粒子滤波器(Particle Filter)
概念
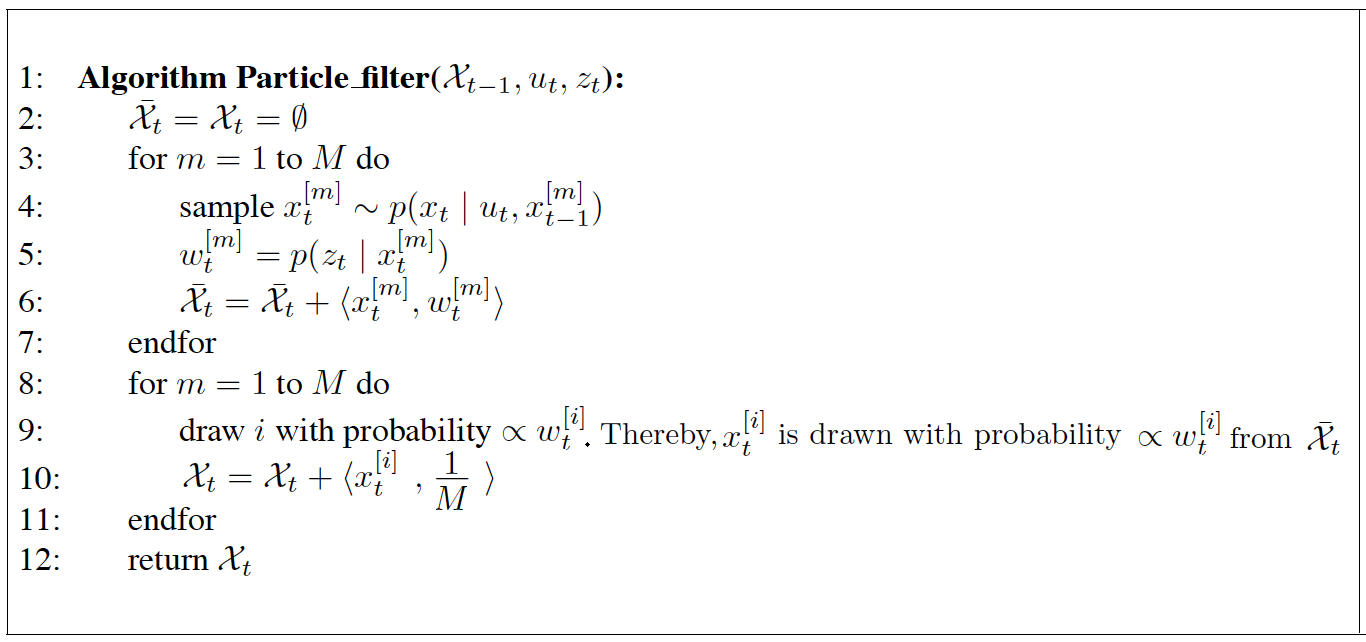
(来源:Probabilistic Robotics, 4.3 The Particle Filter, p96)
解析:
- line 3 - 7: 生成M个新样本(即粒子)
- line 4: 根据重要性(importance weight)采样
- line 5: (重新)计算重要性(re-weight)
- line 6: 更新标准化(update normalization)准确翻译待确认
- line 8 -11: 重采样(resampling or importance sampling)
- line 9:
- line 10:
比喻
待补充
示例程序
"""
Particle Filter localization sample
author: Atsushi Sakai (@Atsushi_twi)
"""
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Estimation parameter of PF
Q = np.diag([0.2]) ** 2 # range error
R = np.diag([2.0, np.deg2rad(40.0)]) ** 2 # input error
# Simulation parameter
Q_sim = np.diag([0.2]) ** 2
R_sim = np.diag([1.0, np.deg2rad(30.0)]) ** 2
DT = 0.1 # time tick [s]
SIM_TIME = 50.0 # simulation time [s]
MAX_RANGE = 20.0 # maximum observation range
# Particle filter parameter
NP = 100 # Number of Particle
NTh = NP / 2.0 # Number of particle for re-sampling
show_animation = True
def calc_input():
v = 1.0 # [m/s]
yaw_rate = 0.1 # [rad/s]
u = np.array([[v, yaw_rate]]).T
return u
def observation(x_true, xd, u, rf_id):
x_true = motion_model(x_true, u)
# add noise to gps x-y
z = np.zeros((0, 3))
for i in range(len(rf_id[:, 0])):
dx = x_true[0, 0] - rf_id[i, 0]
dy = x_true[1, 0] - rf_id[i, 1]
d = math.hypot(dx, dy)
if d <= MAX_RANGE:
dn = d + np.random.randn() * Q_sim[0, 0] ** 0.5 # add noise
zi = np.array([[dn, rf_id[i, 0], rf_id[i, 1]]])
z = np.vstack((z, zi))
# add noise to input
ud1 = u[0, 0] + np.random.randn() * R_sim[0, 0] ** 0.5
ud2 = u[1, 0] + np.random.randn() * R_sim[1, 1] ** 0.5
ud = np.array([[ud1, ud2]]).T
xd = motion_model(xd, ud)
return x_true, z, xd, ud
def motion_model(x, u):
F = np.array([[1.0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1.0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1.0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0]])
B = np.array([[DT * math.cos(x[2, 0]), 0],
[DT * math.sin(x[2, 0]), 0],
[0.0, DT],
[1.0, 0.0]])
x = F.dot(x) + B.dot(u)
return x
def gauss_likelihood(x, sigma):
p = 1.0 / math.sqrt(2.0 * math.pi * sigma ** 2) * \
math.exp(-x ** 2 / (2 * sigma ** 2))
return p
def calc_covariance(x_est, px, pw):
"""
calculate covariance matrix
see ipynb doc
"""
cov = np.zeros((3, 3))
n_particle = px.shape[1]
