给出测试集,不计算测试集准确率,根据loss,保存最优模型
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=100, callbacks=[cp_callback])
model.summary()
# print(model.trainable_variables)
file = open('./weights.txt', 'w') # 参数提取
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.shape) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy()) + '\n')
file.close()
############################################### show ###############################################
# 显示训练集和验证集的acc和loss曲线
acc = history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.title('Training Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.title('Training Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
############### predict #############
preNum = int(input("input the number of test alphabet:"))
for i in range(preNum):
alphabet1 = input("input test alphabet:")
alphabet = [w_to_id[alphabet1]]
# 使alphabet符合Embedding输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数]。
# 此处验证效果送入了1个样本,送入样本数为1;输入1个字母出结果,循环核时间展开步数为1。
alphabet = np.reshape(alphabet, (1, 1))
result = model.predict(alphabet)
pred = tf.argmax(result, axis=1)
pred = int(pred)
tf.print(alphabet1 + '->' + input_word[pred])
用Embedding编码替换独热码实现输入四个字符预测
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, SimpleRNN, Embedding
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
input_word = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
w_to_id = {
'a': 0, 'b': 1, 'c': 2, 'd': 3, 'e': 4,
'f': 5, 'g': 6, 'h': 7, 'i': 8, 'j': 9,
'k': 10, 'l': 11, 'm': 12, 'n': 13, 'o': 14,
'p': 15, 'q': 16, 'r': 17, 's': 18, 't': 19,
'u': 20, 'v': 21, 'w': 22, 'x': 23, 'y': 24, 'z': 25} # 单词映射到数值id的词典
training_set_scaled = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20,
21, 22, 23, 24, 25]
x_train = []
y_train = []
for i in range(4, 26):
x_train.append(training_set_scaled[i - 4:i])
y_train.append(training_set_scaled[i])
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(x_train)
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(y_train)
tf.random.set_seed(7)
# 使x_train符合Embedding输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数] ,
# 此处整个数据集送入所以送入,送入样本数为len(x_train);输入4个字母出结果,循环核时间展开步数为4。
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len(x_train), 4))
y_train = np.array(y_train)
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
Embedding(26, 2),
SimpleRNN(10),
Dense(26, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01),
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/rnn_embedding_4pre1.ckpt"
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index'):
print('-------------load the model-----------------')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
monitor='loss') # 由于fit没有给出测试集,不计算测试集准确率,根据loss,保存最优模型
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=100, callbacks=[cp_callback])
model.summary()
file = open('./weights.txt', 'w') # 参数提取
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.shape) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy()) + '\n')
file.close()
############################################### show ###############################################
# 显示训练集和验证集的acc和loss曲线
acc = history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.title('Training Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.title('Training Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
################# predict ##################
preNum = int(input("input the number of test alphabet:"))
for i in range(preNum):
alphabet1 = input("input test alphabet:")
alphabet = [w_to_id[a] for a in alphabet1]
# 使alphabet符合Embedding输入要求:[送入样本数, 时间展开步数]。
# 此处验证效果送入了1个样本,送入样本数为1;输入4个字母出结果,循环核时间展开步数为4。
alphabet = np.reshape(alphabet, (1, 4))
result = model.predict([alphabet])
pred = tf.argmax(result, axis=1)
pred = int(pred)
tf.print(alphabet1 + '->' + input_word[pred])
循环神经网络实现股票预测
下载股票预测数据
import tushare as ts
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df1 = ts.get_k_data('600519', ktype='D', start='2010-04-26', end='2020-04-26')
datapath1 = "./SH600519.csv"
df1.to_csv(datapath1)
股票预测
