outputstandard output
Ujan has a lot of useless stuff in his drawers, a considerable part of which are his math notebooks: it is time to sort them out. This time he found an old dusty graph theory notebook with a description of a graph.
It is an undirected weighted graph on n vertices. It is a complete graph: each pair of vertices is connected by an edge. The weight of each edge is either 0 or 1; exactly m edges have weight 1, and all others have weight 0.
Since Ujan doesn’t really want to organize his notes, he decided to find the weight of the minimum spanning tree of the graph. (The weight of a spanning tree is the sum of all its edges.) Can you find the answer for Ujan so he stops procrastinating?
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1≤n≤105, 0≤m≤min(n(n−1)2,105)), the number of vertices and the number of edges of weight 1 in the graph.
The i-th of the next m lines contains two integers ai and bi (1≤ai,bi≤n, ai≠bi), the endpoints of the i-th edge of weight 1.
It is guaranteed that no edge appears twice in the input.
Output
Output a single integer, the weight of the minimum spanning tree of the graph.
Examples
inputCopy
6 11
1 3
1 4
1 5
1 6
2 3
2 4
2 5
2 6
3 4
3 5
3 6
outputCopy
2
inputCopy
3 0
outputCopy
0
Note
The graph from the first sample is shown below. Dashed edges have weight 0, other edges have weight 1. One of the minimum spanning trees is highlighted in orange and has total weight 2.
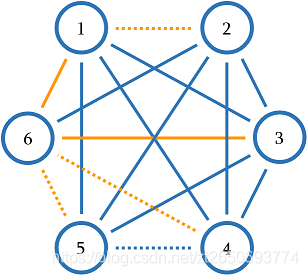
In the second sample, all edges have weight 0 so any spanning tree has total weight 0.
package Main;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int maxn = 1000010;
static int tot=0;
static int[] pre = new int[maxn];
static int[] siz = new int[maxn];
static int[] head = new int[maxn];
static HashMap<Integer,Integer>mp = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
static class Edge{
int to,nxt;
};
static Edge[] edge = new Edge[maxn];
static public void add(int u,int v){
edge[++tot].to=v; edge[tot].nxt=head[u]; head[u]=tot;
edge[++tot].to=u; edge[tot].nxt=head[v]; head[v]=tot;
}
static public void init(){
for(int i=1;i<maxn;i++){
pre[i]=i;
siz[i]=1;
head[i]=-1;
edge[i]=new Edge();
}
}
static int find(int x){
if(pre[x]==x) return x;
return pre[x]=find(pre[x]);
}
static void unite(int a,int b){
int fx=find(a);
int fy=find(b);
if(fx!=fy){
pre[fx]=pre[fy];
siz[fy]+=siz[fx];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
init();
int n = input.nextInt();
int m = input.nextInt();
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int a=input.nextInt();
int b=input.nextInt();
add(a,b);
}
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
mp.clear();
for(int j=head[i];j!=-1;j=edge[j].nxt){
int to=edge[j].to;
if(to>=i) continue;
int fv=find(to);
mp.put(fv,!mp.containsKey(fv)?1:mp.get(fv)+1);
}
for(int j=0;j<list.size();j++){
int t=find((Integer)list.get(j));
int q=find(i);
if(t==q) continue;
if(siz[t]>(mp.get(t)==null?0:mp.get(t))) unite(i,t);
}
int fx=find(i);
if(fx==i) list.add(fx);
}
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(pre[i]==i) cnt++;
}
System.out.println(cnt-1);
}
}