for i in range(n_particle):
dx = (px[:, i:i + 1] - x_est)[0:3]
cov += pw[0, i] * dx @ dx.T
cov *= 1.0 / (1.0 - pw @ pw.T)
return cov
def pf_localization(px, pw, z, u):
"""
Localization with Particle filter
"""
for ip in range(NP):
x = np.array([px[:, ip]]).T
w = pw[0, ip]
# Predict with random input sampling
ud1 = u[0, 0] + np.random.randn() * R[0, 0] ** 0.5
ud2 = u[1, 0] + np.random.randn() * R[1, 1] ** 0.5
ud = np.array([[ud1, ud2]]).T
x = motion_model(x, ud)
# Calc Importance Weight
for i in range(len(z[:, 0])):
dx = x[0, 0] - z[i, 1]
dy = x[1, 0] - z[i, 2]
pre_z = math.hypot(dx, dy)
dz = pre_z - z[i, 0]
w = w * gauss_likelihood(dz, math.sqrt(Q[0, 0]))
px[:, ip] = x[:, 0]
pw[0, ip] = w
pw = pw / pw.sum() # normalize
x_est = px.dot(pw.T)
p_est = calc_covariance(x_est, px, pw)
N_eff = 1.0 / (pw.dot(pw.T))[0, 0] # Effective particle number
if N_eff < NTh:
px, pw = re_sampling(px, pw)
return x_est, p_est, px, pw
def re_sampling(px, pw):
"""
low variance re-sampling
"""
w_cum = np.cumsum(pw)
base = np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 1 / NP)
re_sample_id = base + np.random.uniform(0, 1 / NP)
indexes = []
ind = 0
for ip in range(NP):
while re_sample_id[ip] > w_cum[ind]:
ind += 1
indexes.append(ind)
px = px[:, indexes]
pw = np.zeros((1, NP)) + 1.0 / NP # init weight
return px, pw
def plot_covariance_ellipse(x_est, p_est): # pragma: no cover
p_xy = p_est[0:2, 0:2]
eig_val, eig_vec = np.linalg.eig(p_xy)
if eig_val[0] >= eig_val[1]:
big_ind = 0
small_ind = 1
else:
big_ind = 1
small_ind = 0
t = np.arange(0, 2 * math.pi + 0.1, 0.1)
# eig_val[big_ind] or eiq_val[small_ind] were occasionally negative numbers extremely
# close to 0 (~10^-20), catch these cases and set the respective variable to 0
try:
a = math.sqrt(eig_val[big_ind])
except ValueError:
a = 0
try:
b = math.sqrt(eig_val[small_ind])
except ValueError:
b = 0
x = [a * math.cos(it) for it in t]
y = [b * math.sin(it) for it in t]
angle = math.atan2(eig_vec[big_ind, 1], eig_vec[big_ind, 0])
Rot = np.array([[math.cos(angle), -math.sin(angle)],
[math.sin(angle), math.cos(angle)]])
fx = Rot.dot(np.array([[x, y]]))
px = np.array(fx[0, :] + x_est[0, 0]).flatten()
py = np.array(fx[1, :] + x_est[1, 0]).flatten()
plt.plot(px, py, "--r")
def main():
print(__file__ + " start!!")