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dropout, Dense, SimpleRNN
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error
import math
maotai = pd.read_csv('./SH600519.csv') # 读取股票文件
training_set = maotai.iloc[0:2426 - 300, 2:3].values # 前(2426-300=2126)天的开盘价作为训练集,表格从0开始计数,2:3 是提取[2:3)列,前闭后开,故提取出C列开盘价
test_set = maotai.iloc[2426 - 300:, 2:3].values # 后300天的开盘价作为测试集
# 归一化
sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1)) # 定义归一化:归一化到(0,1)之间
training_set_scaled = sc.fit_transform(training_set) # 求得训练集的最大值,最小值这些训练集固有的属性,并在训练集上进行归一化
test_set = sc.transform(test_set) # 利用训练集的属性对测试集进行归一化
x_train = []
y_train = []
x_test = []
y_test = []
# 测试集:csv表格中前2426-300=2126天数据
# 利用for循环,遍历整个训练集,提取训练集中连续60天的开盘价作为输入特征x_train,第61天的数据作为标签,for循环共构建2426-300-60=2066组数据。
for i in range(60, len(training_set_scaled)):
x_train.append(training_set_scaled[i - 60:i, 0])
y_train.append(training_set_scaled[i, 0])
# 对训练集进行打乱
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(x_train)
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(y_train)
tf.random.set_seed(7)
# 将训练集由list格式变为array格式
x_train, y_train = np.array(x_train), np.array(y_train)
# 使x_train符合RNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]。
# 此处整个数据集送入,送入样本数为x_train.shape[0]即2066组数据;输入60个开盘价,预测出第61天的开盘价,循环核时间展开步数为60; 每个时间步送入的特征是某一天的开盘价,只有1个数据,故每个时间步输入特征个数为1
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (x_train.shape[0], 60, 1))
# 测试集:csv表格中后300天数据
# 利用for循环,遍历整个测试集,提取测试集中连续60天的开盘价作为输入特征x_train,第61天的数据作为标签,for循环共构建300-60=240组数据。
for i in range(60, len(test_set)):
x_test.append(test_set[i - 60:i, 0])
y_test.append(test_set[i, 0])
# 测试集变array并reshape为符合RNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]
x_test, y_test = np.array(x_test), np.array(y_test)
x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (x_test.shape[0], 60, 1))
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
SimpleRNN(80, return_sequences=True),
Dropout(0.2),
SimpleRNN(100),
Dropout(0.2),
Dense(1)
])
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.001),
loss='mean_squared_error') # 损失函数用均方误差
# 该应用只观测loss数值,不观测准确率,所以删去metrics选项,一会在每个epoch迭代显示时只显示loss值
checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/rnn_stock.ckpt"
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index'):
print('-------------load the model-----------------')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
monitor='val_loss')
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=64, epochs=50, validation_data=(x_test, y_test), validation_freq=1,
callbacks=[cp_callback])
model.summary()
file = open('./weights.txt', 'w') # 参数提取
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.shape) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy()) + '\n')
file.close()
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
################## predict ######################
# 测试集输入模型进行预测
predicted_stock_price = model.predict(x_test)
# 对预测数据还原---从(0,1)反归一化到原始范围
predicted_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(predicted_stock_price)
# 对真实数据还原---从(0,1)反归一化到原始范围
real_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(test_set[60:])
# 画出真实数据和预测数据的对比曲线
plt.plot(real_stock_price, color='red', label='MaoTai Stock Price')
plt.plot(predicted_stock_price, color='blue', label='Predicted MaoTai Stock Price')
plt.title('MaoTai Stock Price Prediction')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('MaoTai Stock Price')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
##########evaluate##############
# calculate MSE 均方误差 ---> E[(预测值-真实值)^2] (预测值减真实值求平方后求均值)
mse = mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price)
# calculate RMSE 均方根误差--->sqrt[MSE] (对均方误差开方)
rmse = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price))
# calculate MAE 平均绝对误差----->E[|预测值-真实值|](预测值减真实值求绝对值后求均值)
mae = mean_absolute_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price)
print('均方误差: %.6f' % mse)
print('均方根误差: %.6f' % rmse)
print('平均绝对误差: %.6f' % mae)
长短记忆网络LSTM
通过门控单元改善了RNN长期依赖问题

TensorFlow描述LSTM层
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(记忆体个数,
