142. Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Example 1:
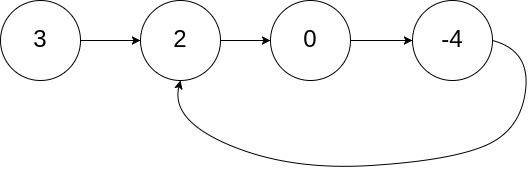
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: tail connects to node index 1
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
Example 2:
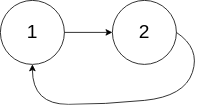
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: tail connects to node index 0
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: no cycle
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.

Follow-up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
fast, slow := head, head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
fast = fast.Next.Next
slow = slow.Next
if fast == slow {
break
}
}
if fast == nil || fast.Next == nil {
return nil
}
slow = head
for slow != fast {
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next
}
return fast
}