time = 0.0
# RF_ID positions [x, y]
rf_id = np.array([[10.0, 0.0],
[10.0, 10.0],
[0.0, 15.0],
[-5.0, 20.0]])
# State Vector [x y yaw v]'
x_est = np.zeros((4, 1))
x_true = np.zeros((4, 1))
px = np.zeros((4, NP)) # Particle store
pw = np.zeros((1, NP)) + 1.0 / NP # Particle weight
x_dr = np.zeros((4, 1)) # Dead reckoning
# history
h_x_est = x_est
h_x_true = x_true
h_x_dr = x_true
while SIM_TIME >= time:
time += DT
u = calc_input()
x_true, z, x_dr, ud = observation(x_true, x_dr, u, rf_id)
x_est, PEst, px, pw = pf_localization(px, pw, z, ud)
# store data history
h_x_est = np.hstack((h_x_est, x_est))
h_x_dr = np.hstack((h_x_dr, x_dr))
h_x_true = np.hstack((h_x_true, x_true))
if show_animation:
plt.cla()
# for stopping simulation with the esc key.
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect('key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
for i in range(len(z[:, 0])):
plt.plot([x_true[0, 0], z[i, 1]], [x_true[1, 0], z[i, 2]], "-k")
plt.plot(rf_id[:, 0], rf_id[:, 1], "*k")
plt.plot(px[0, :], px[1, :], ".r")
plt.plot(np.array(h_x_true[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(h_x_true[1, :]).flatten(), "-b")
plt.plot(np.array(h_x_dr[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(h_x_dr[1, :]).flatten(), "-k")
plt.plot(np.array(h_x_est[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(h_x_est[1, :]).flatten(), "-r")
plot_covariance_ellipse(x_est, PEst)
plt.axis("equal")
plt.grid(True)
plt.pause(0.001)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()核心代码
def pf_localization(px, pw, z, u):
"""
Localization with Particle filter
"""
for ip in range(NP):
x = np.array([px[:, ip]]).T
w = pw[0, ip]
# Predict with random input sampling
ud1 = u[0, 0] + np.random.randn() * R[0, 0] ** 0.5
ud2 = u[1, 0] + np.random.randn() * R[1, 1] ** 0.5
ud = np.array([[ud1, ud2]]).T
x = motion_model(x, ud)
# Calc Importance Weight
for i in range(len(z[:, 0])):
dx = x[0, 0] - z[i, 1]
dy = x[1, 0] - z[i, 2]
pre_z = math.hypot(dx, dy)
dz = pre_z - z[i, 0]
w = w * gauss_likelihood(dz, math.sqrt(Q[0, 0]))
px[:, ip] = x[:, 0]
pw[0, ip] = w
pw = pw / pw.sum() # normalize
x_est = px.dot(pw.T)
p_est = calc_covariance(x_est, px, pw)
N_eff = 1.0 / (pw.dot(pw.T))[0, 0] # Effective particle number
if N_eff < NTh:
px, pw = re_sampling(px, pw)
return x_est, p_est, px, pw
步骤1:初始化
px = np.zeros((4, NP)) # Particle store
pw = np.zeros((1, NP)) + 1.0 / NP # Particle weight步骤2:采样
for ip in range(NP):
x = np.array([px[:, ip]]).T
w = pw[0, ip]
# Predict with random input sampling
ud1 = u[0, 0] + np.random.randn() * R[0, 0] ** 0.5
ud2 = u[1, 0] + np.random.randn() * R[1, 1] ** 0.5
ud = np.array([[ud1, ud2]]).T
x = motion_model(x, ud)
# Calc Importance Weight
for i in range(len(z[:, 0])):
dx = x[0, 0] - z[i, 1]
dy = x[1, 0] - z[i, 2]
pre_z = math.hypot(dx, dy)
dz = pre_z - z[i, 0]
w = w * gauss_likelihood(dz, math.sqrt(Q[0, 0]))
px[:, ip] = x[:, 0]
pw[0, ip] = w
pw = pw / pw.sum() # normalize1)基于模型预测粒子状态:
# Predict with random input sampling
ud1 = u[0, 0] + np.random.randn() * R[0, 0] ** 0.5
ud2 = u[1, 0] + np.random.randn() * R[1, 1] ** 0.5
ud = np.array([[ud1, ud2]]).T
x = motion_model(x, ud)2)计算重要性权重:这部分还有点懵
# Calc Importance Weight
for i in range(len(z[:, 0])):
dx = x[0, 0] - z[i, 1]
dy = x[1, 0] - z[i, 2]
pre_z = math.hypot(dx, dy)
dz = pre_z - z[i, 0]
w = w * gauss_likelihood(dz, math.sqrt(Q[0, 0]))dz = pre_z - z[i, 0]得到的是到地标i距离先验和后验的差别,直觉上理解,与实际值(先验)差别越大,说明该测量值(后验)越不可信,也就是权重越低,与之前的权重w累乘w = w * gauss_likelihood(dz, math.sqrt(Q[0, 0])),那么会得到新的权重值。
步骤3:重采样
if N_eff < NTh:
px, pw = re_sampling(px, pw)参考
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Particle_filter
- Probabilistic Robotics, 4.3 The Particle Filter, p96-113
- Coursera: Robotics-Estimation-and-Learning, Course5-Estimation-and-Learning: AssignmentWEEK4