return_sequences=True or False #是否返回输出默认false仅最后输出 true各时间步输出
)
LSTM实现股票预测
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dropout, Dense, LSTM
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error
import math
maotai = pd.read_csv('./SH600519.csv') # 读取股票文件
training_set = maotai.iloc[0:2426 - 300, 2:3].values # 前(2426-300=2126)天的开盘价作为训练集,表格从0开始计数,2:3 是提取[2:3)列,前闭后开,故提取出C列开盘价
test_set = maotai.iloc[2426 - 300:, 2:3].values # 后300天的开盘价作为测试集
# 归一化
sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1)) # 定义归一化:归一化到(0,1)之间
training_set_scaled = sc.fit_transform(training_set) # 求得训练集的最大值,最小值这些训练集固有的属性,并在训练集上进行归一化
test_set = sc.transform(test_set) # 利用训练集的属性对测试集进行归一化
x_train = []
y_train = []
x_test = []
y_test = []
# 测试集:csv表格中前2426-300=2126天数据
# 利用for循环,遍历整个训练集,提取训练集中连续60天的开盘价作为输入特征x_train,第61天的数据作为标签,for循环共构建2426-300-60=2066组数据。
for i in range(60, len(training_set_scaled)):
x_train.append(training_set_scaled[i - 60:i, 0])
y_train.append(training_set_scaled[i, 0])
# 对训练集进行打乱
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(x_train)
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(y_train)
tf.random.set_seed(7)
# 将训练集由list格式变为array格式
x_train, y_train = np.array(x_train), np.array(y_train)
# 使x_train符合RNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]。
# 此处整个数据集送入,送入样本数为x_train.shape[0]即2066组数据;输入60个开盘价,预测出第61天的开盘价,循环核时间展开步数为60; 每个时间步送入的特征是某一天的开盘价,只有1个数据,故每个时间步输入特征个数为1
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (x_train.shape[0], 60, 1))
# 测试集:csv表格中后300天数据
# 利用for循环,遍历整个测试集,提取测试集中连续60天的开盘价作为输入特征x_train,第61天的数据作为标签,for循环共构建300-60=240组数据。
for i in range(60, len(test_set)):
x_test.append(test_set[i - 60:i, 0])
y_test.append(test_set[i, 0])
# 测试集变array并reshape为符合RNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]
x_test, y_test = np.array(x_test), np.array(y_test)
x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (x_test.shape[0], 60, 1))
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
LSTM(80, return_sequences=True),
Dropout(0.2),
LSTM(100),
Dropout(0.2),
Dense(1)
])
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.001),
loss='mean_squared_error') # 损失函数用均方误差
# 该应用只观测loss数值,不观测准确率,所以删去metrics选项,一会在每个epoch迭代显示时只显示loss值
checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/LSTM_stock.ckpt"
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index'):
print('-------------load the model-----------------')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
monitor='val_loss')
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=64, epochs=50, validation_data=(x_test, y_test), validation_freq=1,
callbacks=[cp_callback])
model.summary()
file = open('./weights.txt', 'w') # 参数提取
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.shape) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy()) + '\n')
file.close()
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
################## predict ######################
# 测试集输入模型进行预测
predicted_stock_price = model.predict(x_test)
# 对预测数据还原---从(0,1)反归一化到原始范围
predicted_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(predicted_stock_price)
# 对真实数据还原---从(0,1)反归一化到原始范围
real_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(test_set[60:])
# 画出真实数据和预测数据的对比曲线
plt.plot(real_stock_price, color='red', label='MaoTai Stock Price')
plt.plot(predicted_stock_price, color='blue', label='Predicted MaoTai Stock Price')
plt.title('MaoTai Stock Price Prediction')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('MaoTai Stock Price')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
##########evaluate##############
# calculate MSE 均方误差 ---> E[(预测值-真实值)^2] (预测值减真实值求平方后求均值)
mse = mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price)
# calculate RMSE 均方根误差--->sqrt[MSE] (对均方误差开方)
rmse = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price))
# calculate MAE 平均绝对误差----->E[|预测值-真实值|](预测值减真实值求绝对值后求均值)
mae = mean_absolute_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price)
print('均方误差: %.6f' % mse)
print('均方根误差: %.6f' % rmse)
print('平均绝对误差: %.6f' % mae)
GRU网络
使记忆体ht融合了长期记忆和短期记忆
TensorFlow描述GRU层
