本文介绍fminunc的使用,结合bfgs的例子一起说一说、
关于BFGS的用法,自己找资料看一下原理,基本上意思就是用一个近似的方法将原有的Hessian矩阵替代掉:下面的截图来自陆吾生老师:

验证下来BFGS要比DFP收敛效果更好。Matlab里面我们举例子就用BFGS
我们现在给出优化函数:
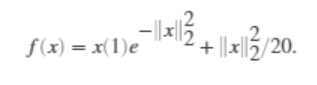
去这个函数的最小值,不带任何约束。
写成func@ 的形式
fun = @(x)x(1)*exp(-(x(1)^2 + x(2)^2)) + (x(1)^2 + x(2)^2)/20;
然后我们还要设置一个初始值
x0 = [1,2];
最后直接调用fminunc求解:
[x,fval] = fminunc(fun,x0)
能够获得的信息就是最后的最后的函数最优点和函数值,以及迭代次数等
Local minimum found.
Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than
the value of the optimality tolerance.
<stopping criteria details>
x =
-0.6691 0.0000
fval =
-0.4052
exitflag =
1
output =
struct with fields:
iterations: 9
funcCount: 42
stepsize: 2.9345e-04
lssteplength: 1
firstorderopt: 8.0839e-07
algorithm: 'quasi-newton'
message: '↵Local minimum found.↵↵Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than↵the value of the optimality tolerance.↵↵<stopping criteria details>↵↵Optimization completed: The first-order optimality measure, 6.891345e-07, is less ↵than options.OptimalityTolerance = 1.000000e-06.↵↵'
但是,为了获得更多的结算信息,我们可以根据上一个博客中提到的set parameter的方法,加入一个options人工的添加一些你感兴趣的信息来显示:
clc
clear all
options = optimoptions(@fminunc,'Display','iter','Algorithm','quasi-newton');
fun = @(x)x(1)*exp(-(x(1)^2 + x(2)^2)) + (x(1)^2 + x(2)^2)/20;
%fun = @(x)3*x(1)^2 + 2*x(1)*x(2) + x(2)^2 - 4*x(1) + 5*x(2);
x0 = [1,2];
[x,fval,exitflag,output] = fminunc(fun,x0,options)
结果是:
First-order
Iteration Func-count f(x) Step-size optimality
0 3 0.256738 0.173
1 6 0.222149 1 0.131
2 9 0.15717 1 0.158
3 18 -0.227902 0.438133 0.386
4 21 -0.299271 1 0.46
5 30 -0.404028 0.102071 0.0458
6 33 -0.404868 1 0.0296
7 36 -0.405236 1 0.00119
8 39 -0.405237 1 0.000252
9 42 -0.405237 1 8.08e-07
Local minimum found.
Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than
the value of the optimality tolerance.
<stopping criteria details>
x =
-0.6691 0.0000
fval =
-0.4052
exitflag =
1
output =
struct with fields:
iterations: 9
funcCount: 42
stepsize: 2.9345e-04
lssteplength: 1
firstorderopt: 8.0839e-07
algorithm: 'quasi-newton'
message: '↵Local minimum found.↵↵Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than↵the value of the optimality tolerance.↵↵<stopping criteria details>↵↵Optimization completed: The first-order optimality measure, 6.891345e-07, is less ↵than options.OptimalityTolerance = 1.000000e-06.↵↵'
>>
我们在这里就获得了更多地迭代过程中的中间信息。
另外一种写法,依然是使用一个例子来说明:

要最小化以上函数:
clc
clear all
options = optimoptions('fminunc','Display','iter','Algorithm','quasi-newton');
problem.options = options;
problem.x0 = [1;2];
problem.objective = @func;
problem.solver = 'fminunc';
x = fminunc(problem)
设置了使用拟牛顿法求解:
First-order
Iteration Func-count f(x) Step-size optimality
0 3 100 400
1 9 0.164722 0.000892027 11.2
2 12 0.131169 1 4.88
3 15 0.122653 1 0.242
4 21 0.1222 10 0.528
5 24 0.120055 1 1.65
6 27 0.113967 1 3.75
7 30 0.104296 1 6.04
8 33 0.0909524 1 7.19
9 36 0.0657965 1 6.56
10 39 0.0337093 1 2.53
11 42 0.0195464 1 3.87
12 45 0.00649517 1 0.422
13 51 0.00315672 0.660962 1.58
14 54 0.00103291 1 0.767
15 57 0.000151308 1 0.238
16 60 1.3137e-05 1 0.114
17 63 6.02652e-06 1 0.0868
18 66 2.77992e-07 1 0.00588
19 69 1.0918e-09 1 0.000443
First-order
Iteration Func-count f(x) Step-size optimality
20 72 2.30071e-11 1 4e-05
Local minimum found.
Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than
the value of the optimality tolerance.
<stopping criteria details>
x =
1.0000
1.0000
>>
当然我们还可以使用置信区间法求解,这里要求设置梯度为真:
clc
clear all
options = optimoptions('fminunc','Display','iter','Algorithm','trust-region','SpecifyObjectiveGradient',true);
% options = optimoptions('fminunc','Display','iter','Algorithm','quasi-newton');
problem.options = options;
problem.x0 = [1;2];
problem.objective = @func;
problem.solver = 'fminunc';
x = fminunc(problem)
function [f,g] = func(x)
% Calculate objective f
f = 100*(x(2) - x(1)^2)^2 + (1-x(1))^2;
if nargout > 1 % gradient required
g = [-400*(x(2)-x(1)^2)*x(1)-2*(1-x(1));
200*(x(2)-x(1)^2)];
end
end
我们为了使用梯度,引入了一个自己写的函数fun, 这里面包括了函数本身以及他的梯度,在options里面我们也设置了相关使用梯度的参数:“‘trust-region’,‘SpecifyObjectiveGradient’,true);”,要注意这里如果使用置信区间那就必须要使用梯度,两者要同时出现。
结果如下:
Norm of First-order
Iteration f(x) step optimality CG-iterations
0 100 400
1 100 10 400 1
2 100 2.5 400 0
3 27.8984 0.625 341 0
4 0.374736 0.505714 1.25 1
5 0.29229 0.625 19.8 1
6 0.138484 0.13794 2.45 1
7 0.138484 0.663579 2.45 1
8 0.100293 0.15625 1.74 0
9 0.0560498 0.3125 6.18 1
10 0.0220561 0.145628 1.94 1
11 0.00854943 0.205656 3.09 1
12 0.00128111 0.0527322 0.332 1
13 0.000111288 0.0713324 0.401 1
14 4.3117e-07 0.00656459 0.00568 1
15 1.9432e-11 0.00143547 0.00017 1
Local minimum possible.
fminunc stopped because the final change in function value relative to
its initial value is less than the value of the function tolerance.
<stopping criteria details>
x =
1.0000
1.0000
>>