tf.keras.layers.GRU(记忆体个数,
return_sequences=True or False #是否返回输出默认false仅最后输出 true各时间步输出
)
LSTM实现股票预测
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dropout, Dense, GRU
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error
import math
maotai = pd.read_csv('./SH600519.csv') # 读取股票文件
training_set = maotai.iloc[0:2426 - 300, 2:3].values # 前(2426-300=2126)天的开盘价作为训练集,表格从0开始计数,2:3 是提取[2:3)列,前闭后开,故提取出C列开盘价
test_set = maotai.iloc[2426 - 300:, 2:3].values # 后300天的开盘价作为测试集
# 归一化
sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1)) # 定义归一化:归一化到(0,1)之间
training_set_scaled = sc.fit_transform(training_set) # 求得训练集的最大值,最小值这些训练集固有的属性,并在训练集上进行归一化
test_set = sc.transform(test_set) # 利用训练集的属性对测试集进行归一化
x_train = []
y_train = []
x_test = []
y_test = []
# 测试集:csv表格中前2426-300=2126天数据
# 利用for循环,遍历整个训练集,提取训练集中连续60天的开盘价作为输入特征x_train,第61天的数据作为标签,for循环共构建2426-300-60=2066组数据。
for i in range(60, len(training_set_scaled)):
x_train.append(training_set_scaled[i - 60:i, 0])
y_train.append(training_set_scaled[i, 0])
# 对训练集进行打乱
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(x_train)
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(y_train)
tf.random.set_seed(7)
# 将训练集由list格式变为array格式
x_train, y_train = np.array(x_train), np.array(y_train)
# 使x_train符合RNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]。
# 此处整个数据集送入,送入样本数为x_train.shape[0]即2066组数据;输入60个开盘价,预测出第61天的开盘价,循环核时间展开步数为60; 每个时间步送入的特征是某一天的开盘价,只有1个数据,故每个时间步输入特征个数为1
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (x_train.shape[0], 60, 1))
# 测试集:csv表格中后300天数据
# 利用for循环,遍历整个测试集,提取测试集中连续60天的开盘价作为输入特征x_train,第61天的数据作为标签,for循环共构建300-60=240组数据。
for i in range(60, len(test_set)):
x_test.append(test_set[i - 60:i, 0])
y_test.append(test_set[i, 0])
# 测试集变array并reshape为符合RNN输入要求:[送入样本数, 循环核时间展开步数, 每个时间步输入特征个数]
x_test, y_test = np.array(x_test), np.array(y_test)
x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (x_test.shape[0], 60, 1))
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
GRU(80, return_sequences=True),
Dropout(0.2),
GRU(100),
Dropout(0.2),
Dense(1)
])
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.001),
loss='mean_squared_error') # 损失函数用均方误差
# 该应用只观测loss数值,不观测准确率,所以删去metrics选项,一会在每个epoch迭代显示时只显示loss值
checkpoint_save_path = "./checkpoint/stock.ckpt"
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path + '.index'):
print('-------------load the model-----------------')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
monitor='val_loss')
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=64, epochs=50, validation_data=(x_test, y_test), validation_freq=1,
callbacks=[cp_callback])
model.summary()
file = open('./weights.txt', 'w') # 参数提取
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.shape) + '\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy()) + '\n')
file.close()
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
plt.plot(loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
################## predict ######################
# 测试集输入模型进行预测
predicted_stock_price = model.predict(x_test)
# 对预测数据还原---从(0,1)反归一化到原始范围
predicted_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(predicted_stock_price)
# 对真实数据还原---从(0,1)反归一化到原始范围
real_stock_price = sc.inverse_transform(test_set[60:])
# 画出真实数据和预测数据的对比曲线
plt.plot(real_stock_price, color='red', label='MaoTai Stock Price')
plt.plot(predicted_stock_price, color='blue', label='Predicted MaoTai Stock Price')
plt.title('MaoTai Stock Price Prediction')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('MaoTai Stock Price')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
##########evaluate##############
# calculate MSE 均方误差 ---> E[(预测值-真实值)^2] (预测值减真实值求平方后求均值)
mse = mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price)
# calculate RMSE 均方根误差--->sqrt[MSE] (对均方误差开方)
rmse = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price))
# calculate MAE 平均绝对误差----->E[|预测值-真实值|](预测值减真实值求绝对值后求均值)
mae = mean_absolute_error(predicted_stock_price, real_stock_price)
print('均方误差: %.6f' % mse)
print('均方根误差: %.6f' % rmse)
print('平均绝对误差: %.6f' % mae)